©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 99662
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.99662
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.99662
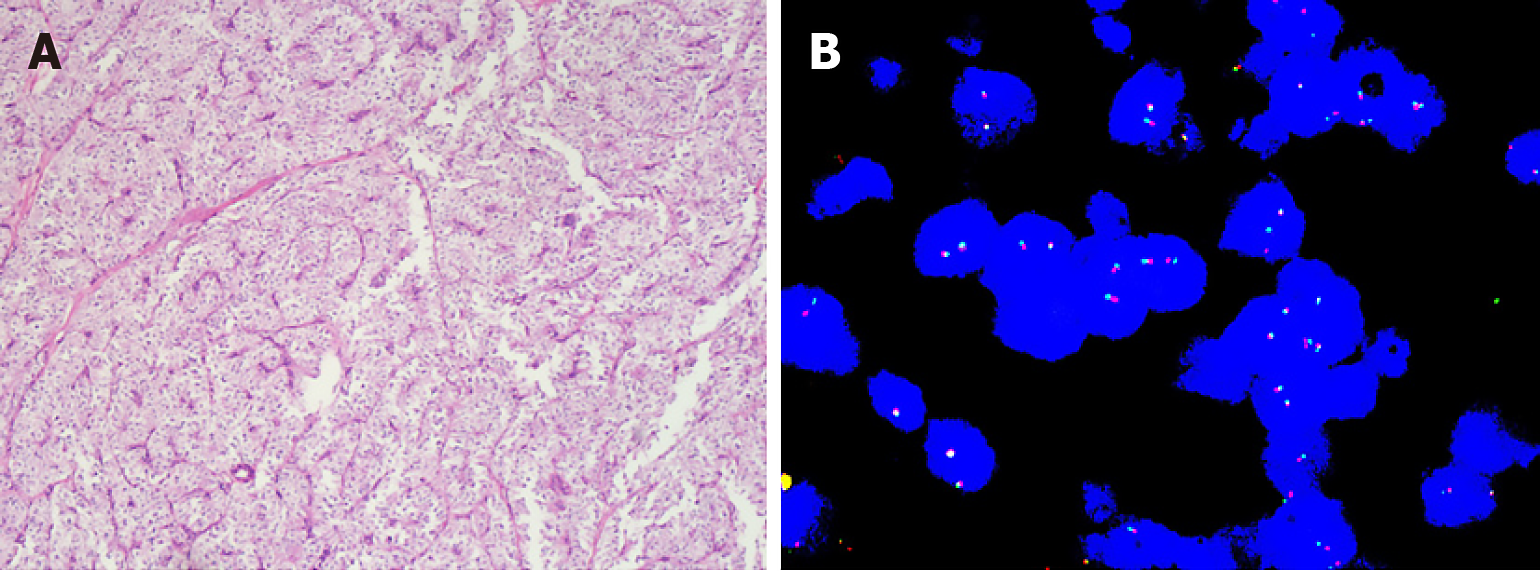
Figure 1 Pathological results of colorectal malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor.
A: High magnification view showing epithelioid and spindly tumor cells (hematoxylin and eosin stain); B: Ewing Sarcoma protein RNA binding protein 1 detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization.
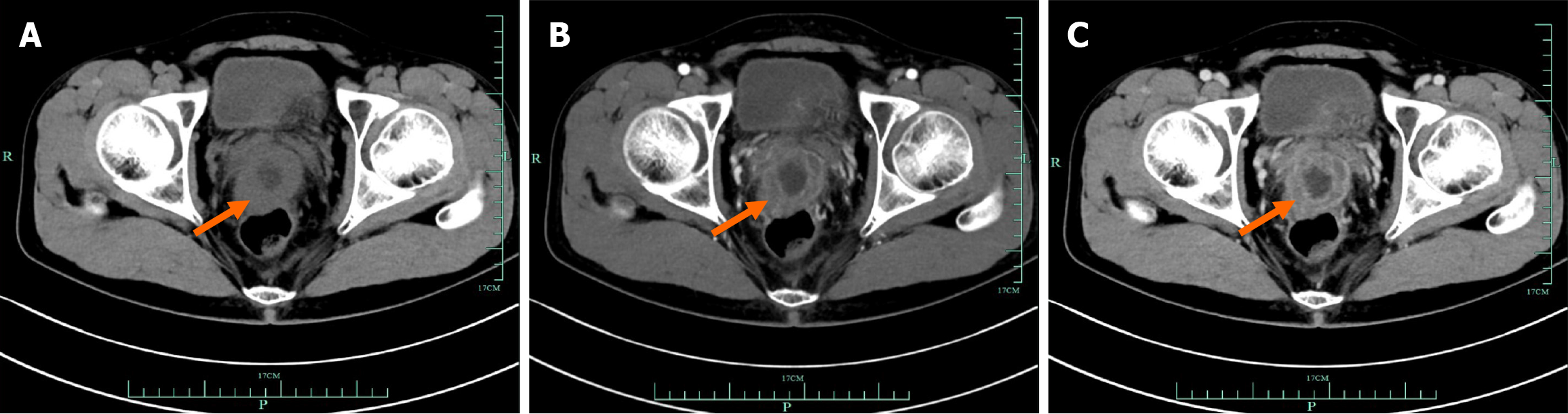
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan showed an invasive lesion (orange arrow) located in the anterior wall of the rectum (case 7).
A: Non contrast; B: Arterial phase; C: Venous phase.
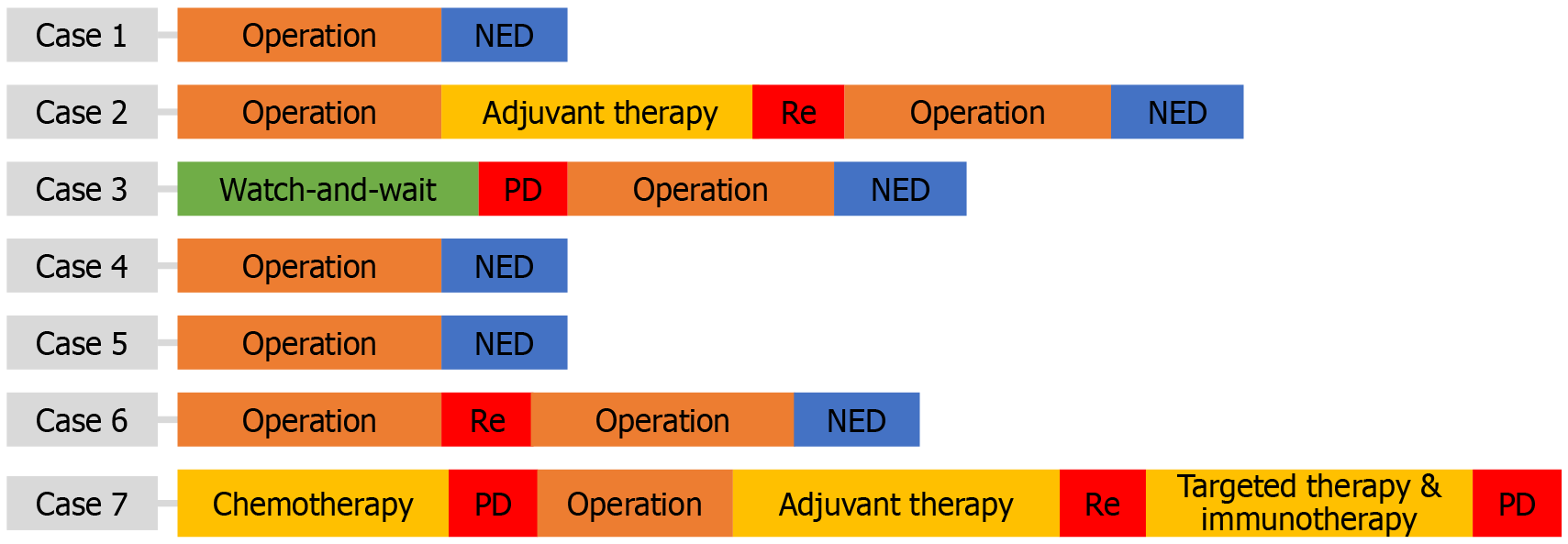
Figure 3 Treatment process and efficacy evaluation of the 7 cases.
NED: No evidence of disease; PD: Progressive disease; Re: Relapse.
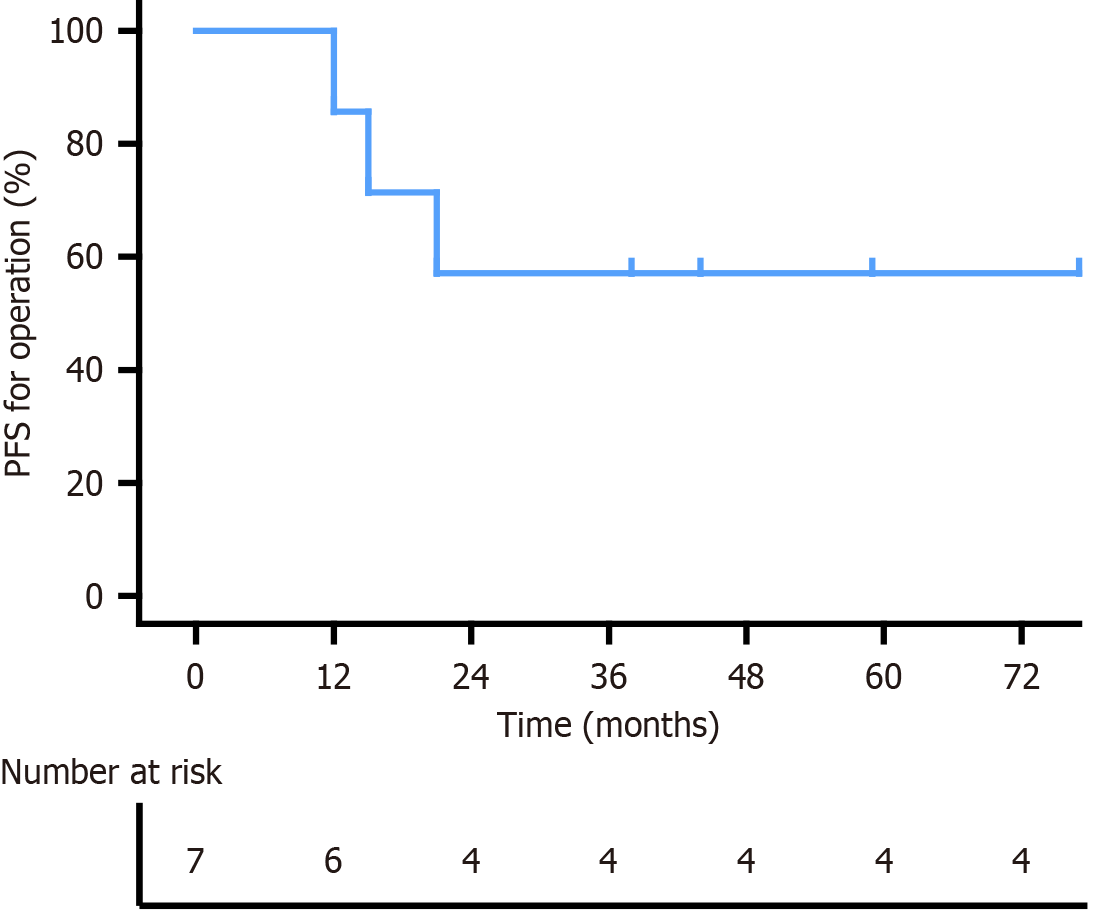
Figure 4 Kaplan–Meier curve for progression-free survival of patients with colorectal malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor treated by operation.
PFS: Progression-free survival.
- Citation: Ma MF, Chi ZY, Zhao LJ, Zhai W, Zhong W, Wang S. Malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the colorectum: Clinicopathological characterization, diagnosis and treatment process of 7 cases. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 99662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/99662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.99662