©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2014; 6(5): 129-138
Published online May 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i5.129
Published online May 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i5.129
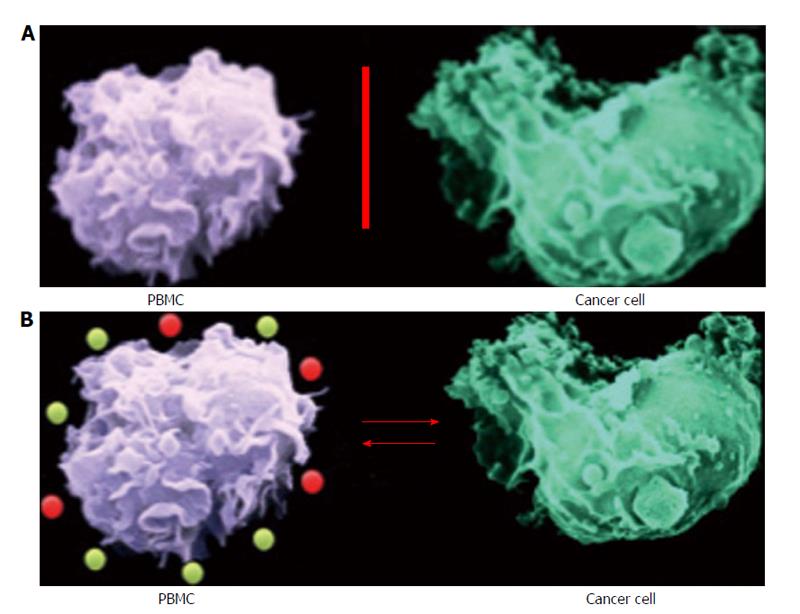
Figure 1 Interrelationship between peripheral blood mononuclear cells and human colon cancer cells.
A: Unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) do not release significant amount of inflammatory cytokines. B: Following direct contact with cancer cells PBMC are stimulated for pro-inflammatory (red dots) and anti-inflammatory (yellow dots) cytokine production.
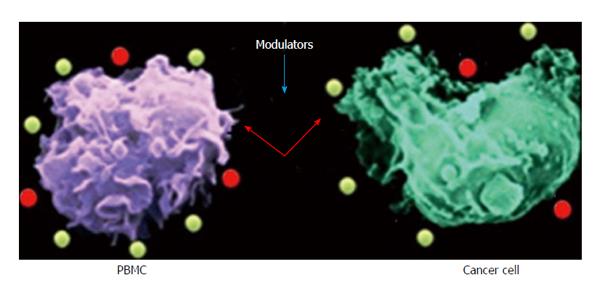
Figure 2 Schematic presentation of the way immune modulators modify the cross-talk between peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cancer cells.
Following alteration of the immune dialogue between these two cell types, the modulators inhibit cancer cell-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to generate pro-inflammatory cytokine (red dots), acting as cancer promoters.
- Citation: Djaldetti M, Bessler H. Modulators affecting the immune dialogue between human immune and colon cancer cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2014; 6(5): 129-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v6/i5/129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v6.i5.129