©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 102696
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102696
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102696
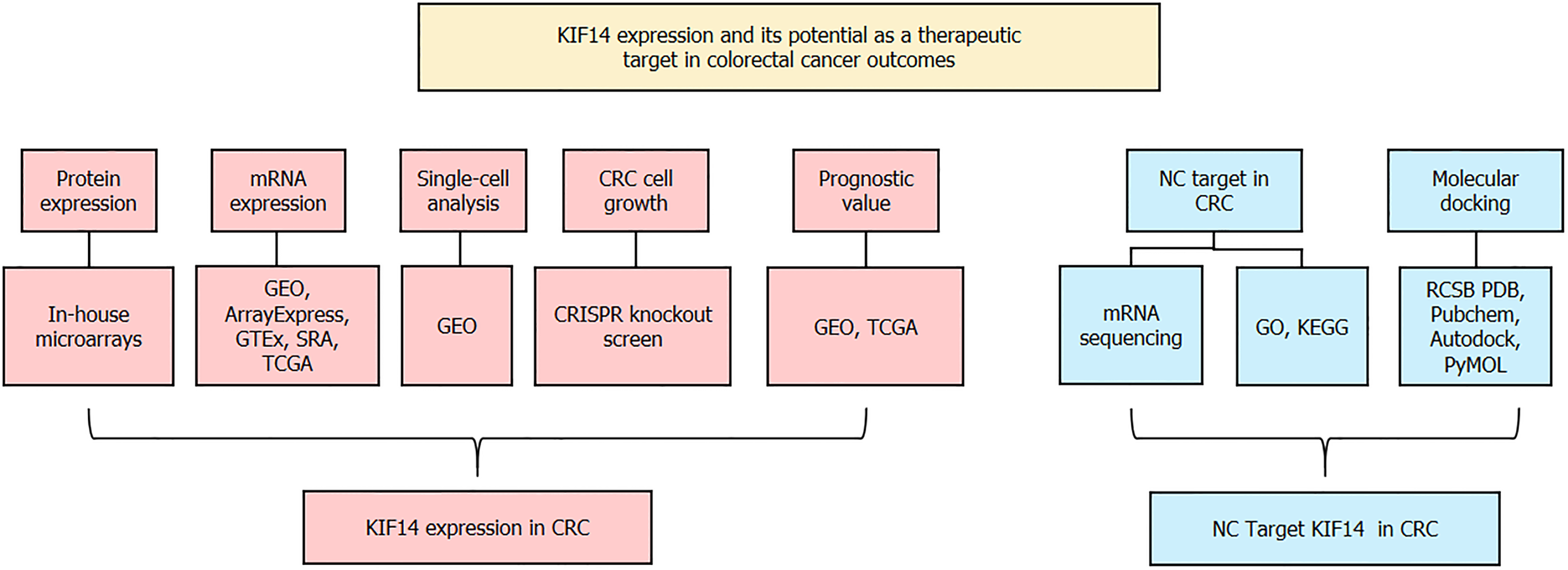
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the research framework.
CRC: Colorectal cancer; GEO: Gene Expression Omnibus; GTEx: The Genotype-Tissue Expression; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; SRA: The Sequence Read Archive; SMD: Standardized mean difference; CRISPR: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; NC: Nitidine chloride; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; GO: Gene Ontology; RCSB PDB: RCSB Protein Data Bank; KIF14: Kinesin family member 14.
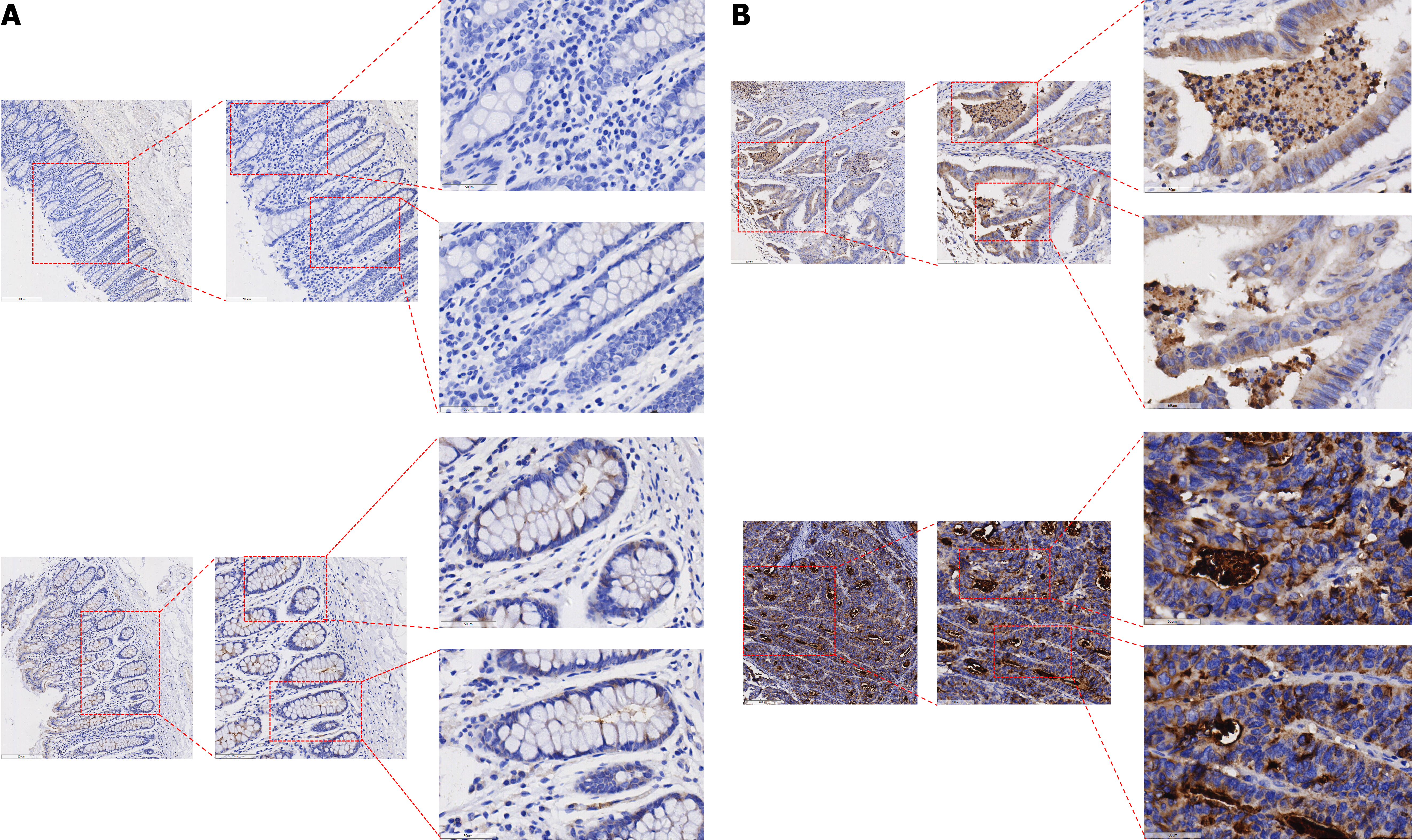
Figure 2 Kinesin family member 14 protein expression.
A: Kinesin family member 14 (KIF14) protein expression in adjacent non-tumor tissue of colorectal cancer (CRC) with tissue images at 200 μm, 100 μm, and 50 μm; B: KIF14 protein expression in CRC tissues with tissue images at 200 μm, 100 μm, and 50 μm.
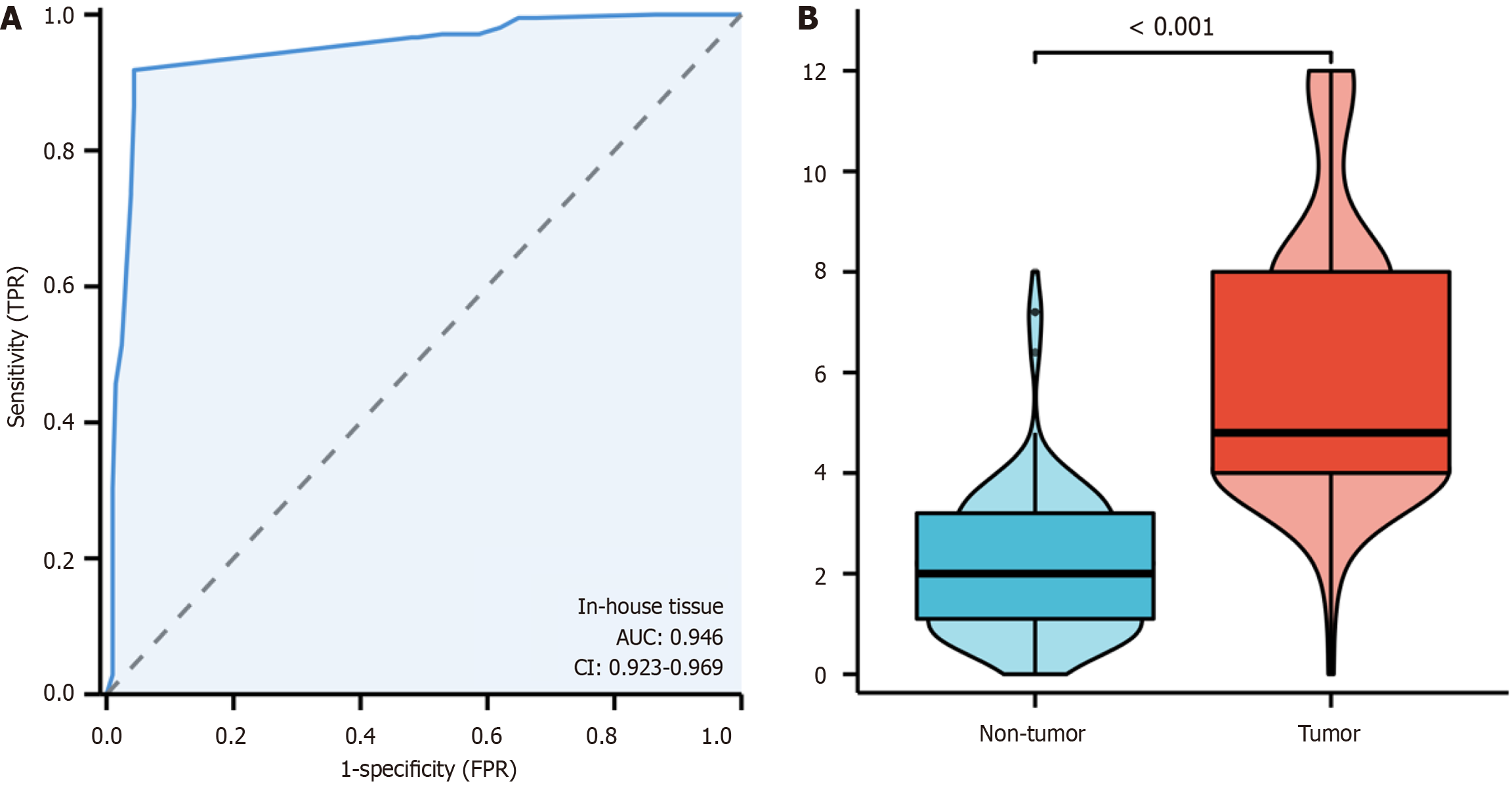
Figure 3 Enhanced expression of Kinesin family member 14 protein in colorectal cancer tissue.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curve; B: Violin plot. AUC: Area under the curve; TPR: True positive rate; FPR: False positive rate.
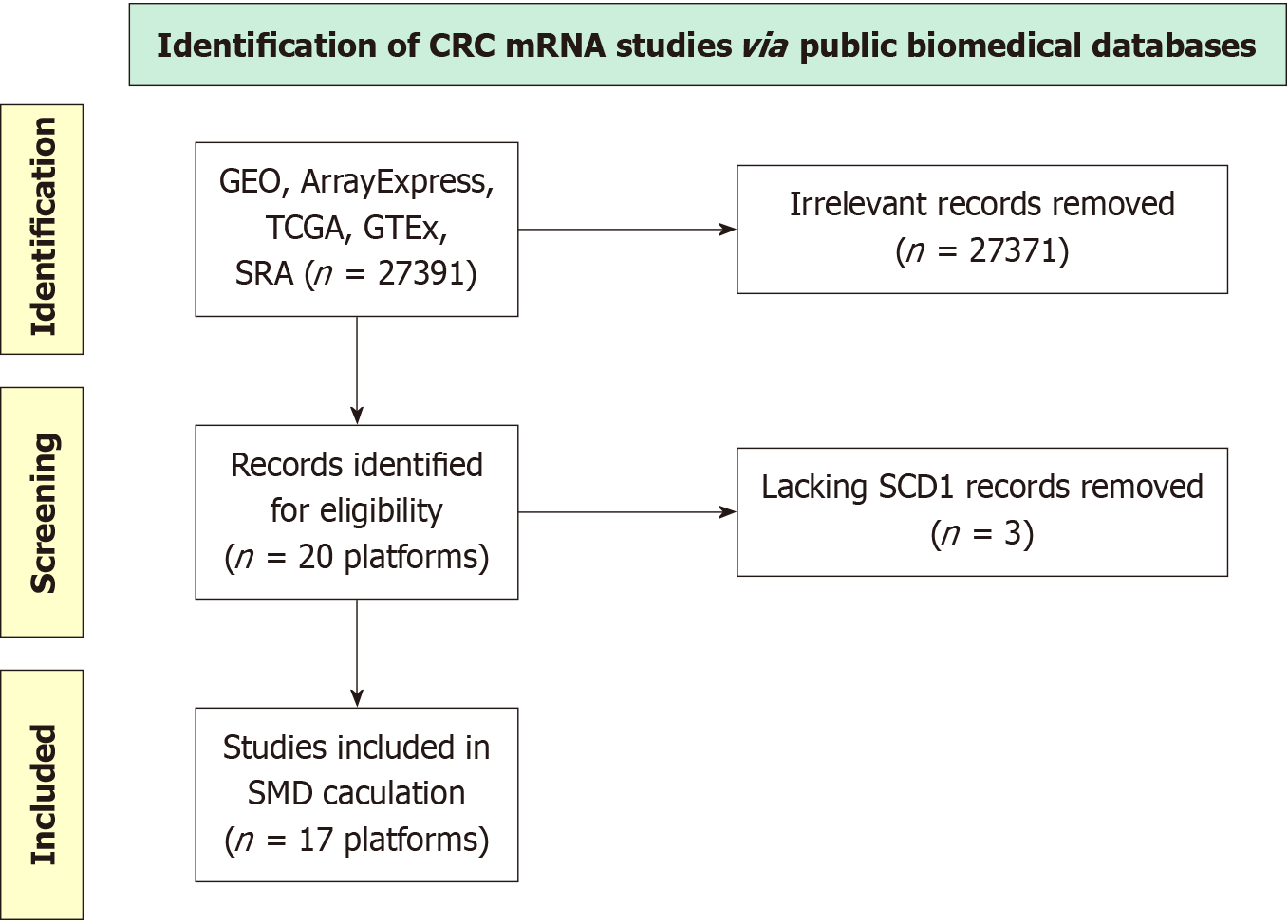
Figure 4 Diagram depicting the screening process used for analyzing the Kinesin family member 14 mRNA dataset.
CRC: Colorectal cancer; GEO: Gene Expression Omnibus; GTEx: The Genotype-Tissue Expression; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; SRA: The Sequence Read Archive; SMD: Standardized mean difference.
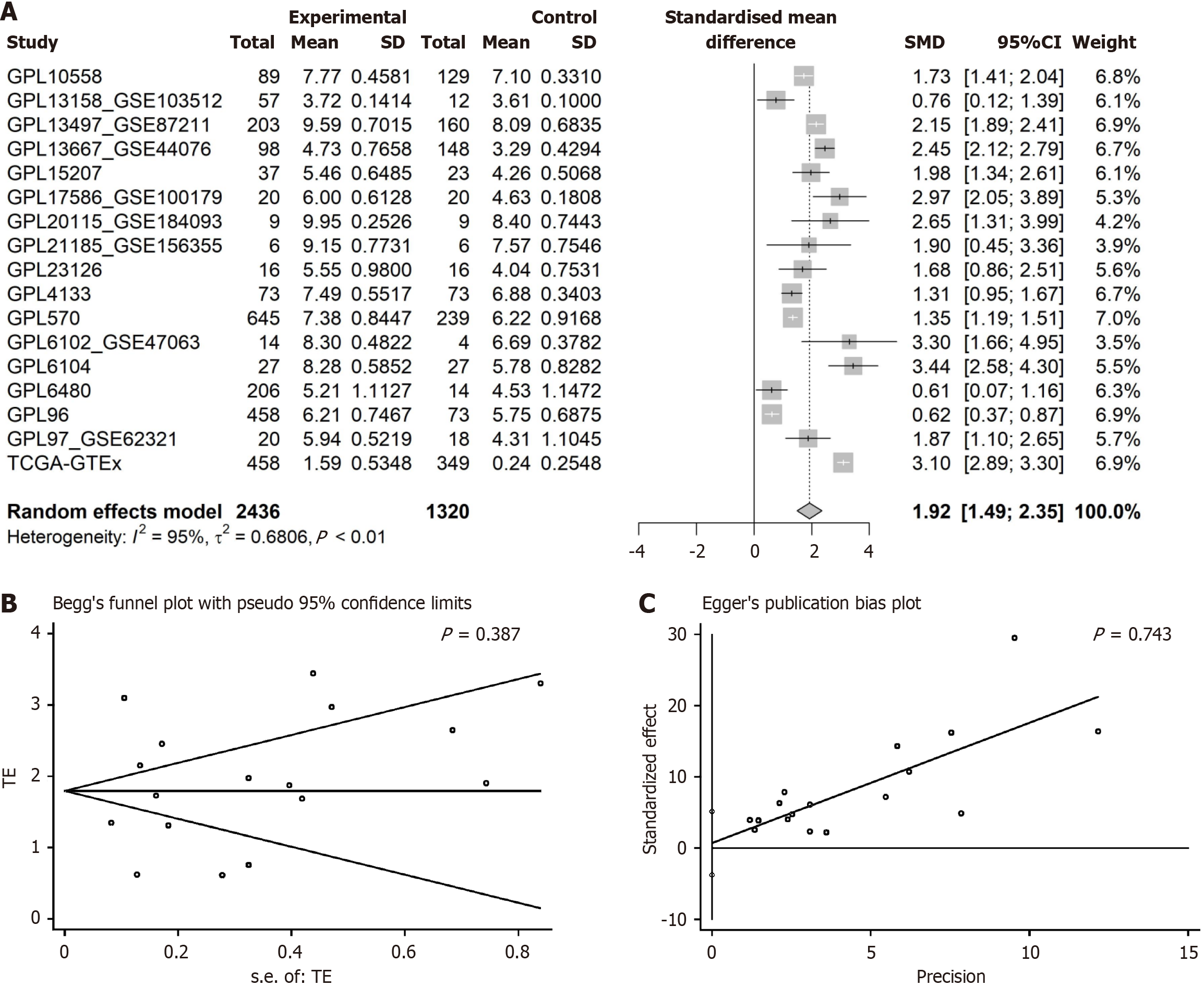
Figure 5 Analysis of Kinesin family member 14 mRNA expression in colorectal cancer.
A: Representation of increased Kinesin family member 14 expression in colorectal cancer compared to normal colorectal tissue; B and C: Results from Egger’s and Begg’s tests showing no publication bias. SMD: Standardized mean difference.
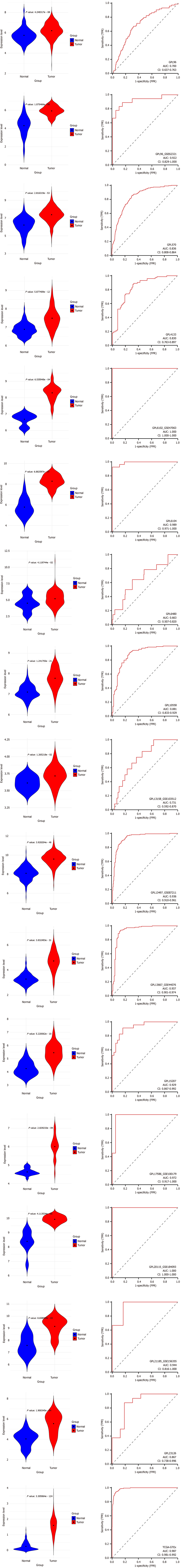
Figure 6 Visualization of Kinesin family member 14 expression disparities between colorectal cancer samples (red) and non-colorectal cancer samples (blue) across selected datasets.
Statistical significance validated at P < 0.05. GTEx: The Genotype-Tissue Expression; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; AUC: Area under the curve; TPR: True positive rate; FPR: False positive rate.
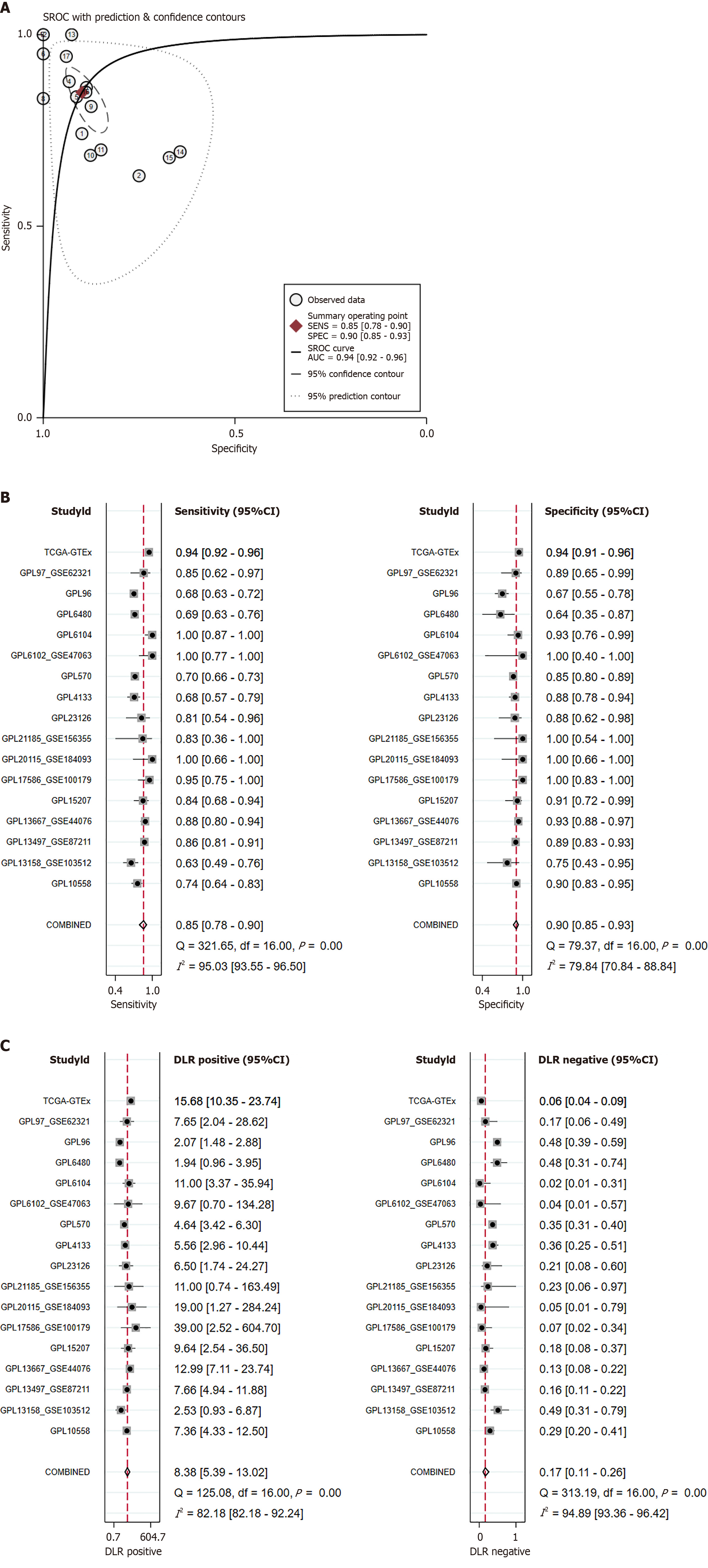
Figure 7 Detailed evaluation of Kinesin family member 14 expression levels in colorectal cancer.
A: Summary receiver operating characteristic curve; B: Sensitivity and specificity; C: Positive diagnostic likelihood ratio (DLR) and negative DLR. DLR: Diagnostic likelihood ratio; sROC: Summary receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under the curve.
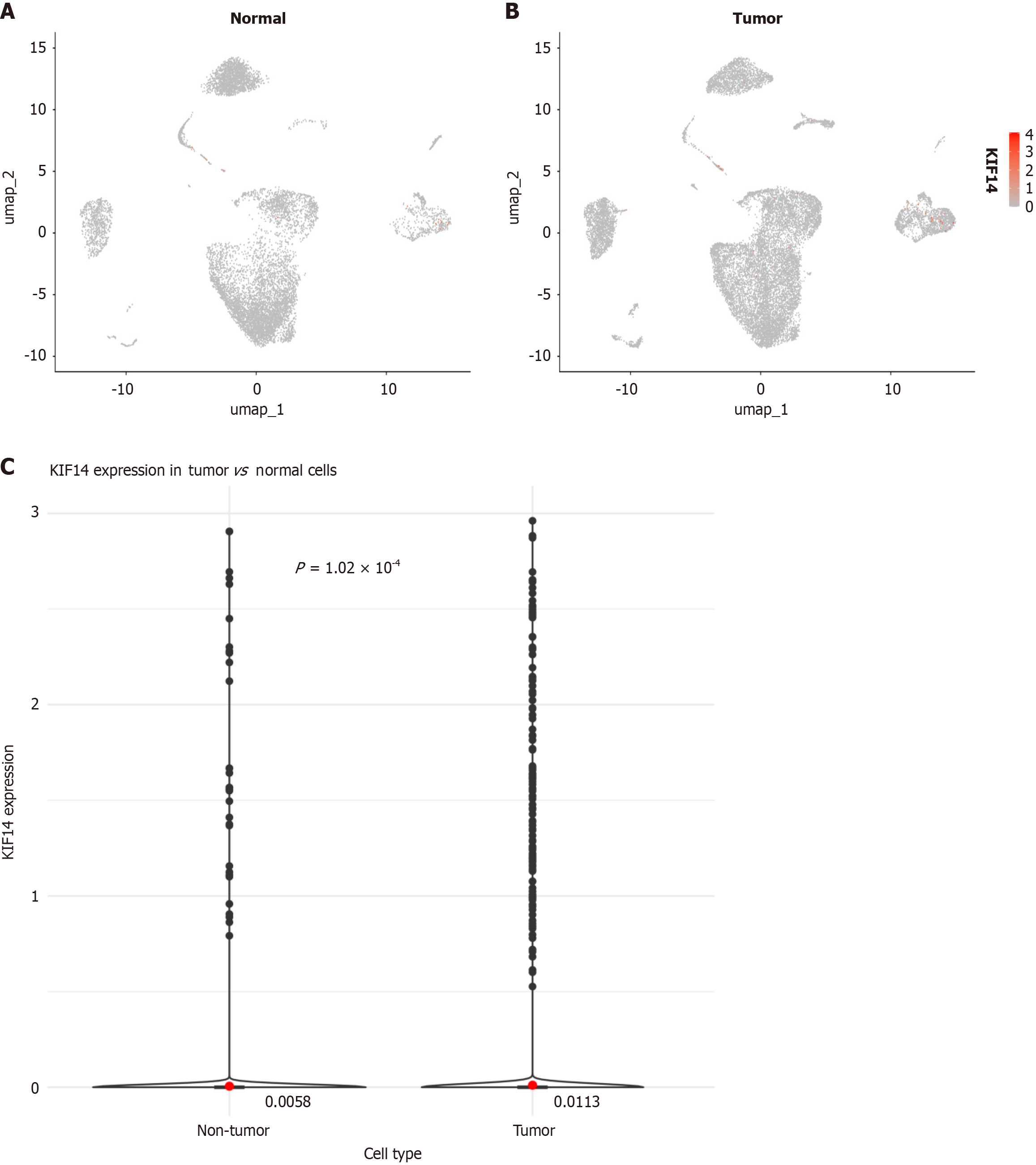
Figure 8 Evaluation of Kinesin family member 14 expression in single cells.
A: Distribution in normal colorectal samples; B: Distribution in colorectal cancer (CRC) samples; C: Comparative analysis of Kinesin family member 14 expression between CRC and normal colorectal cells; KIF14: Kinesin family member 14.
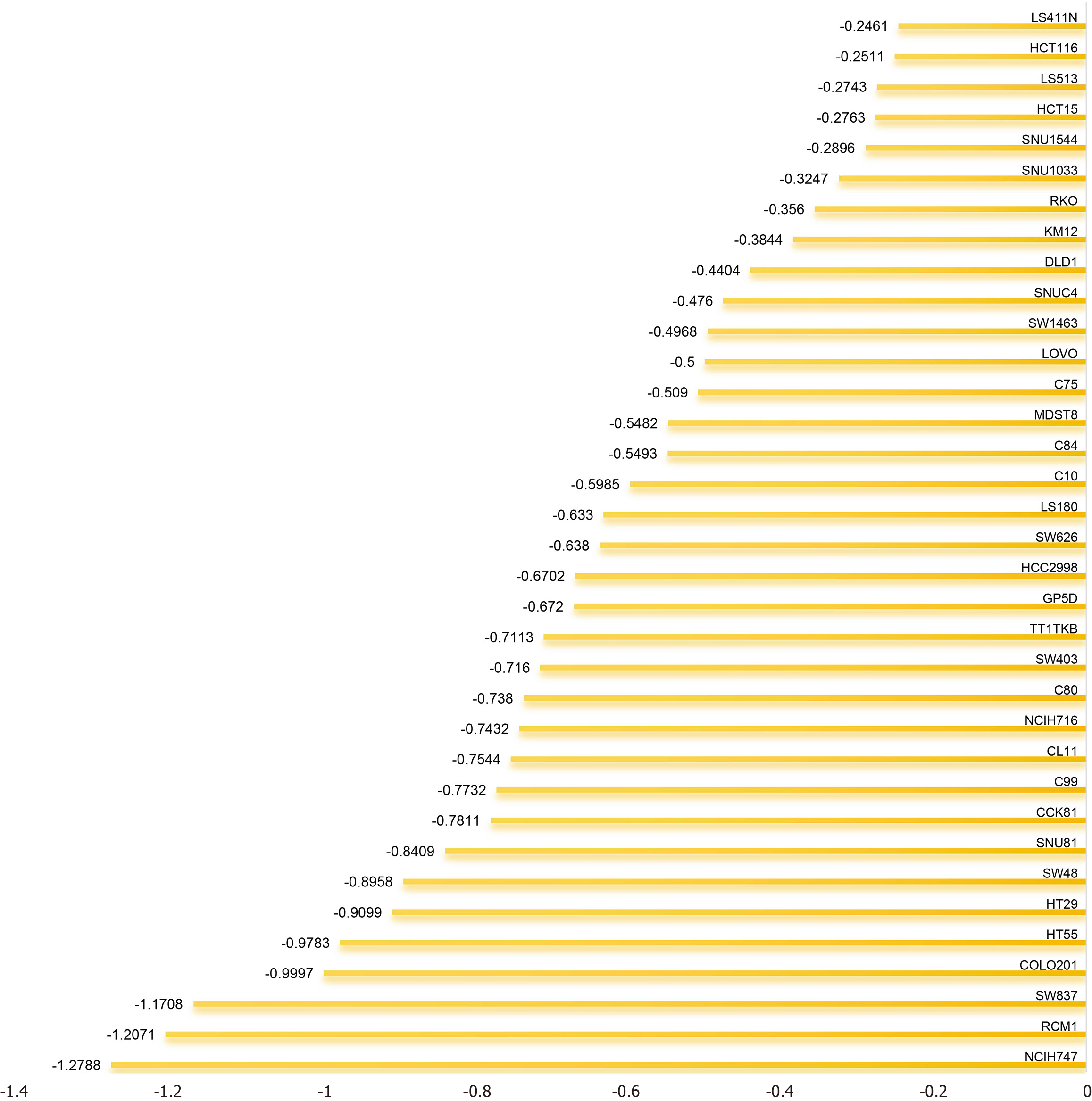
Figure 9 Influence of the Kinesin family member 14 gene on 35 colorectal cancer cell lines.
The horizontal axis represents the impact assessment of the Kinesin family member 14 gene across each individual cell line, while the vertical axis enumerates the diverse colorectal cancer cell lines.
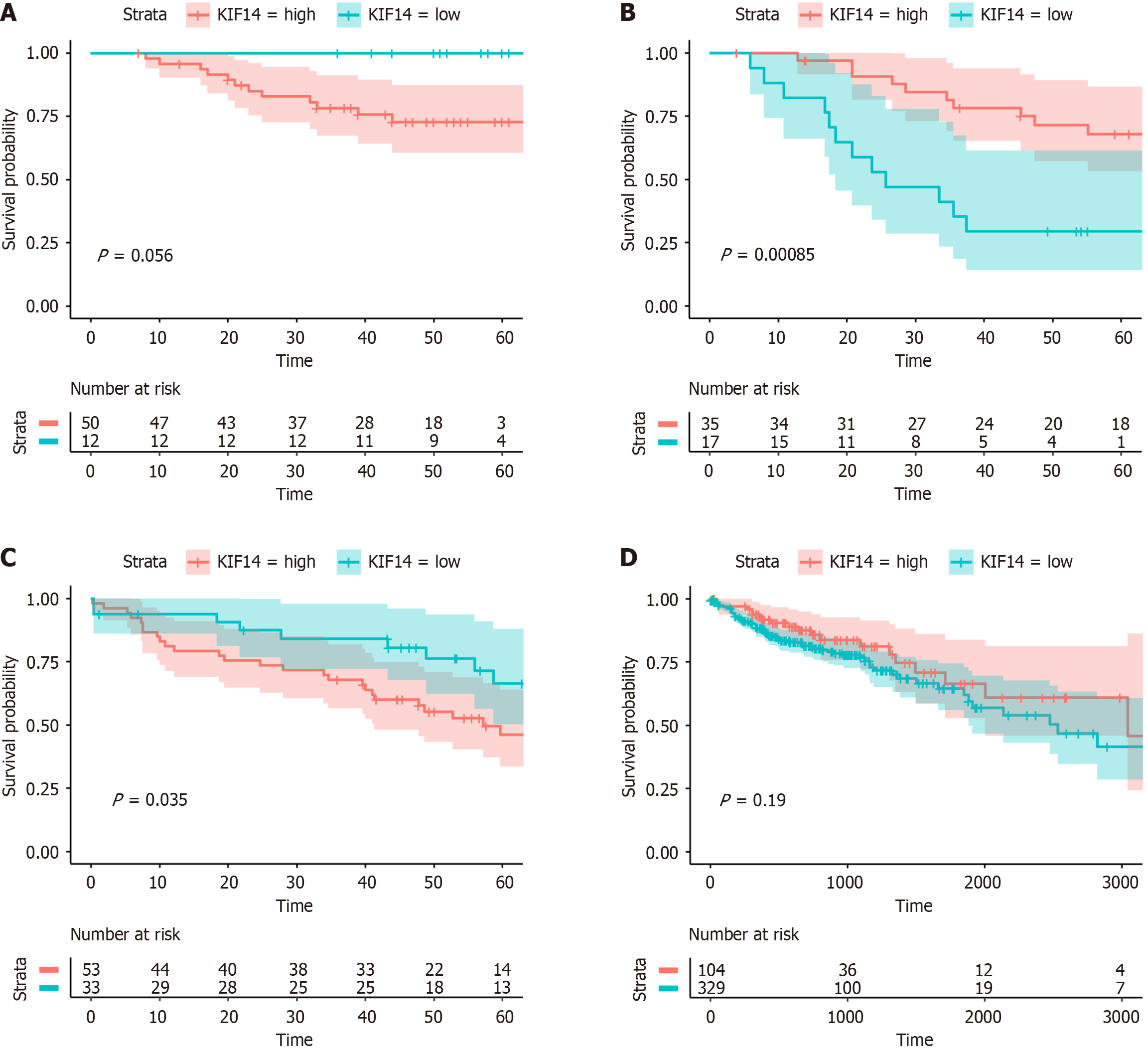
Figure 10 Prognostic analysis of Kinesin family member 14 in colorectal cancer.
A: GSE12945; B: GSE71187; C: GSE103679; D: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
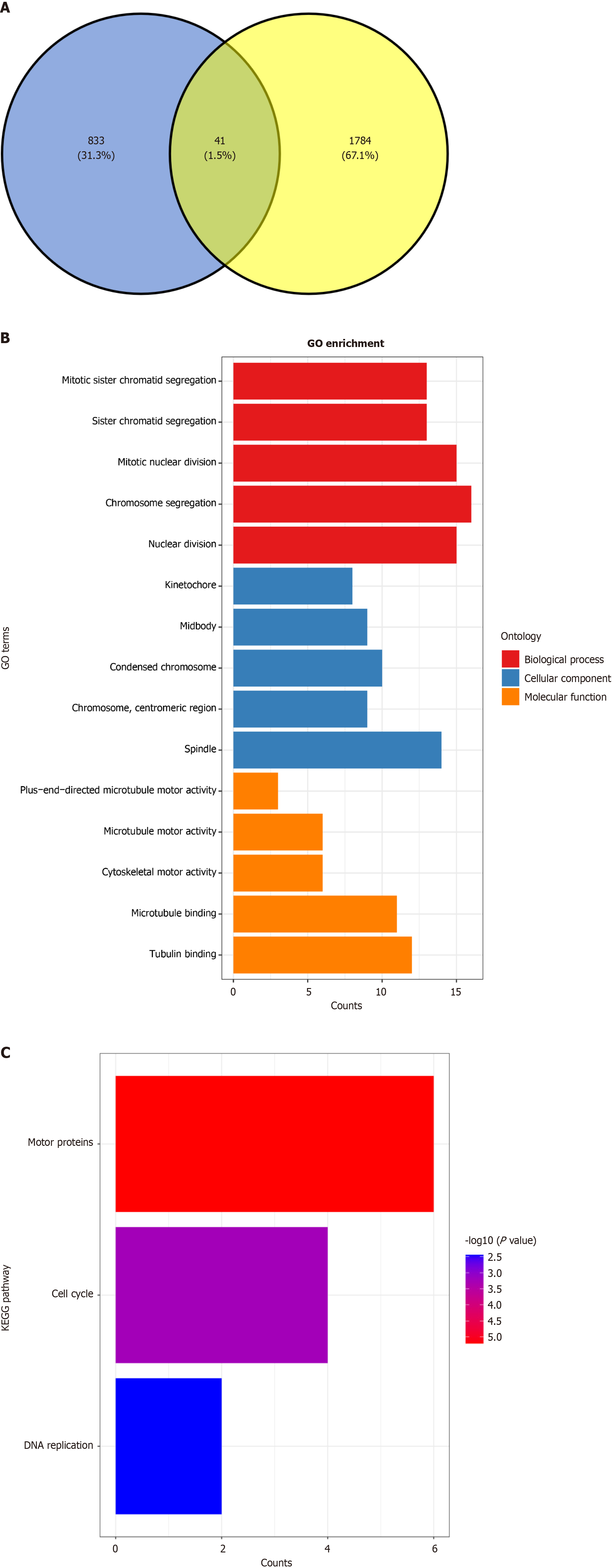
Figure 11 Exploring the molecular mechanisms by which nitidine chloride impacts colorectal cancer progression.
A: Identification of common genes via overexpressed genes (in blue) and differentially expressed genes (in yellow) intersection; B: Functional enrichment analysis of common genes using Gene Ontology; C: Pathway analysis of common genes using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; GO: Gene Ontology.
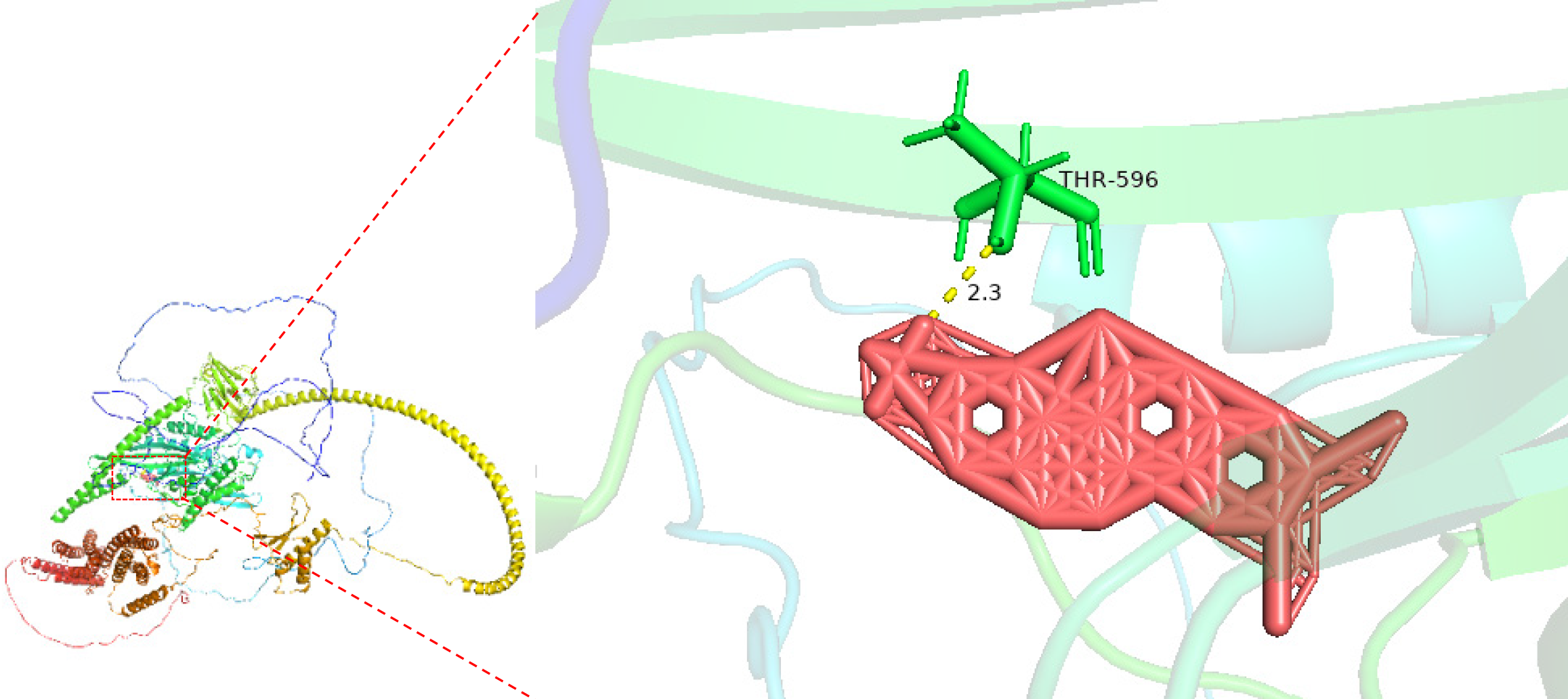
Figure 12 Molecular interaction between nitidine chloride and Kinesin family member 14 (Binding energy: -10.
3 kcal/mol).
- Citation: Qin K, Luo JY, Zeng DT, Huang WY, Li B, Li Q, Zhan YT, He RQ, Huang WJ, Chen G, Chen ZY, Chi BT, Tang YX, Tang RX, Li H. Kinesin family member 14 expression and its clinical implications in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 102696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/102696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102696