©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2020; 11(12): 572-583
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.572
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.572
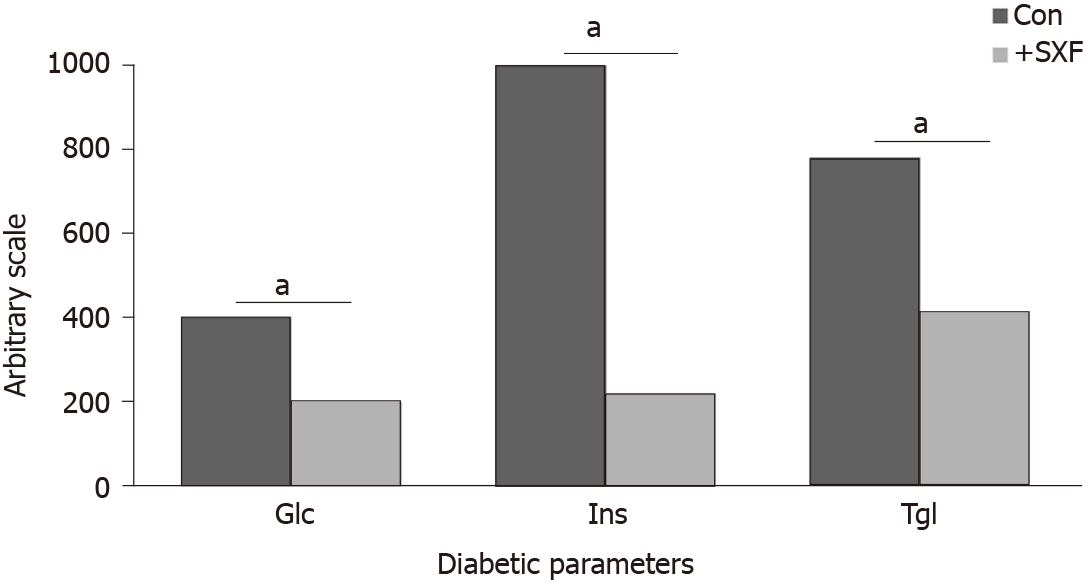
Figure 1 Effects of crude SX-fraction on three diabetic parameters in diabetic mice.
In this study, the levels of three diabetic parameters, glucose, insulin, and triglyceride, in diabetic mice were compared between the experimental group (with crude SXF) and the control (sham) group after an 8-wk trial. All data are mean of 5 mice from each group (aP < 0.03 vs control) and expressed with an arbitrary scale (without units). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin; Tgl: Triglyceride.
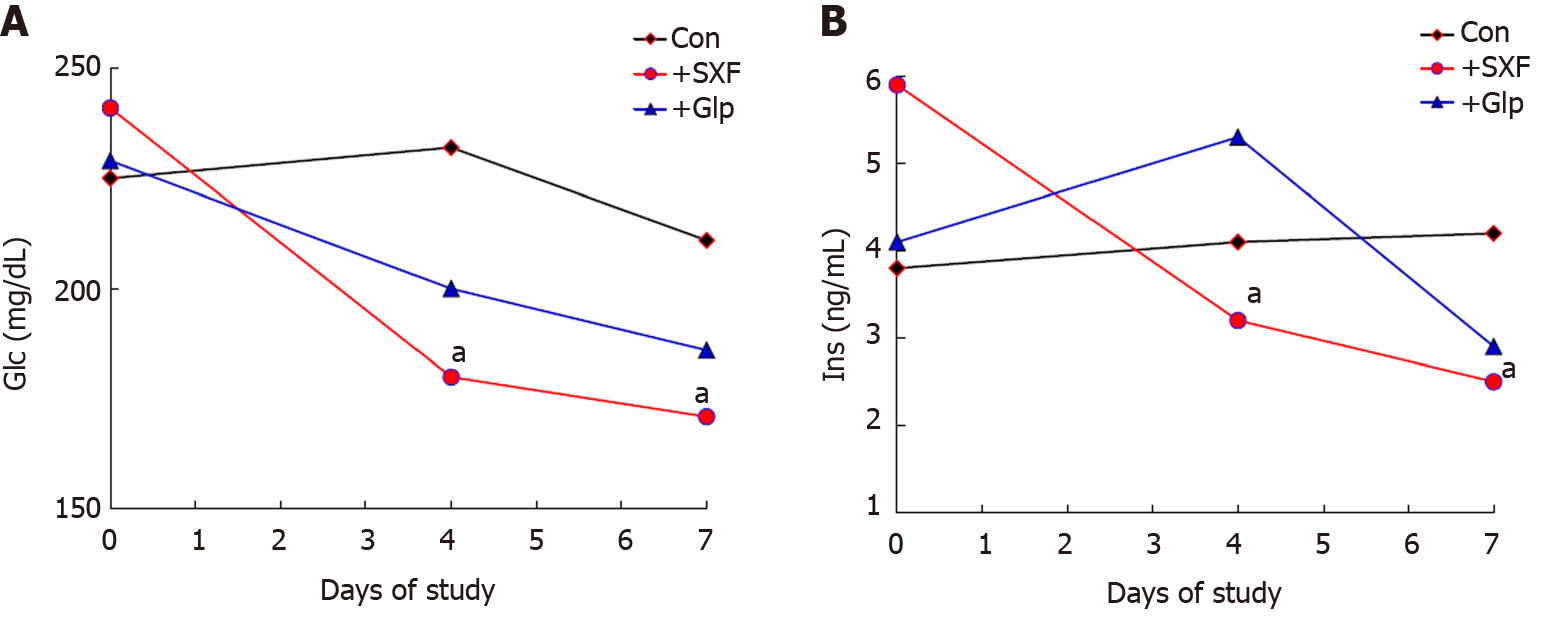
Figure 2 Effects of formulated SX-fraction and anti-diabetic drug (glipizide) on diabetic parameters in mice.
The two diabetic parameters, glucose and insulin, in the control, SX-fraction, and glipizide groups were analyzed at indicated periods in a one-week trial. The results of glucose and insulin in the three groups are shown in the panels (A) and (B), respectively. All data are mean of 5 mice from each group (aP < 0.05 vs control). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin; Glp: Glipizide.
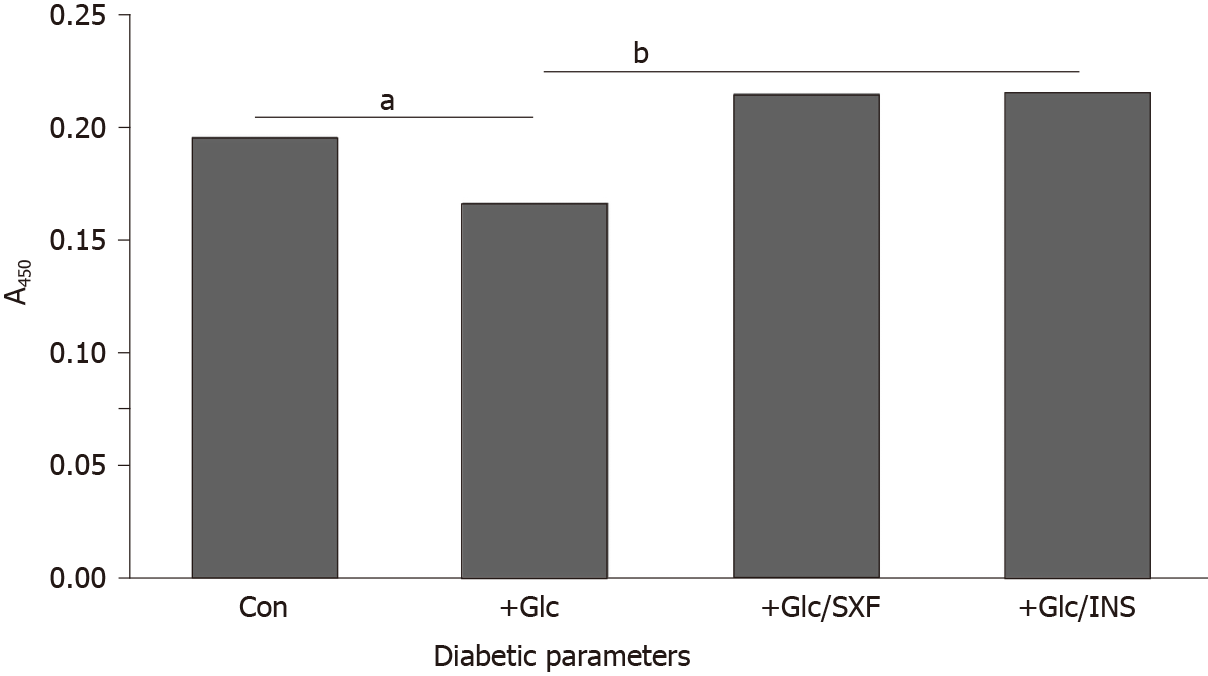
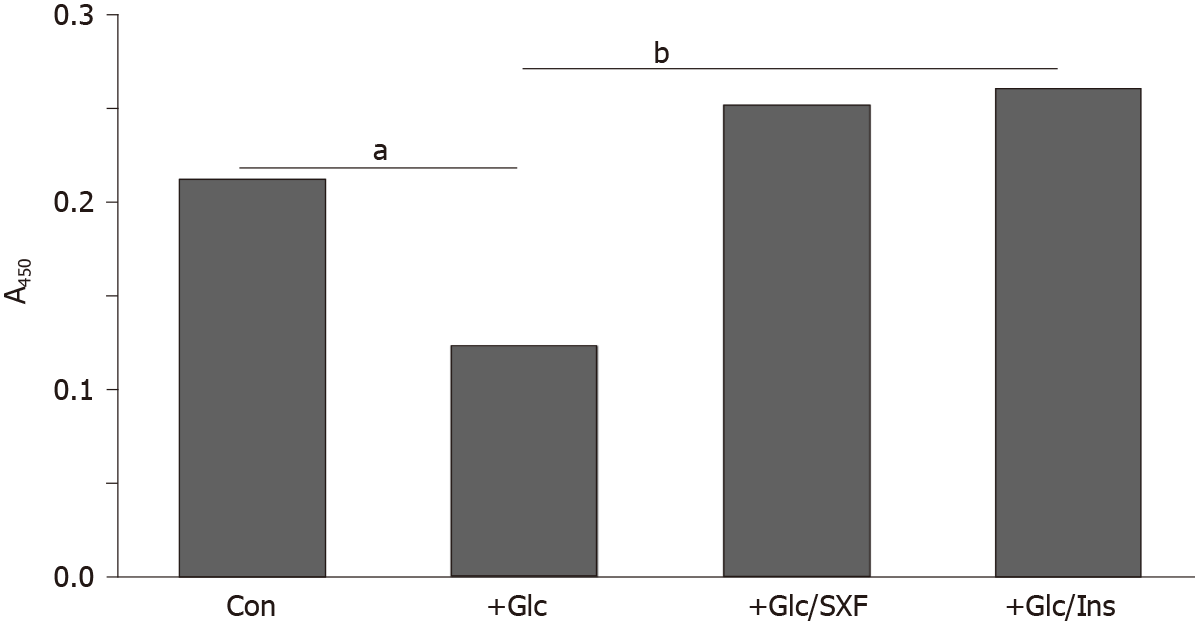
Figure 3 Effects of SX-fraction or insulin on insulin receptor (y) [IR(y)] phosphorylation under high (35 mmol/L) glucose.
Following a 24-h high glucose (35 mmol/L) treatment, cells were exposed to SX-fraction (300 µg/mL) or Insulin (100 nmol/L) for 15 min and subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IR(y). All data are mean ± SD (standard deviation) from three independent experiments (aP < 0.05 vs control or bP < 0.05 vs glucose-treated). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin; IR(y): Insulin receptor (y).
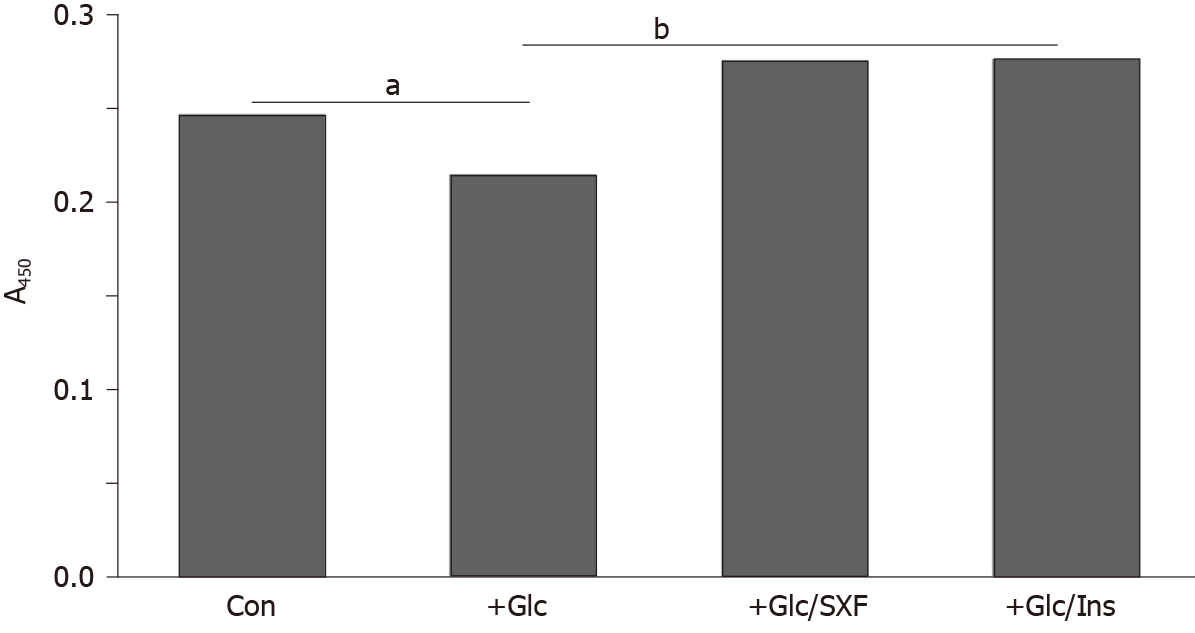
Figure 4 Effects of SX-fraction or insulin on insulin receptor substrate 1 (y) [IRS-1(y)] phosphorylation under high glucose.
Cells were treated exactly as described in Figure 3 but analyzed for IRS-1(y) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All data are mean ± SD from three separate experiments (aP < 0.05 vs control or bP < 0.05 vs glucose-treated). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin; IRS-1(y): Insulin receptor substrate 1 (y).
Figure 5 Effects of SX-fraction or insulin on protein kinase B (s) [Akt(s)] phosphorylation under high glucose.
Cells were treated as described in Figure 3 but analyzed for Akt(s). All data are mean ± SD from three separate experiments (aP < 0.03 vs control or bP < 0.01 vs glucose-treated). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin; Akt(s): Protein kinase B (s).
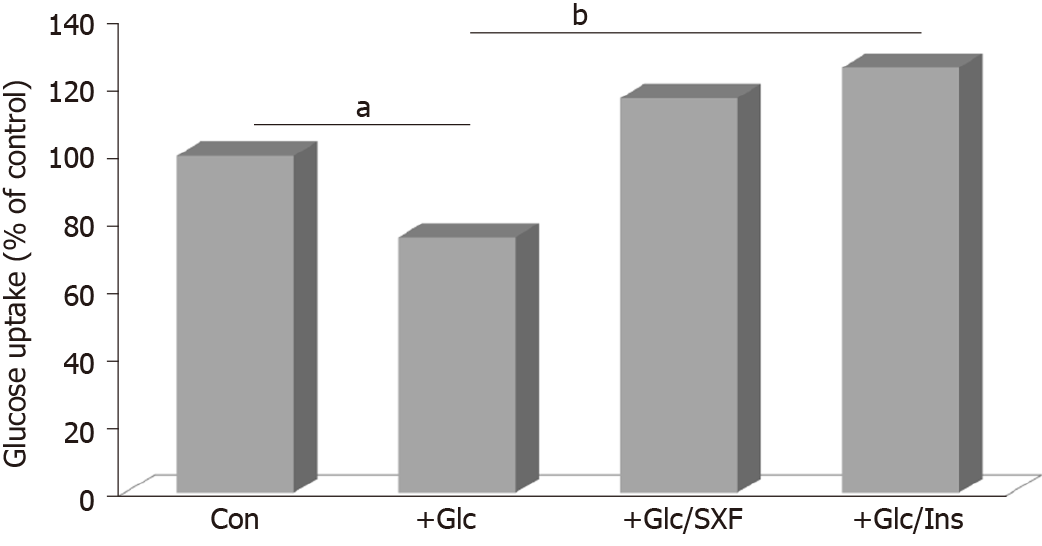
Figure 6 Effects of SX-fraction or insulin on glucose uptake.
Following a 24-h glucose treatment and a 15-min SX-fraction or insulin exposure, glucose uptake was measured using a radioactive ligand and expressed by the % relative to control (100%). All data are mean ± SD from three separate experiments (aP < 0.05 vs control or bP < 0.03 vs glucose-treated). SXF: SX-fraction; Glc: Glucose; Ins: Insulin.
- Citation: Konno S. SX-fraction: Promise for novel treatment of type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(12): 572-583
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i12/572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.572