©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2022; 13(9): 696-716
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i9.696
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i9.696
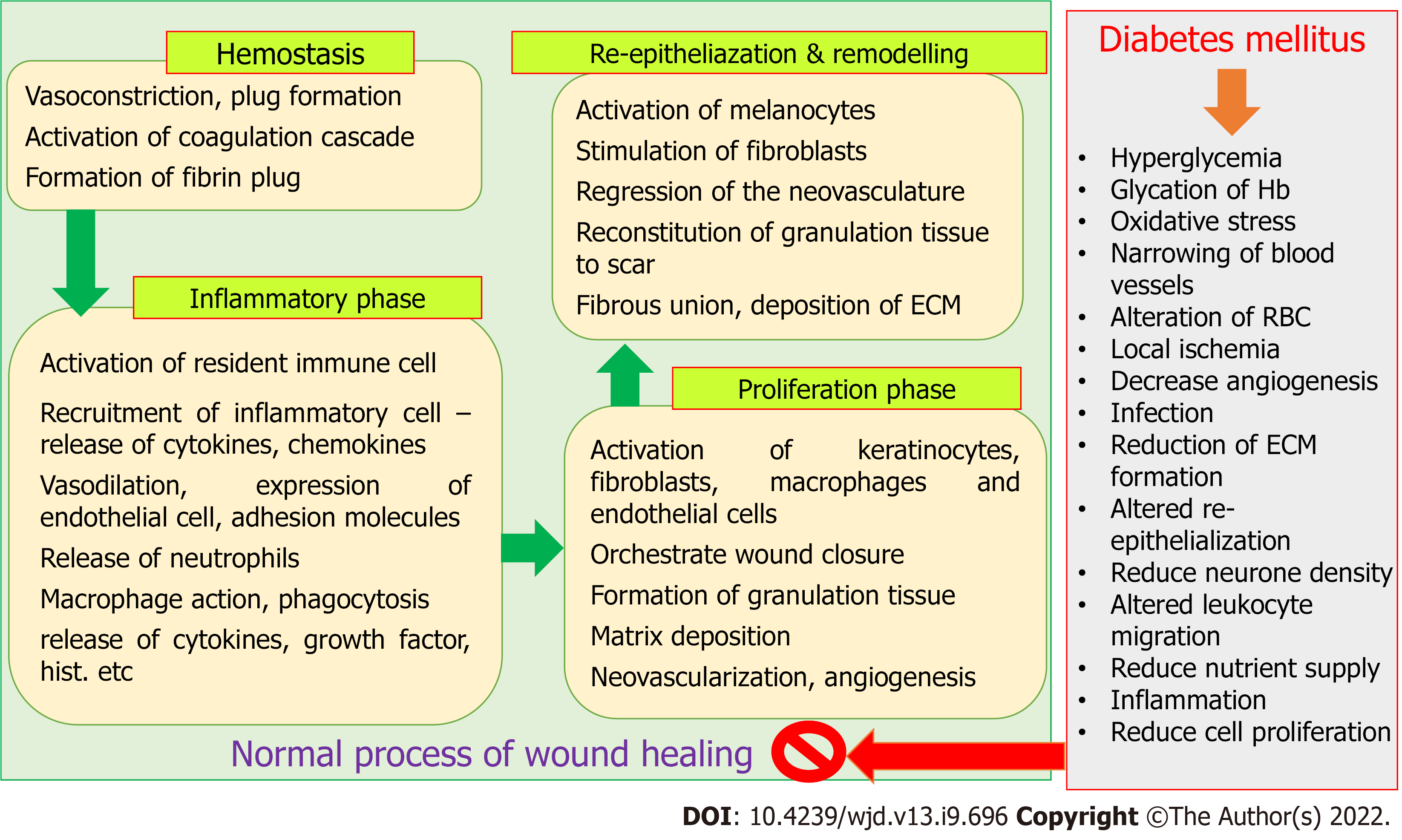
Figure 1 Normal process of wound healing and effect of diabetes mellitus.
ECM: Extracellular matrix.
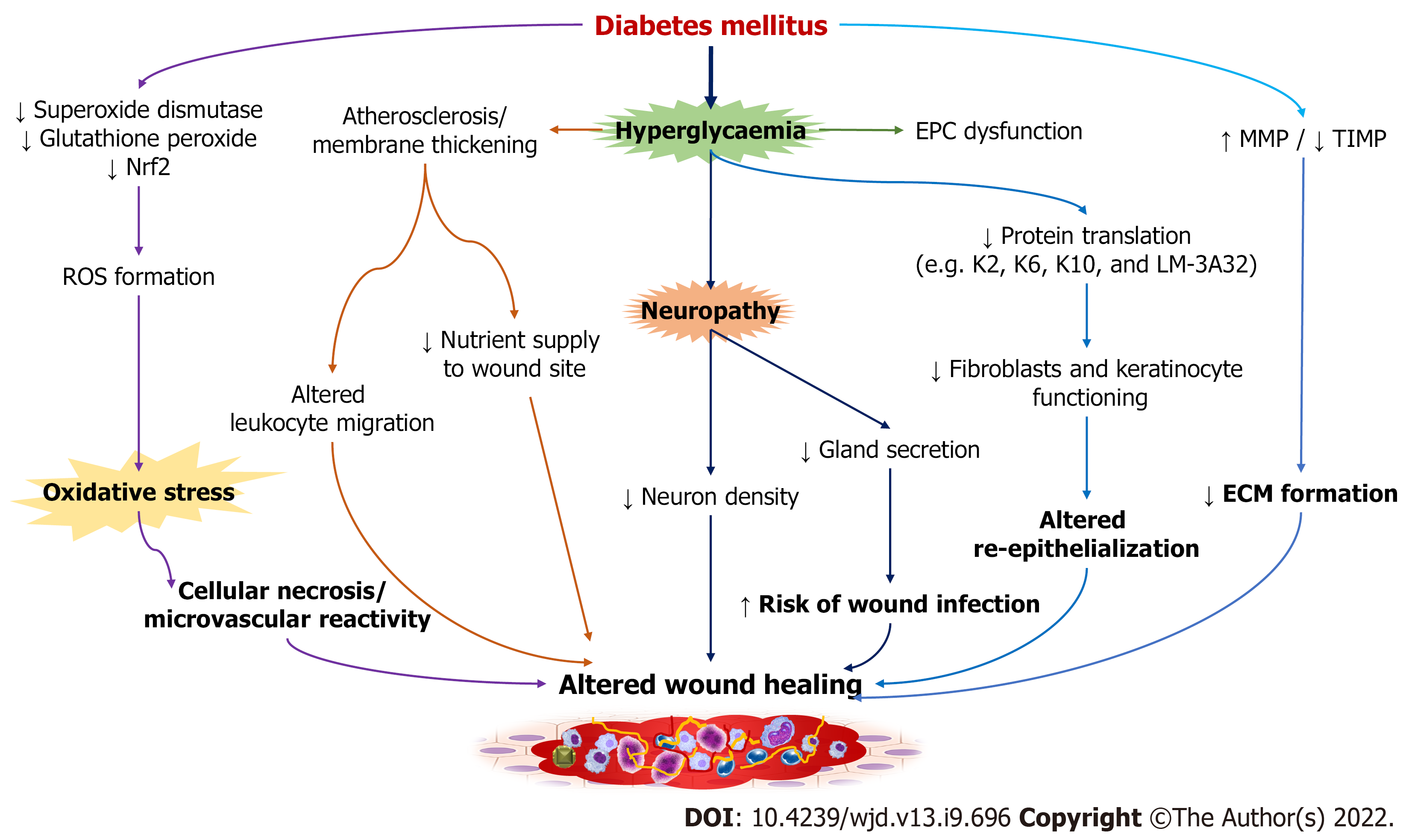
Figure 2 Altered cellular factors and biochemical mediators involved in the development of diabetic wound.
Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid factor 2-related factor 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; EPC: Endothelial progenitor cell; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
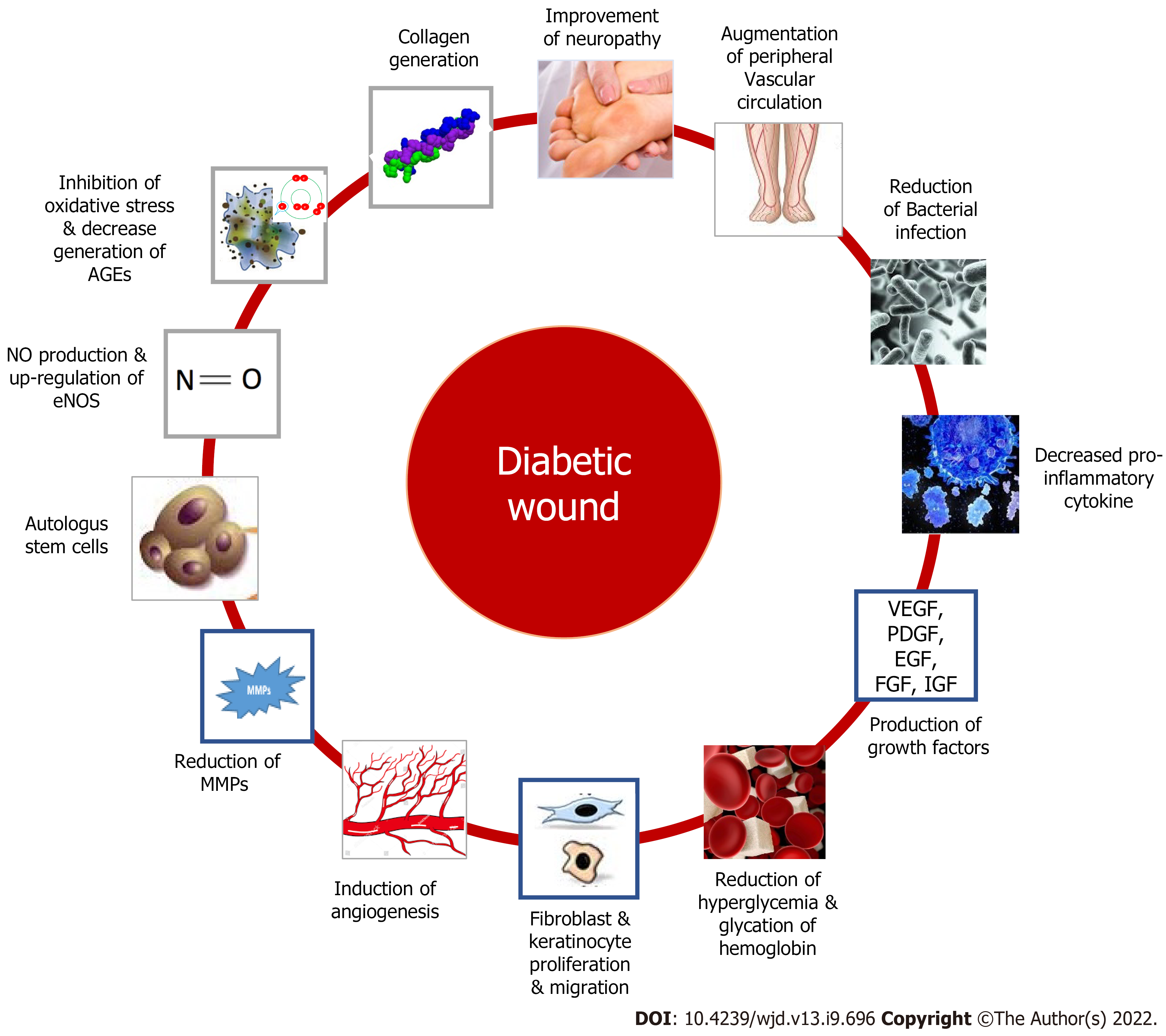
Figure 3 Plausible drug targets for diabetic wound.
AGEs: Advanced glycation end-products; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor.
- Citation: Chakraborty R, Borah P, Dutta PP, Sen S. Evolving spectrum of diabetic wound: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic targets. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(9): 696-716
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i9/696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i9.696