©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2022; 13(12): 1154-1167
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1154
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1154
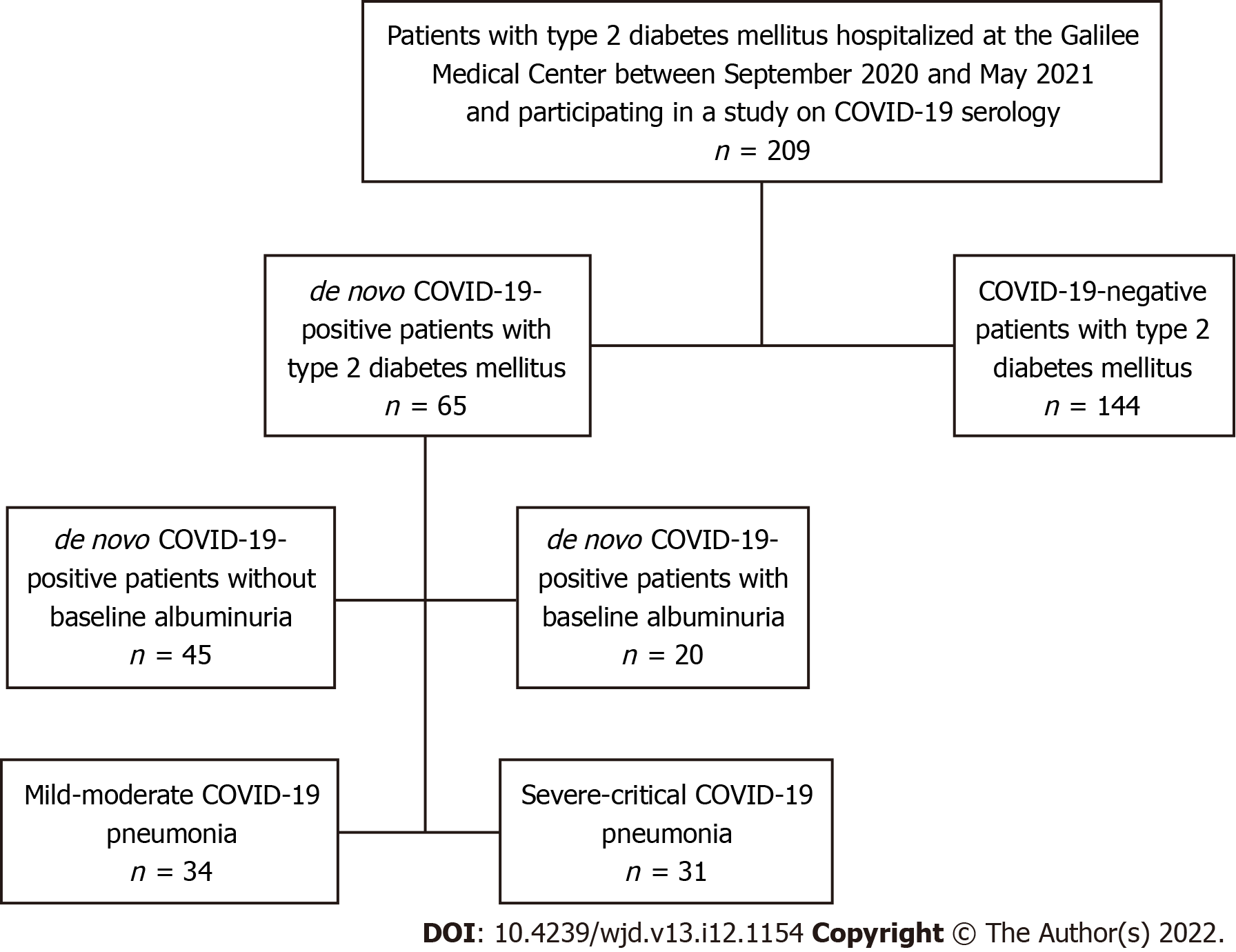
Figure 1 Enrolled participants and analysis groups.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
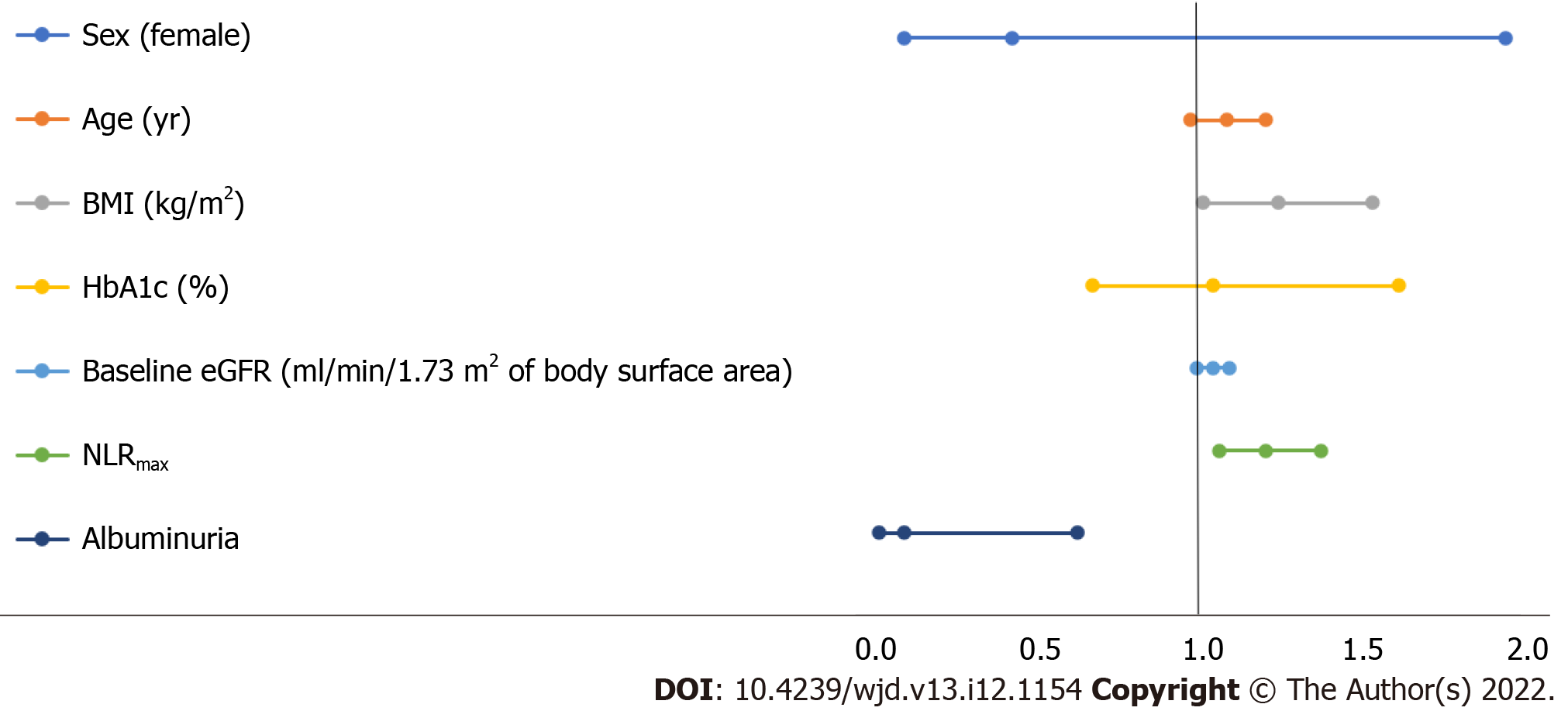
Figure 2 Multivariable logistic regression Model 3 as shown in Table 4.
The dependent variable is the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia, while the following parameters are independent variables: age, sex, body mass index, last estimated glomerular filtration rate measured before hospitalization, glycosylated hemoglobin, maximum neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio, and albuminuria before hospitalization. BMI: Body mass index; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c: Glycosylated hemoglobin; NLRmax: Maximum neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio.
- Citation: Bashkin A, Shehadeh M, Shbita L, Namoura K, Haiek R, Kuyantseva E, Boulos Y, Yakir O, Kruzel-Davila E. Baseline moderate-range albuminuria is associated with protection against severe COVID-19 pneumonia. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(12): 1154-1167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i12/1154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1154