©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2019; 10(5): 291-303
Published online May 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i5.291
Published online May 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i5.291
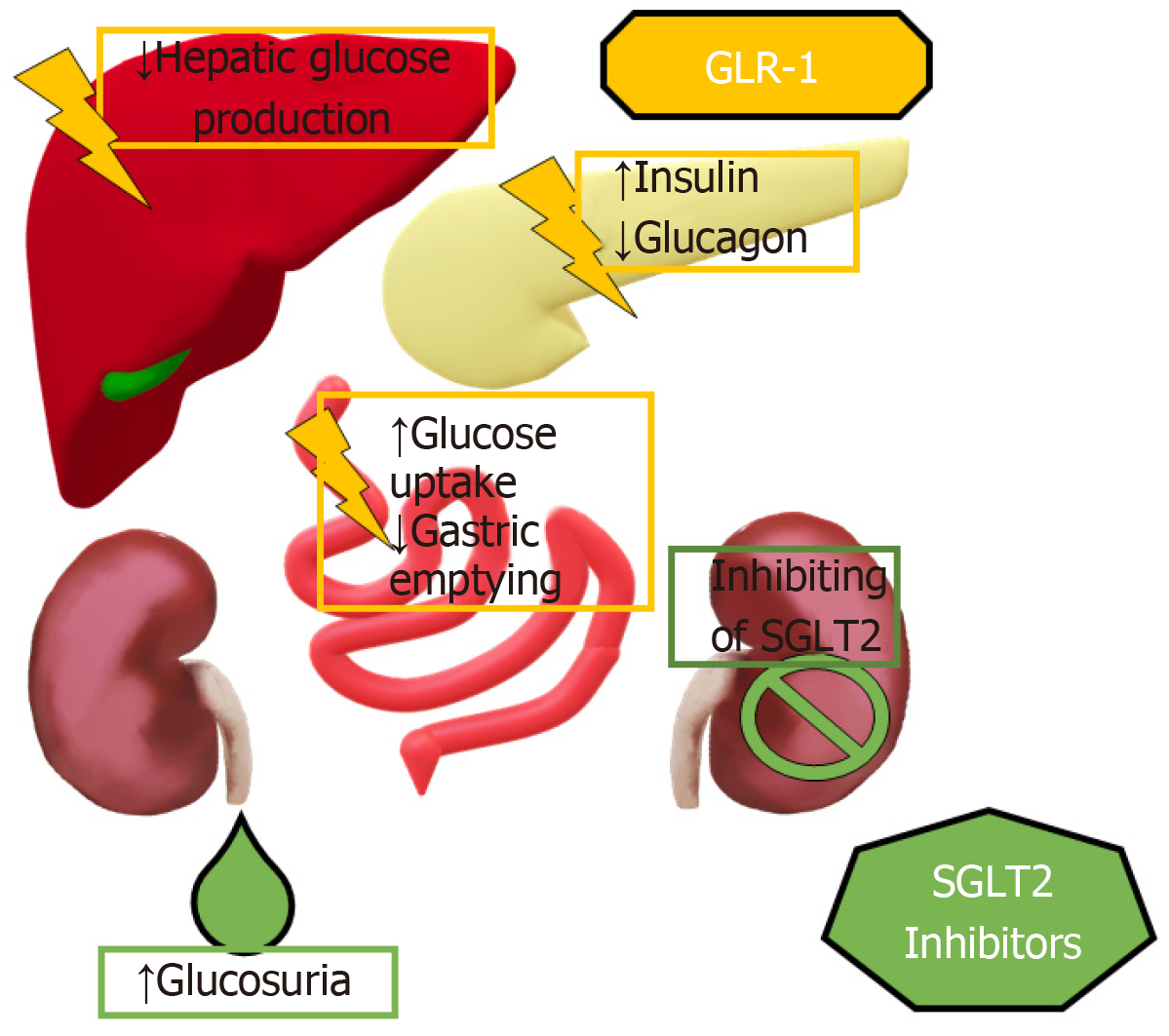
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and the glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists.
Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists slows gastric emptying, suppresses glucagon secretion while also stimulating insulin secretion by inhibiting and stimulating, respectively, Alfa and Beta cells in the pancreas. This in turn inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis with subsequent increase in glucose uptake in the skeletal muscles, diminishing hyperglycemia. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors reduce glucose reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule, inherently enhancing glucosuria. This created a global hypovolemic and hypocaloric state, which diminishes hyperglycemia. SGLT2: Sodium glucose cotransporter 2; GLP-1: Glucagon-like-peptide-1.
- Citation: Pozo L, Bello F, Suarez A, Ochoa-Martinez FE, Mendez Y, Chang CH, Surani S. Novel pharmacological therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus with established cardiovascular disease: Current evidence. World J Diabetes 2019; 10(5): 291-303
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v10/i5/291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i5.291