©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3471-3480
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3471
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3471
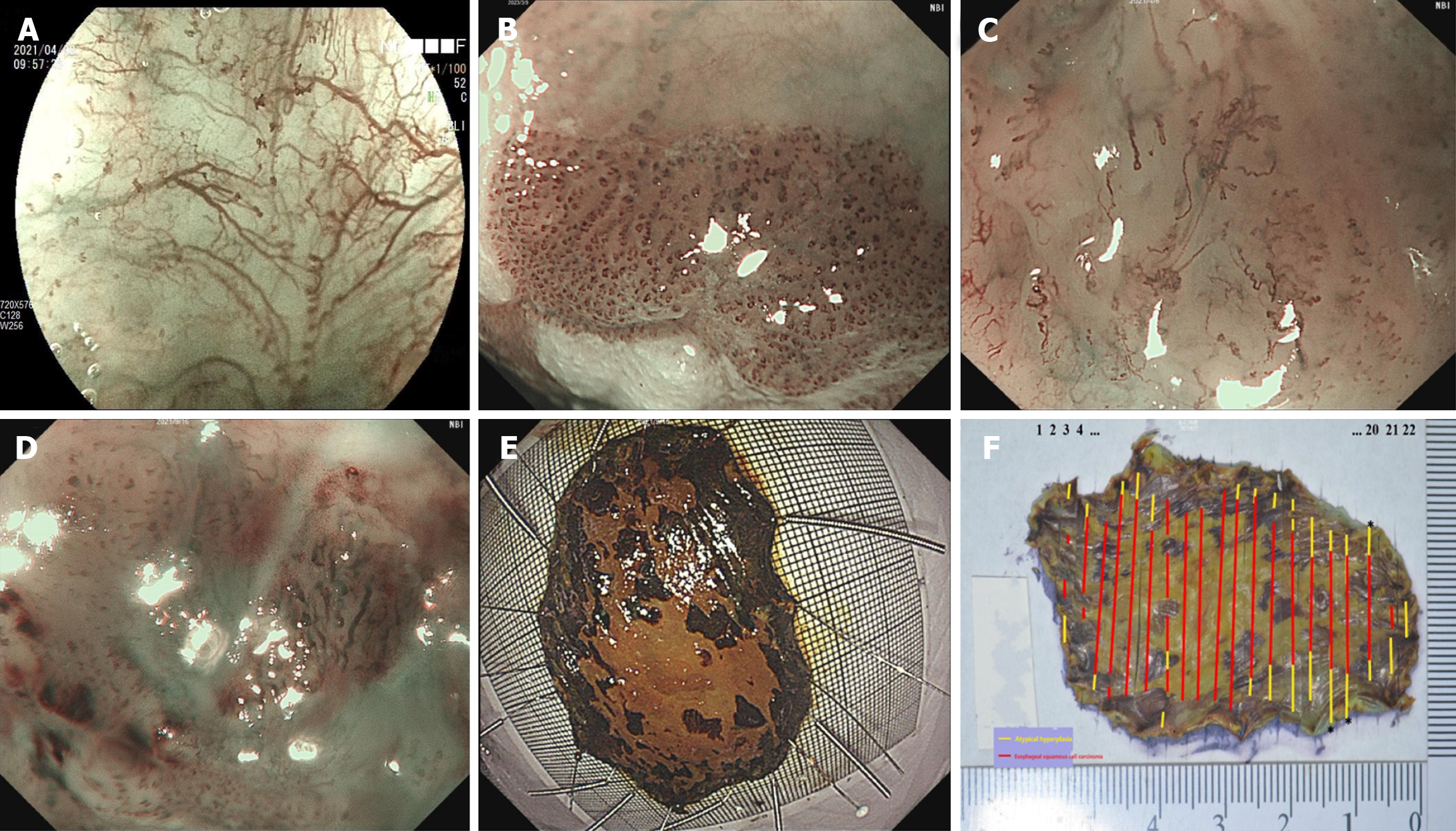
Figure 1 Intrapapillary capillary loops in superficial esophageal lesions under magnifying endoscopy and photographic recordings of both fresh and fixed specimens.
A: Intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs) of type A under narrow-band imaging or blue laser imaging combined with magnifying endoscopy (ME-NBI/BLI) (magnification: × 80); B: IPCLs of type B1 under ME-NBI/BLI (magnification: × 80); C: IPCLs of type B2 under ME-NBI/BLI (magnification: × 80); D: IPCLs of type B3 under ME-NBI/BLI (magnification: × 80); E: Flesh specimen after endoscopic resection; F: Pathologically fixed specimen with the red line marking the extent of the cancer and the yellow line marking the extent of intraepithelial neoplasia.
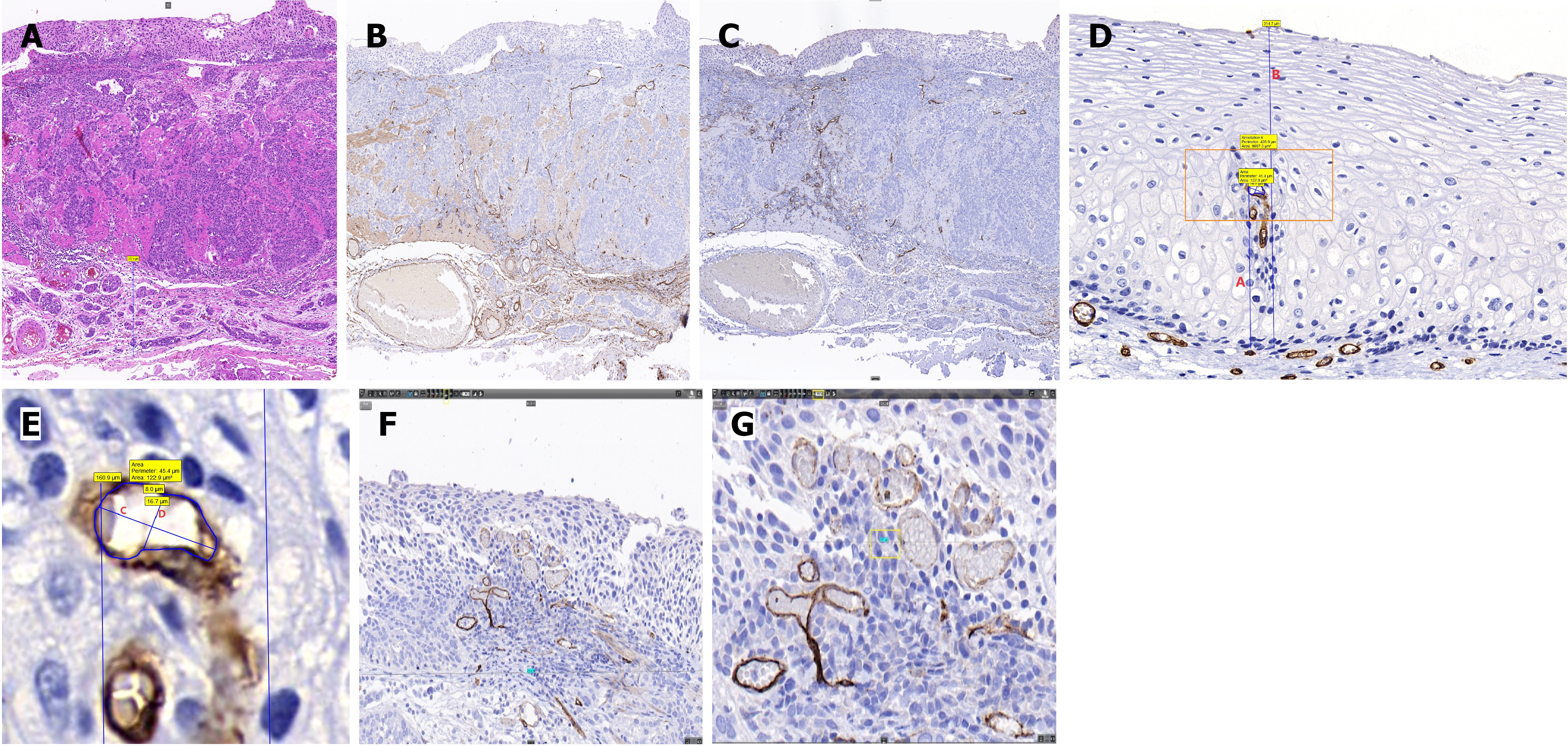
Figure 2 Pathological data collection using Case Viewer software.
A: Pathological slide stained with hematoxylin and eosin (magnification: × 100); B: Pathological slide stained for CD34 (magnification: × 100); C: Pathological slide stained for D2-40 (magnification: × 100); D: Measurement of intrapapillary capillary loop (IPCL)-related characteristics (red A: Apical distance from the vertex of the IPCL to the basement membrane; red B: Thickness of the epithelial layer); E: Enlarged orange region in picture D (red C: Short caliber of the IPCL; red D: Long caliber of the IPCL; and the region enclosed by the blue line is the area of the IPCL); F: Pathological slide stained for CD34 (magnification: × 800); the transverse diameter of each field of view was 719.8 μm; G: Pathological slide stained for CD34 (magnification: × 2000); the transverse diameter of each field of view is 287.9 μm.
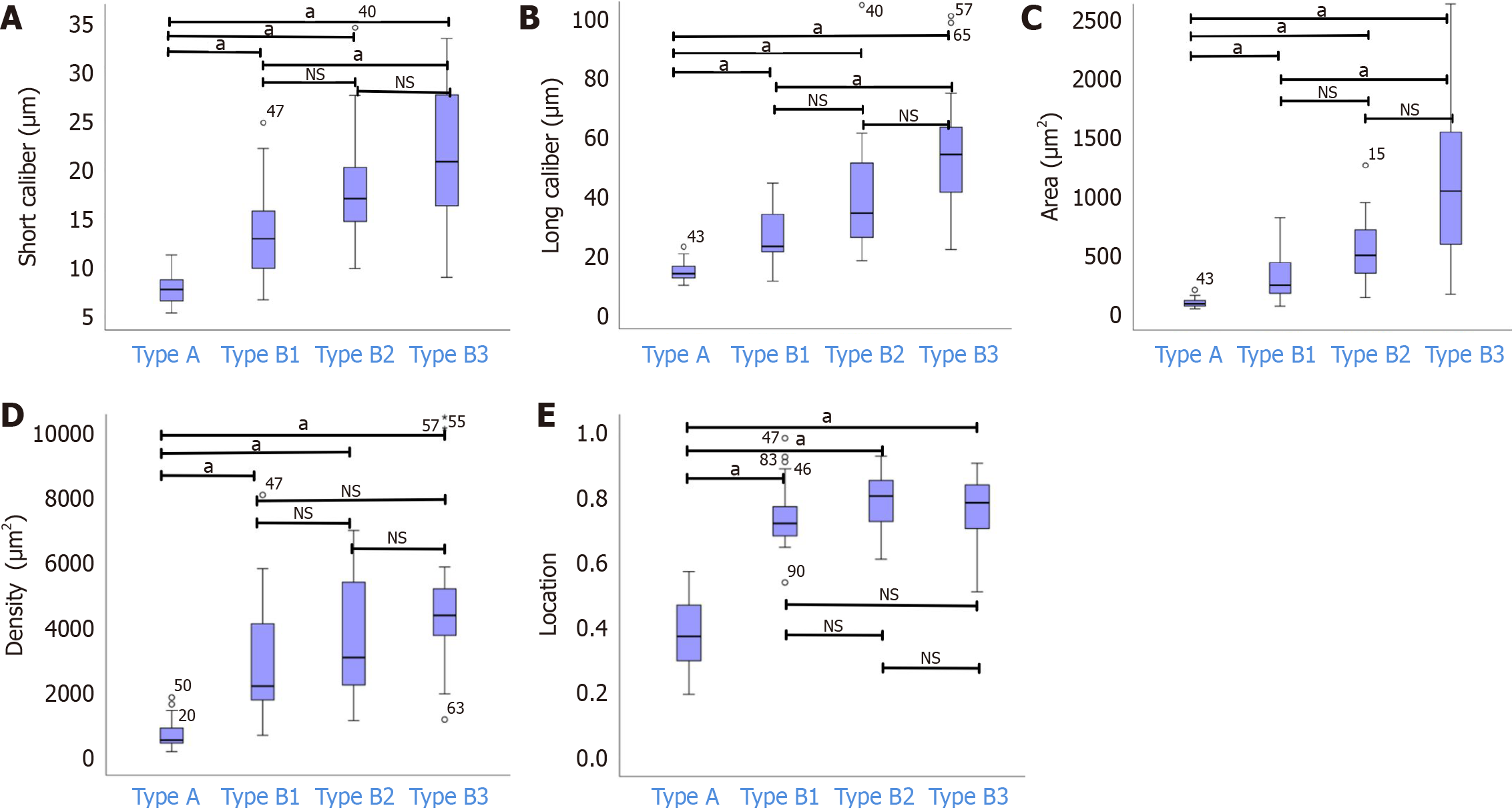
Figure 3 Nonparametric test results in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for short caliber, long caliber, area, density, and location of intrapapillary capillary loops.
A: Nonparametric test in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for the short caliber of intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs); B: Nonparametric test in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for long caliber of IPCLs; C: Nonparametric test in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for area of IPCLs; D: Nonparametric test in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for density of IPCLs; E: Nonparametric test in types A, B1, B2, and B3 for location of IPCLs. aP < 0.05; NS: P > 0.05.
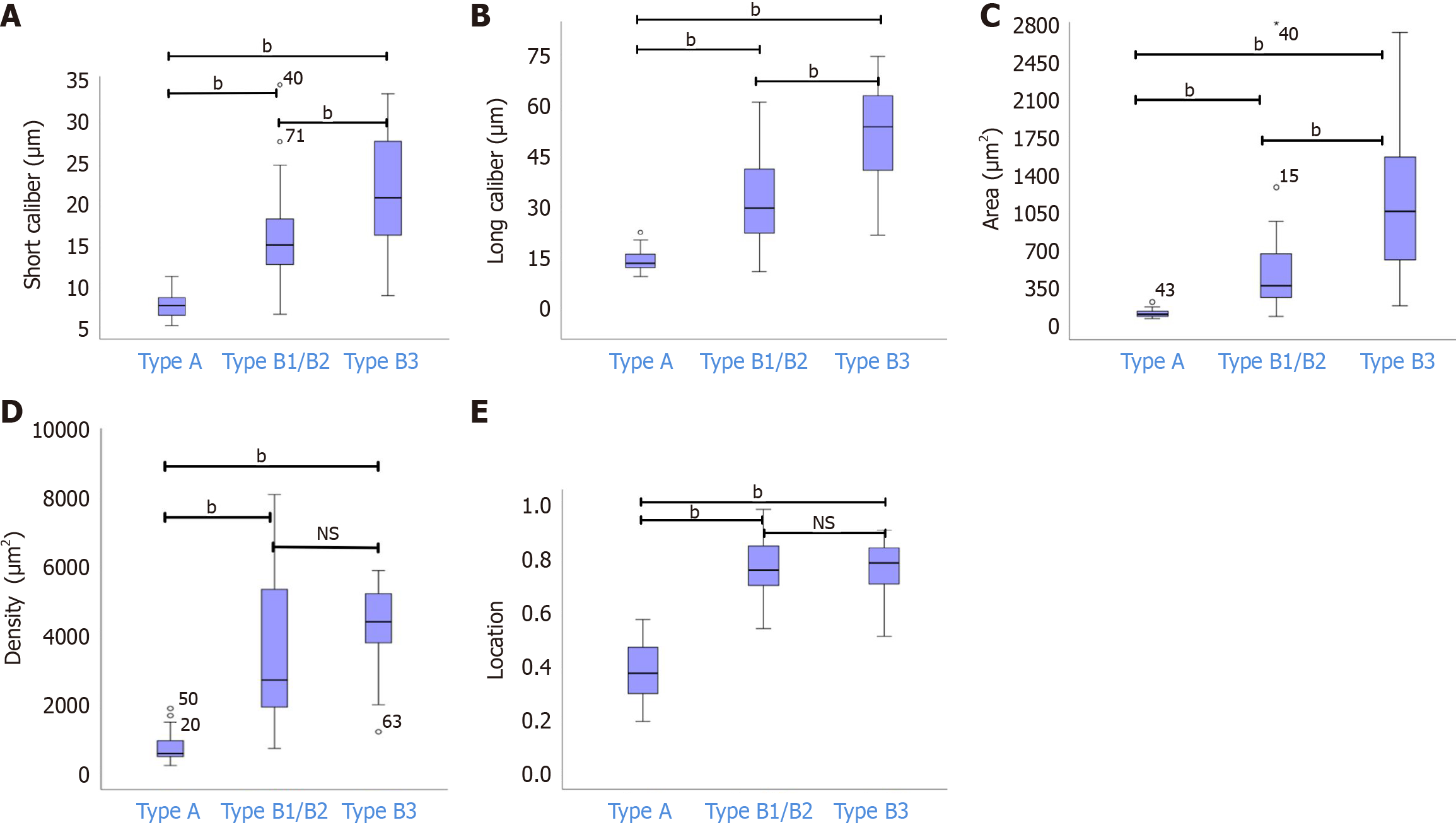
Figure 4 Nonparametric test results in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for short caliber, long caliber, area, density, and location of Intrapapillary capillary loops.
A: Nonparametric test in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for short caliber of Intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs); B: Nonparametric test in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for long caliber of IPCLs; C: Nonparametric test in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for area of IPCLs; D: Nonparametric test in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for density of IPCLs; E: Nonparametric test in types A, B1/B2, and B3 for location of IPCLs. bP < 0.05; NS: P > 0.05.
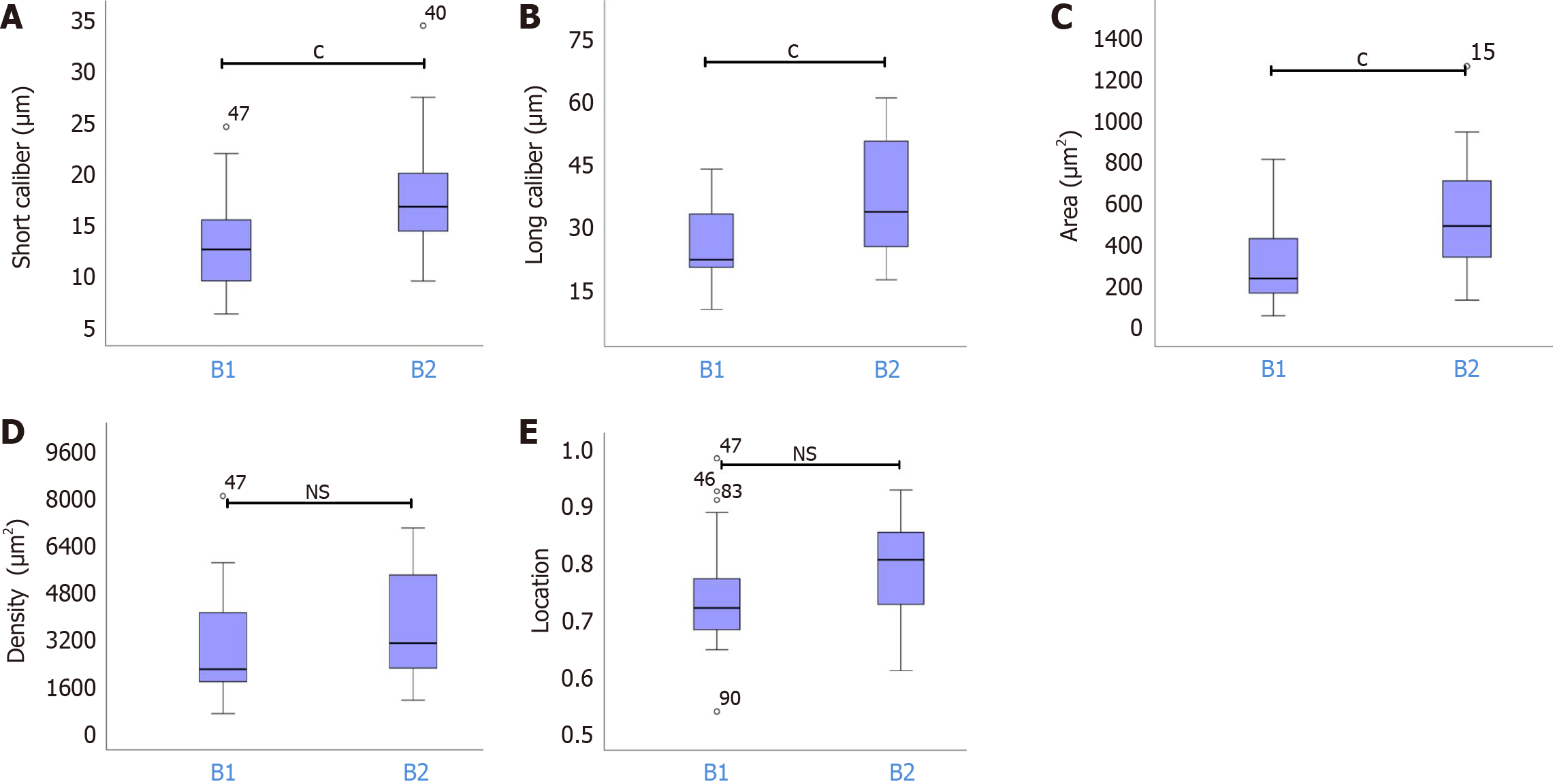
Figure 5 T-test results between types B1 and B2 for short caliber, long caliber, area, density, and location of Intrapapillary capillary loops.
A: Nonparametric test in types B1 and B2 for short caliber of intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs); B: Nonparametric test in types B1 and B2 for long caliber of IPCLs; C: Nonparametric test in types B1 and B2 for area of IPCLs; D: Nonparametric test in types B1 and B2 for density of IPCLs; E: Nonparametric test in types B1 and B2 for location of IPCLs. cP < 0.05; NS: P > 0.05.
- Citation: Shu WY, Shi YY, Huang JT, Meng LM, Zhang HJ, Cui RL, Li Y, Ding SG. Microvascular structural changes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma pathology according to intrapapillary capillary loop types under magnifying endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3471-3480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3471.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3471