©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2013; 5(12): 207-221
Published online Dec 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i12.207
Published online Dec 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i12.207
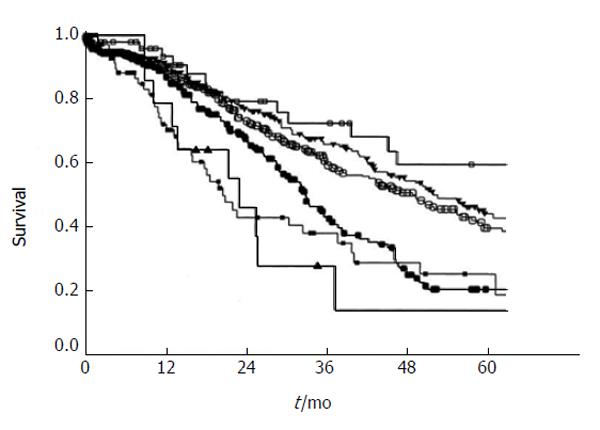
Figure 1 Survival after hepatic resection stratified by the clinical risk score.
Open box: score 0 (n = 52); filled triangle: score 1 (n = 262); open circle: score 2 (n = 350); filled circle: score 3 (n = 243); filled box: score 4 (n = 80); open triangle: score 5 (n = 14). P < 0.0001 (from Fong et al[9]). Used with permission.
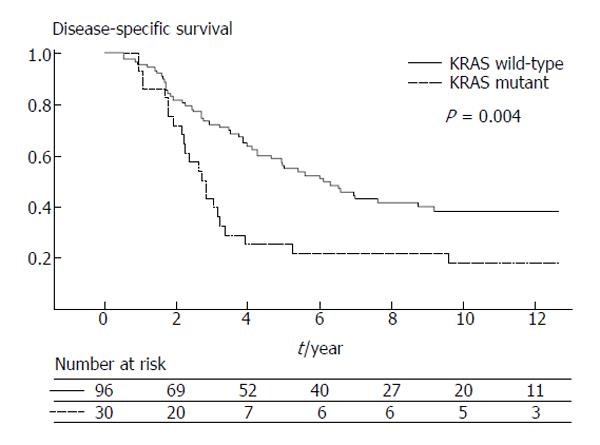
Figure 2 Disease specific survival after liver resection stratified by KRAS mutation (from Nash et al[110]).
Used with permission.
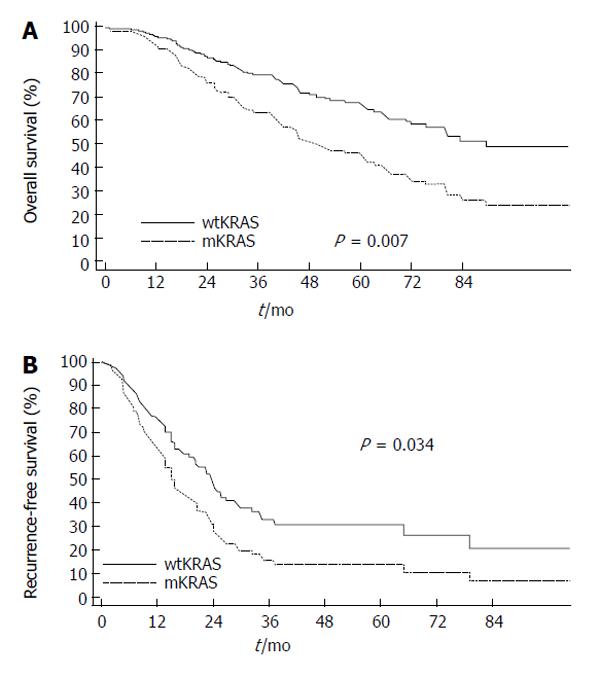
Figure 3 Overall (A) and disease-free (B) survival after hepatic surgery for colorectal liver metastasis depicted by KRAS mutation status (multivariate Cox model) (wtKRAS, wild type KRAS; mKRAS, mutated KRAS) (from Karagkounis et al[111]).
Used with permission.
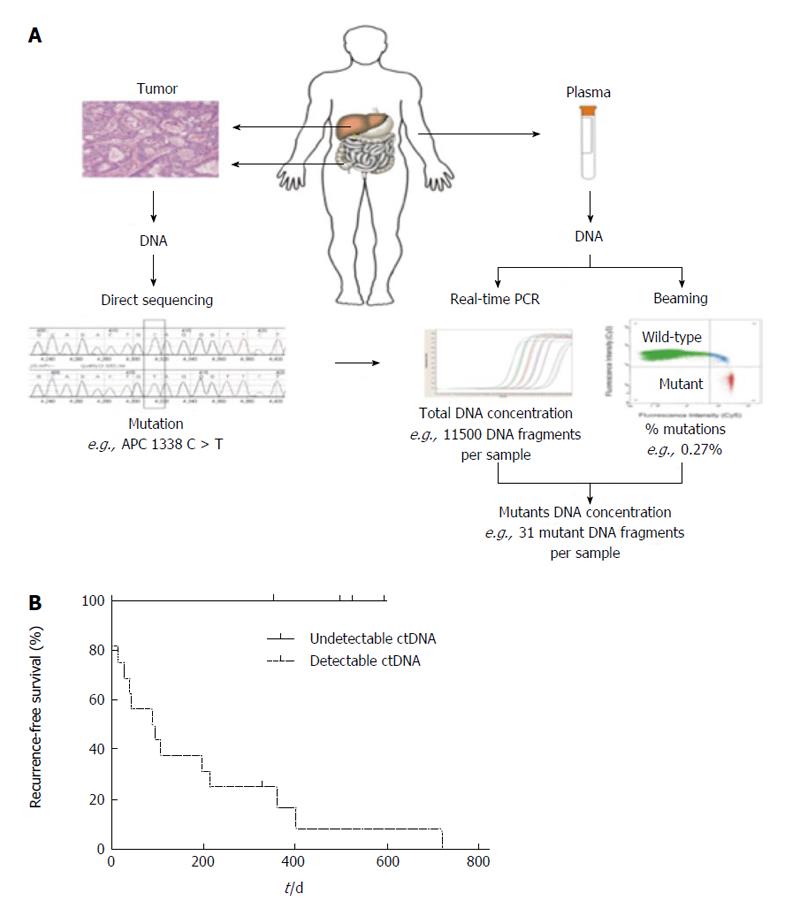
Figure 4 Patients with detectable ctDNA following resection of colorectal liver metastasis, recurrence was universal.
A: Depiction of process by which ctDNA is detected and amplified from the specimen and plasma of patients; B: Representative flow cytometric data of ctDNA of one subject who underwent resection of colorectal liver metastasis. Note that the notable difference in recurrence-free survival in subjects with detectable vs undetectable ctDNA (from Diehl et al[141]). Used with permission. PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
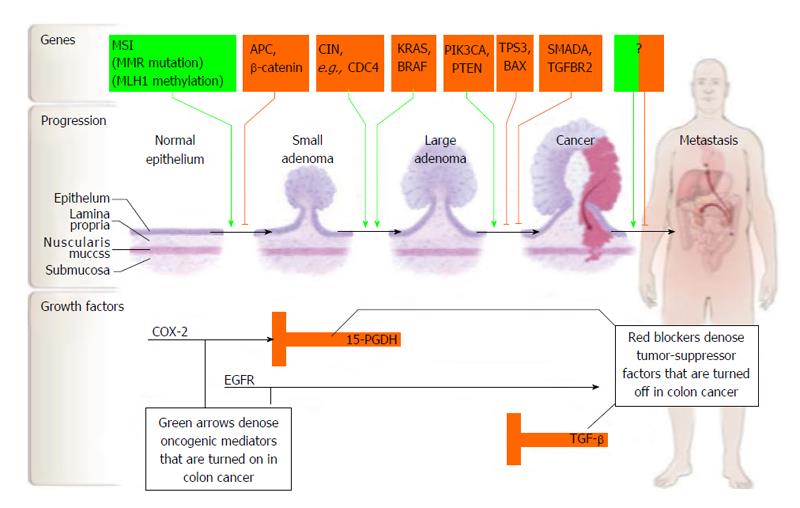
Figure 5 Carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer (from Markowitz et al[145]).
Used with permission. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2.
- Citation: Spolverato G, Ejaz A, Azad N, Pawlik TM. Surgery for colorectal liver metastases: The evolution of determining prognosis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2013; 5(12): 207-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v5/i12/207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v5.i12.207