©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2024; 16(1): 30-50
Published online Jan 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i1.30
Published online Jan 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i1.30
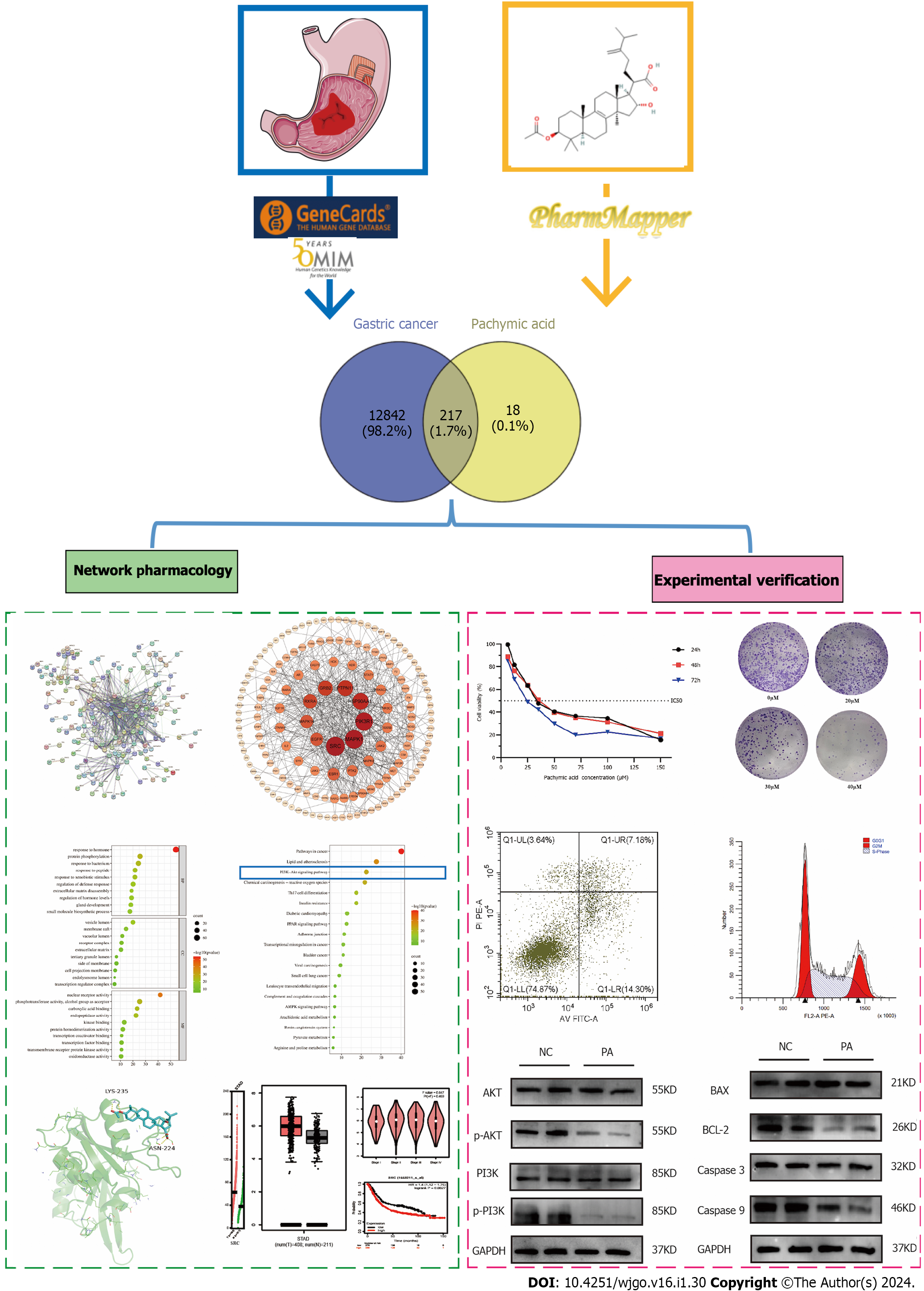
Figure 1 Flow chart.
A variety of databases used to find the targets of gastric cancer (GC) and pachymic acid (PA), and the common targets were obtained. The possible targets and pathways of PA in the treatment of GC were analyzed by network pharmacology, and finally verified by experiments.
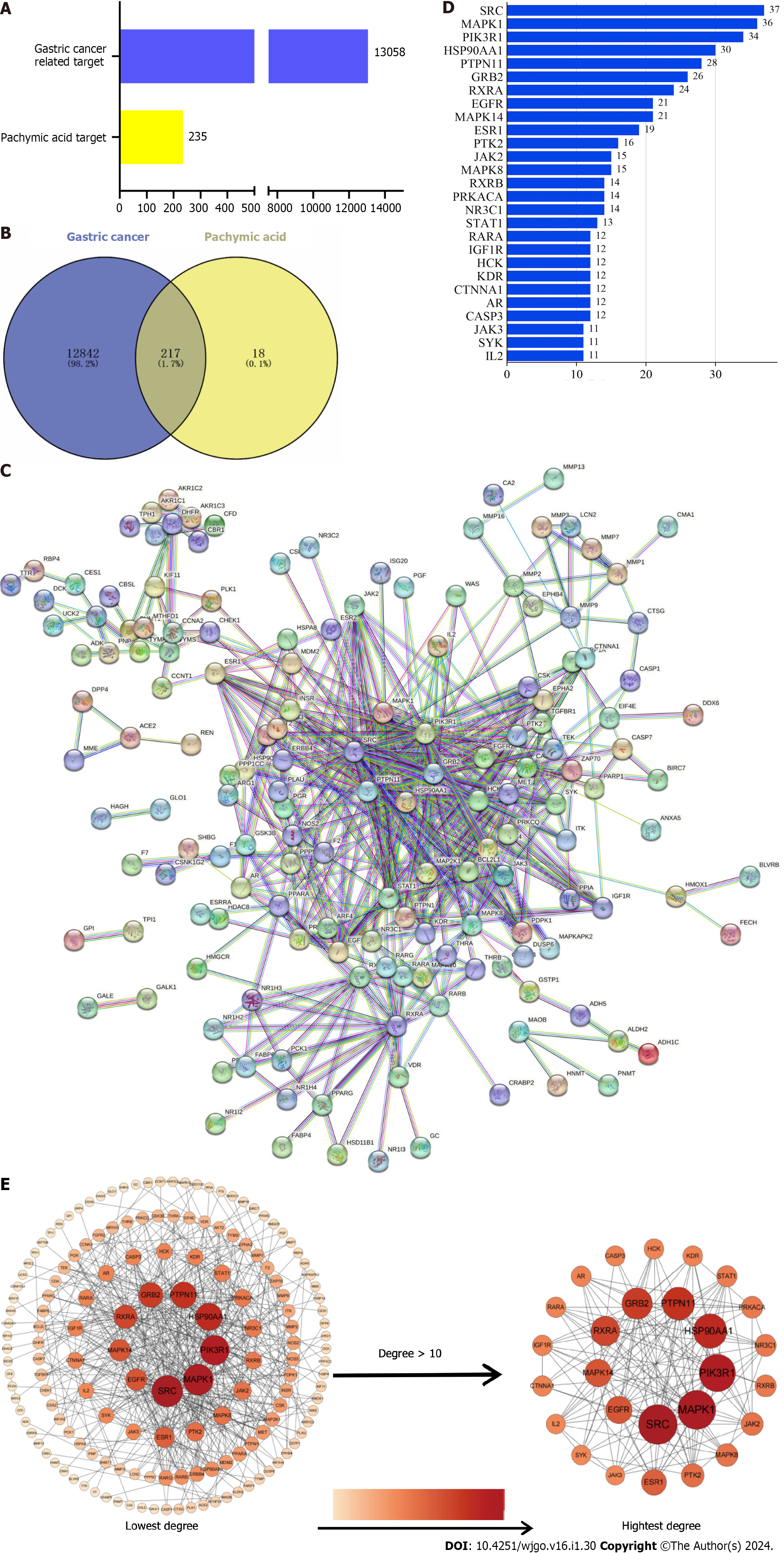
Figure 2 Prediction of core targets.
A: Number of gastric cancer (GC) targets and pachymic acid (PA) targets; B: Venn diagram of intersection of target PA targets in GC; C: Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network diagram of intersection targets; D: Degree values of core targets; E: PPI network graph sorted by degree value, and core targets were screened according to degree value greater than 10. SRC: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; MAPK1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; PI3KR1: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha; HSP90AA1: Heat shock protein 90-alpha; PTPN11: Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11; GRB2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; RXRA: Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ESR1: Estrogen receptor; JAK2: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2; PRKACA: cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; NR3C1: Glucocorticoid receptor; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta; RARA: Retinoic acid receptor alpha; IGF1R: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; HCK: Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK; KDR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; CTNNA1: Catenin alpha-1; AR: Androgen receptor; CASP3: Caspase-3; SYK: Syrosine-protein kinase SYK; IL2: Interleukin-2.
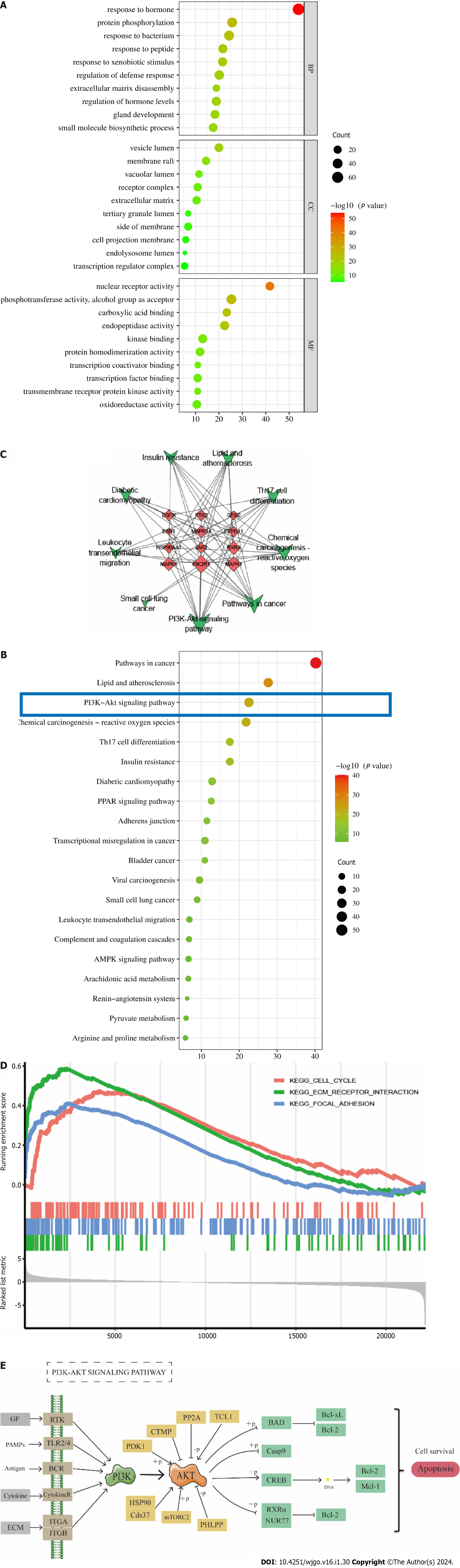
Figure 3 Enrichment analysis.
A: Gene Ontology enrichment analysis; B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis; C: Protein-protein interaction network diagram of KEGG pathways and top 12 core targets, green represents pathways and red represents core targets; D: Gene set enrichment analysis analyzed the results; E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. GF: Growth factor; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; ECM: von Willebrand factor; TLR2/4: Toll-like receptor 2/4; BCR: Breakpoint cluster region protein; ITGA: Integrin alpha; ITGB: Integrin beta; PDK1: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; PP2A: Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit; TCL1: T-cell leukemia/lymphoma protein 1A; HSP90: Heat shock protein 90; mTORC2: CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2; PHLPP: PH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase 1; BAD: Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death; CREB: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase creB.
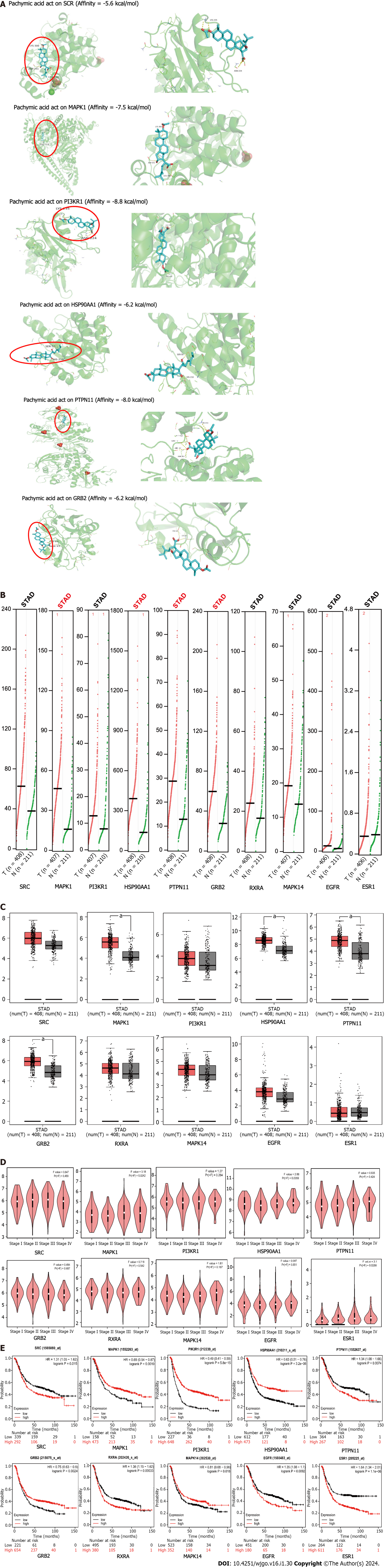
Figure 4 Analysis of molecular docking and clinical relevance.
A: Pachymic acid docked with the top 6 core target molecules with degree value; B: Copy number analysis of the top ten core targets in gastric cancer (GC); C: Correlation analysis between GC and paracancerous sites of the top ten core targets; D: GC grading and staging analysis of the top ten core targets; E: Survival analysis of the top ten core targets. SRC: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; MAPK1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; PI3KR1: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha; HSP90AA1: Heat shock protein 90-alpha; PTPN11: Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11; GRB2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; RXRA: Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ESR1: Estrogen receptor.
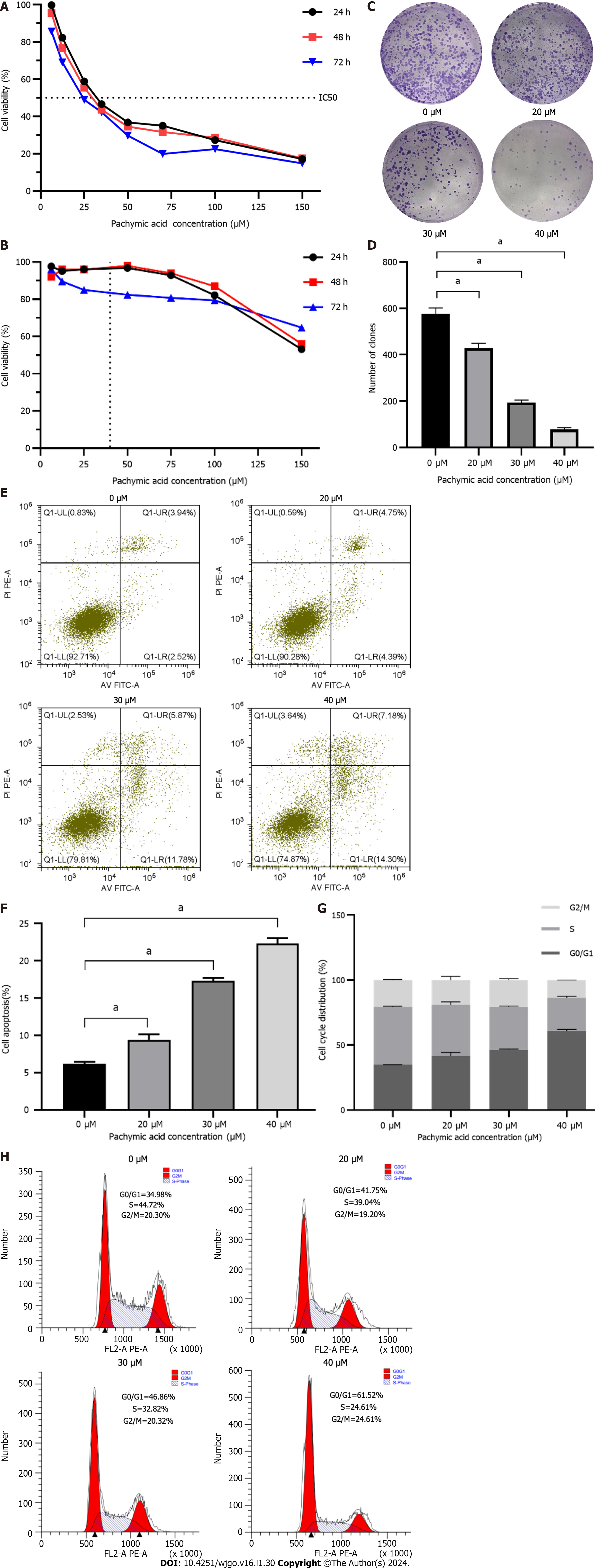
Figure 5 Effect of pachymic acid on the phenotype of gastric cancer cells.
A: The viability of HGC-27 cells treated with pachymic acid (PA) for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h were determined; B: The viability of gastric epithelial GES-1 cells treated with PA for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h were determined; C and D: The quantity of generated cell clones; E and F: Apoptosis rate; G and H: Cell cycle distribution. All experiments were repeated three times and the data were expressed as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
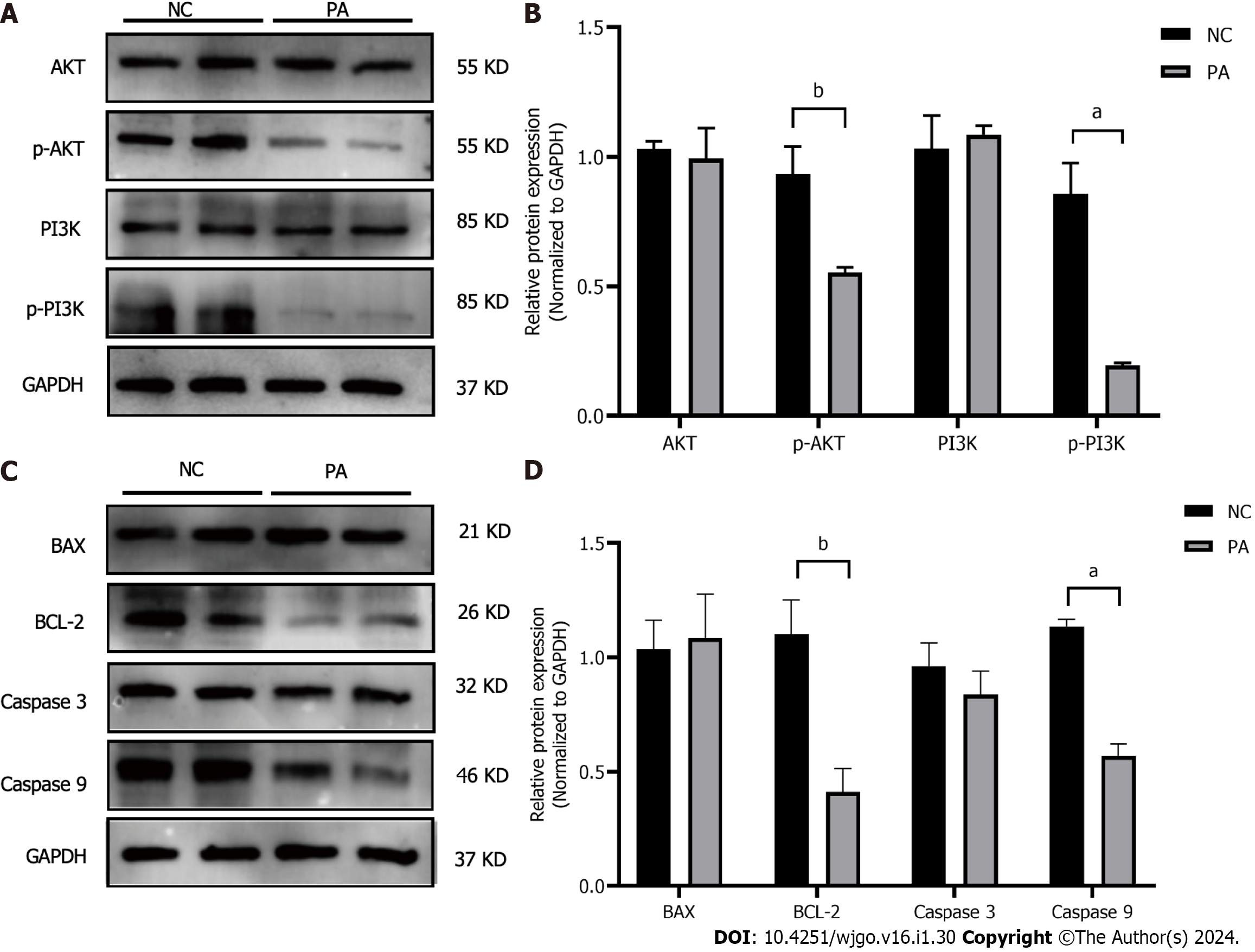
Figure 6 Effect of pachymic acid on the expression of PI3K/AKT pathway and apoptosis-related proteins in gastric cancer cell line HGC-27.
A and B: The impact of pachymic acid (PA) on the expression of proteins connected to the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in HGC-27 cells; C and D: The impact of PA on the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in HGC-27 cells. All experiments were repeated three times and the data were expressed as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. NC: Negative control; PA: Pachymic acid.
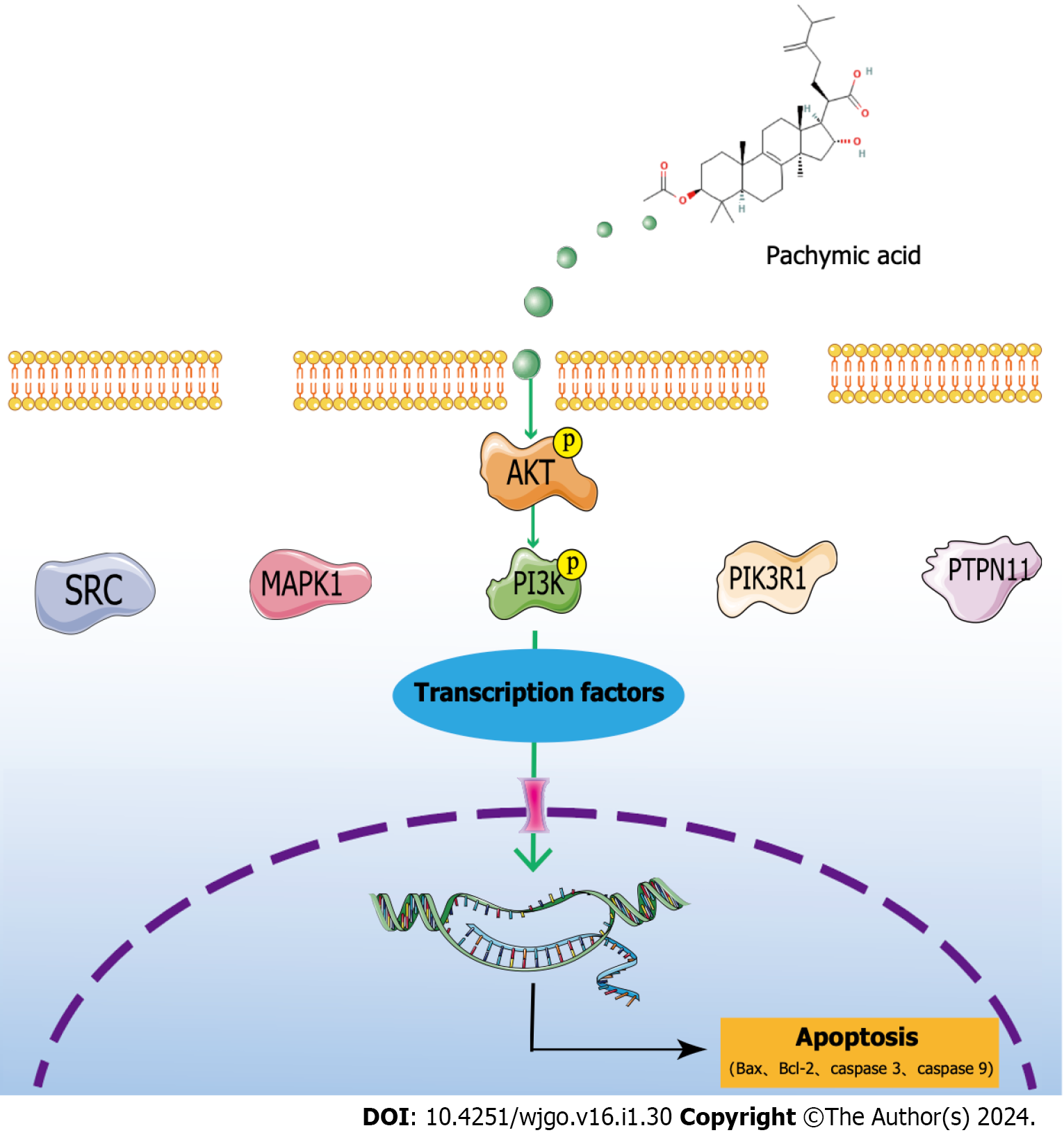
Figure 7 Graphic summary.
SRC: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; MAPK1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: RAC serine/threonine-protein kinase; PIK3R1: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha; HSP90AA1: Heat shock protein 90-alpha; PTPN11: Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11.
- Citation: Du YH, Zhao JJ, Li X, Huang SC, Ning N, Chen GQ, Yang Y, Nan Y, Yuan L. Mechanism of pachymic acid in the treatment of gastric cancer based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(1): 30-50
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i1/30.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i1.30