©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2023; 15(7): 1271-1282
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1271
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1271
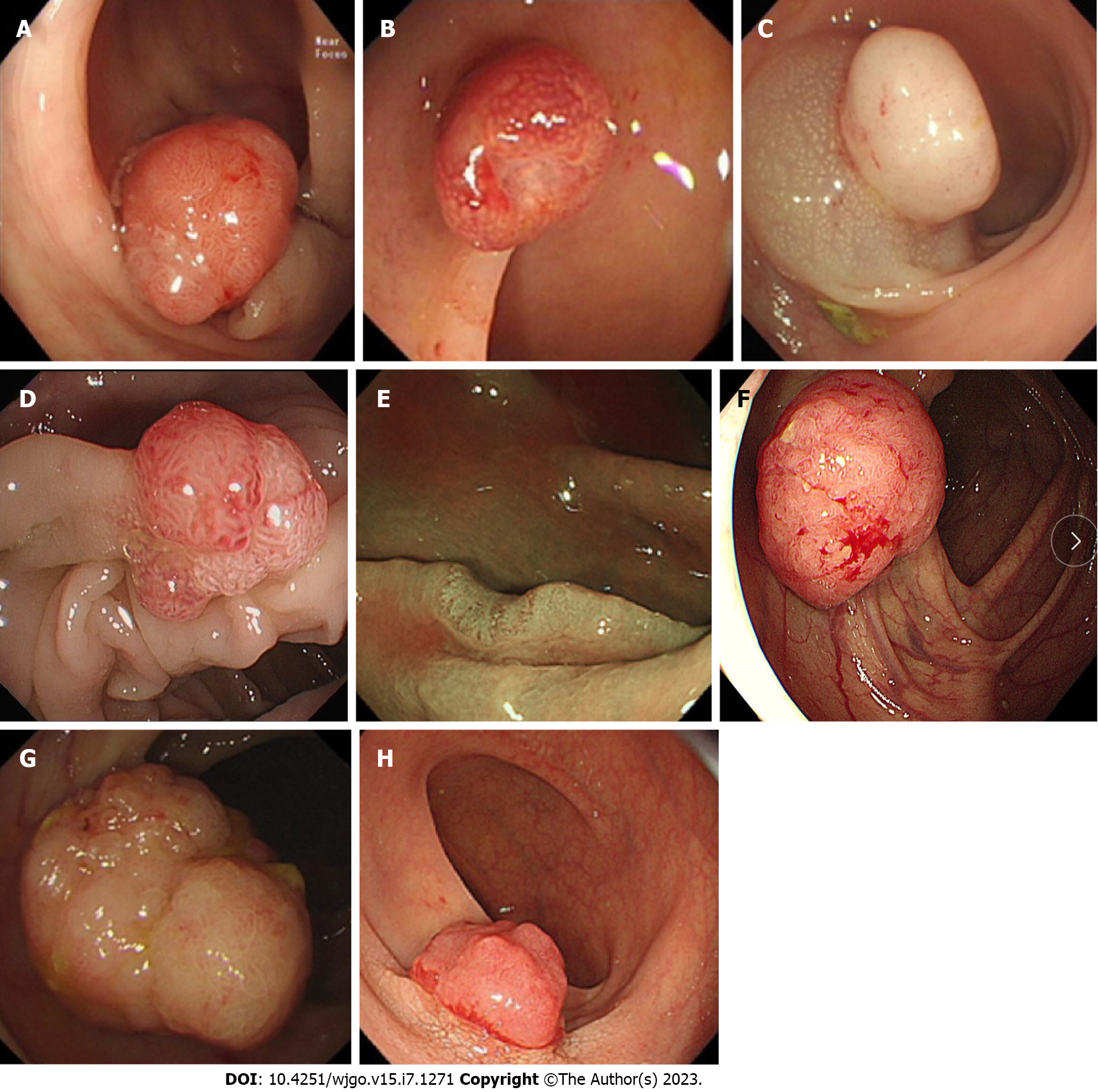
Figure 1 The definitions of the eight endoscopic findings.
A: Hyperemia: redness on the surface of a tumor; B: Erosion: erosion and hyperemia on the surface of a tumor; C: Acanthosis: chicken skin mucosa beside the tumor; D: Lobulation: multiple nodules on the surface of a tumor; E: Depression: depressed demarcation on the surface of a tumor; F: Expansive appearance: a bursting appearance due to the expansive growth of a tumor; G: Larger nodule: nodules larger than 10 mm; H: Uneven surface: surface with bulges and depressions.
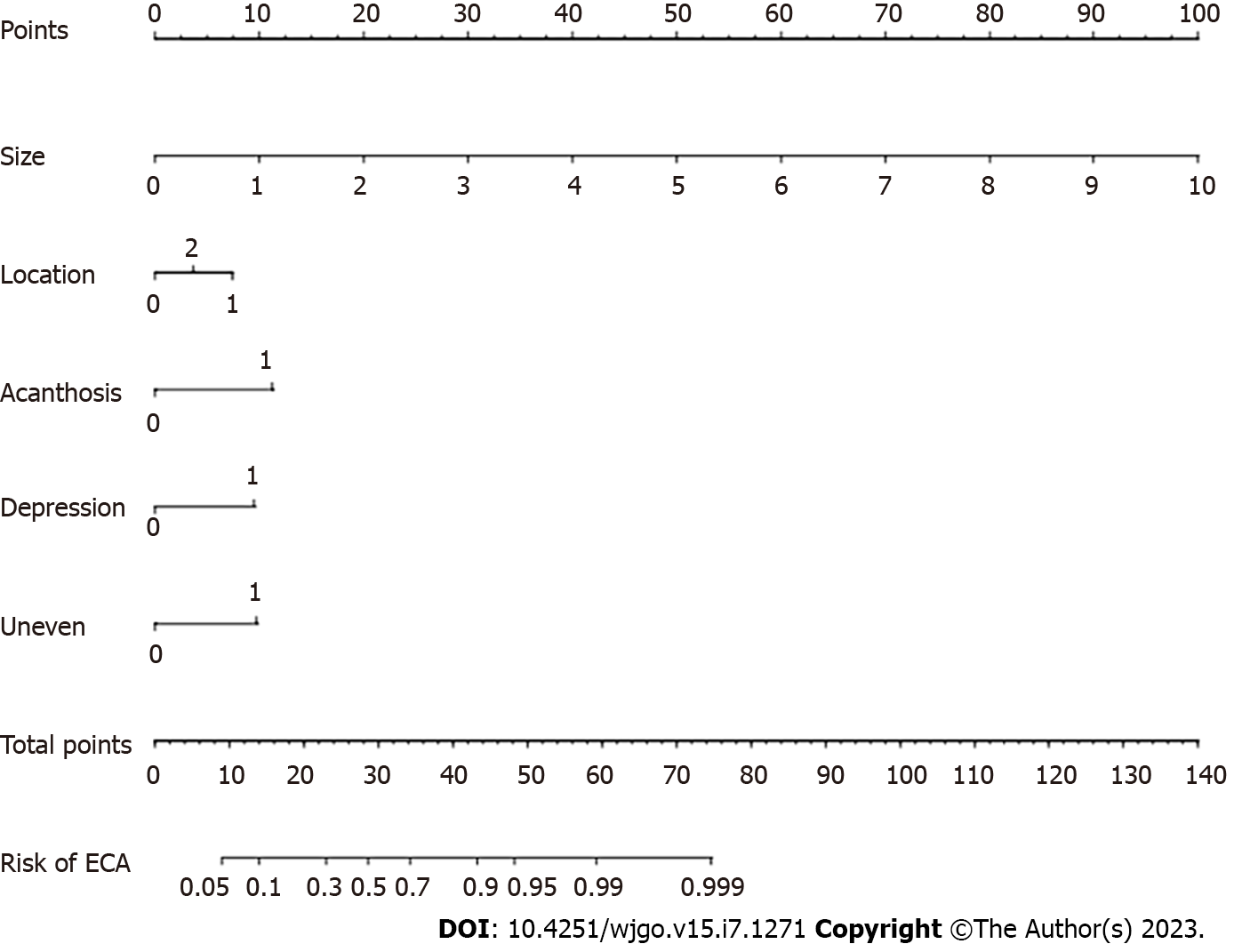
Figure 2 Nomogram for predicting the pathological nature of colorectal tumors.
ECA: Early colorectal adenocarcinoma.
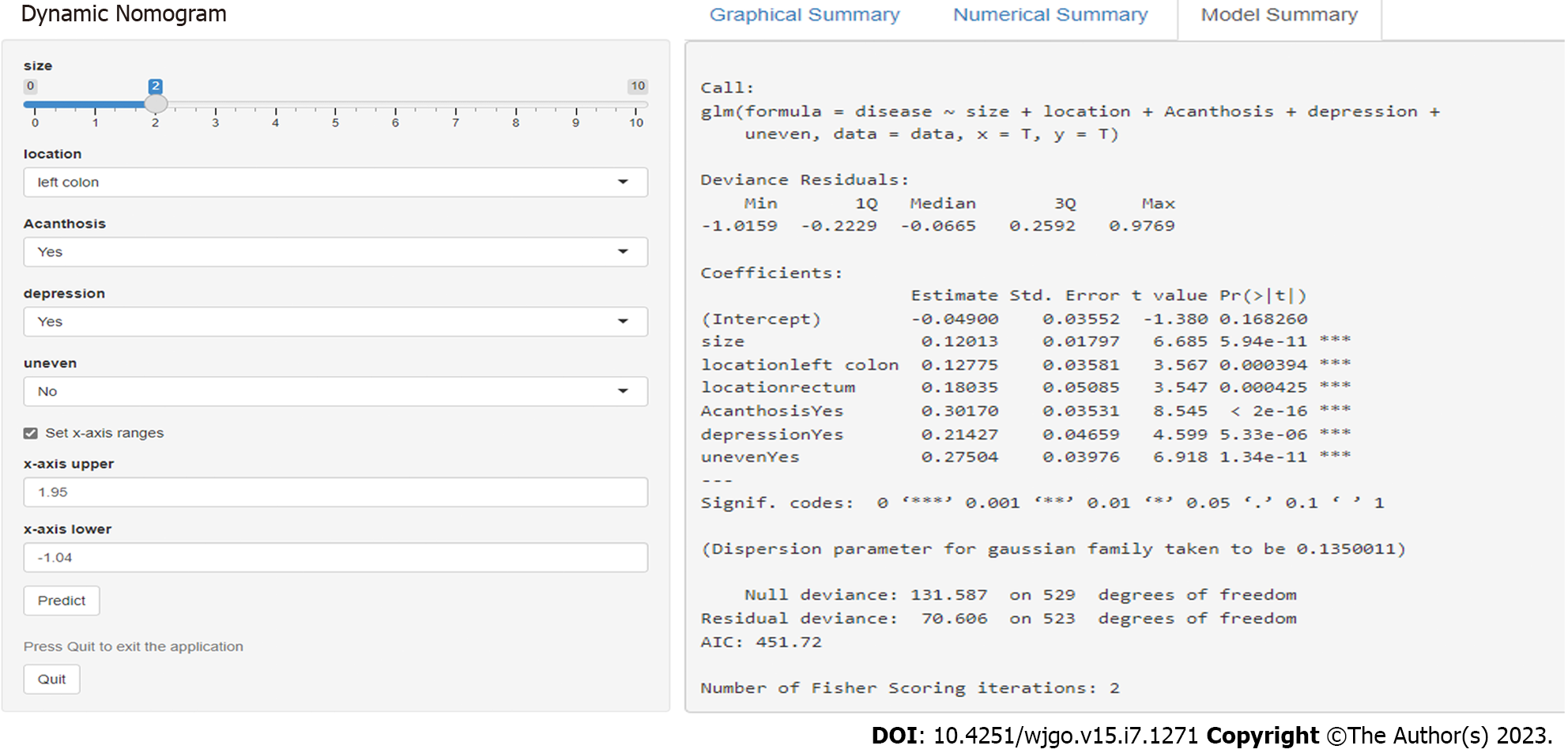
Figure 3 Internet browser-based online calculator.
The online tool: (https://nomogram7474.shinyapps.io/DynNomapp/).
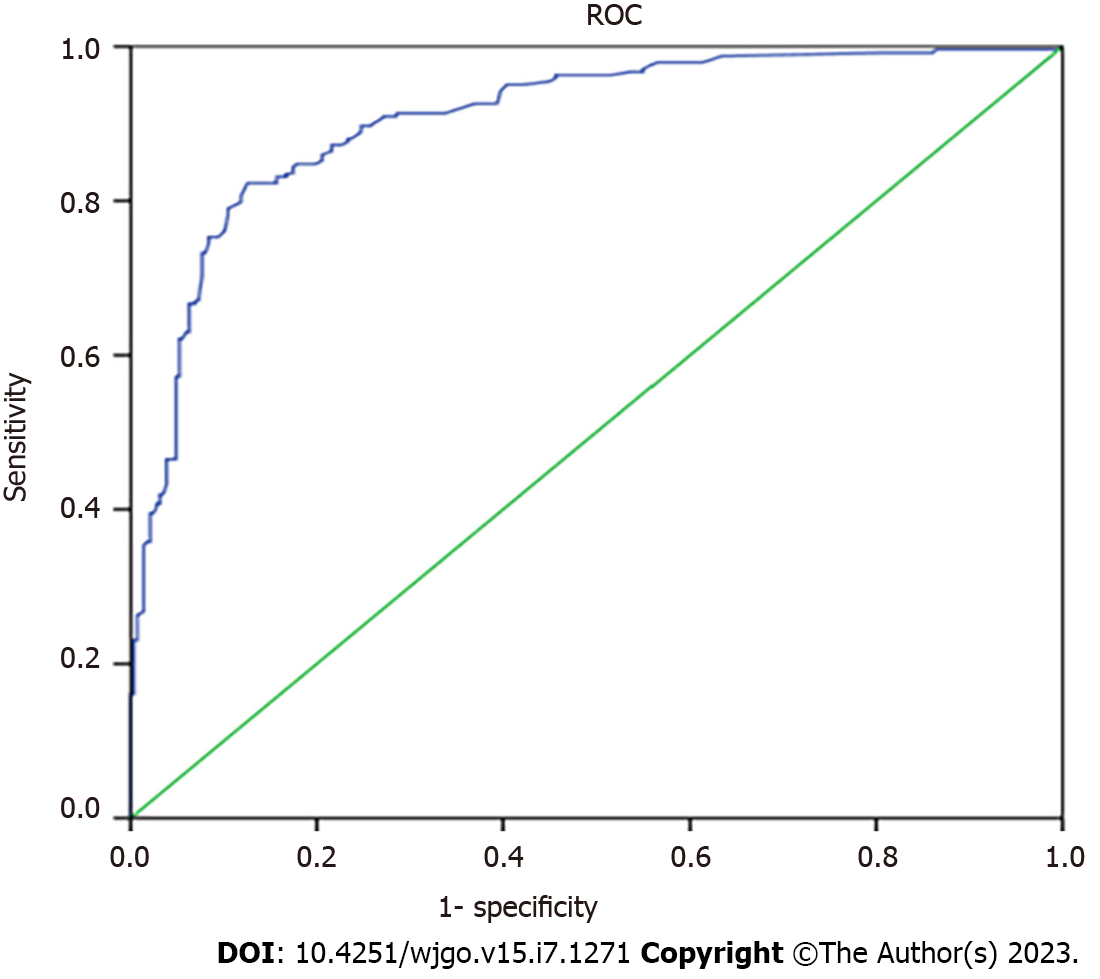
Figure 4 Receiver operator characteristic curve in the validation cohort.
ROC: The receiver operator characteristic curve.
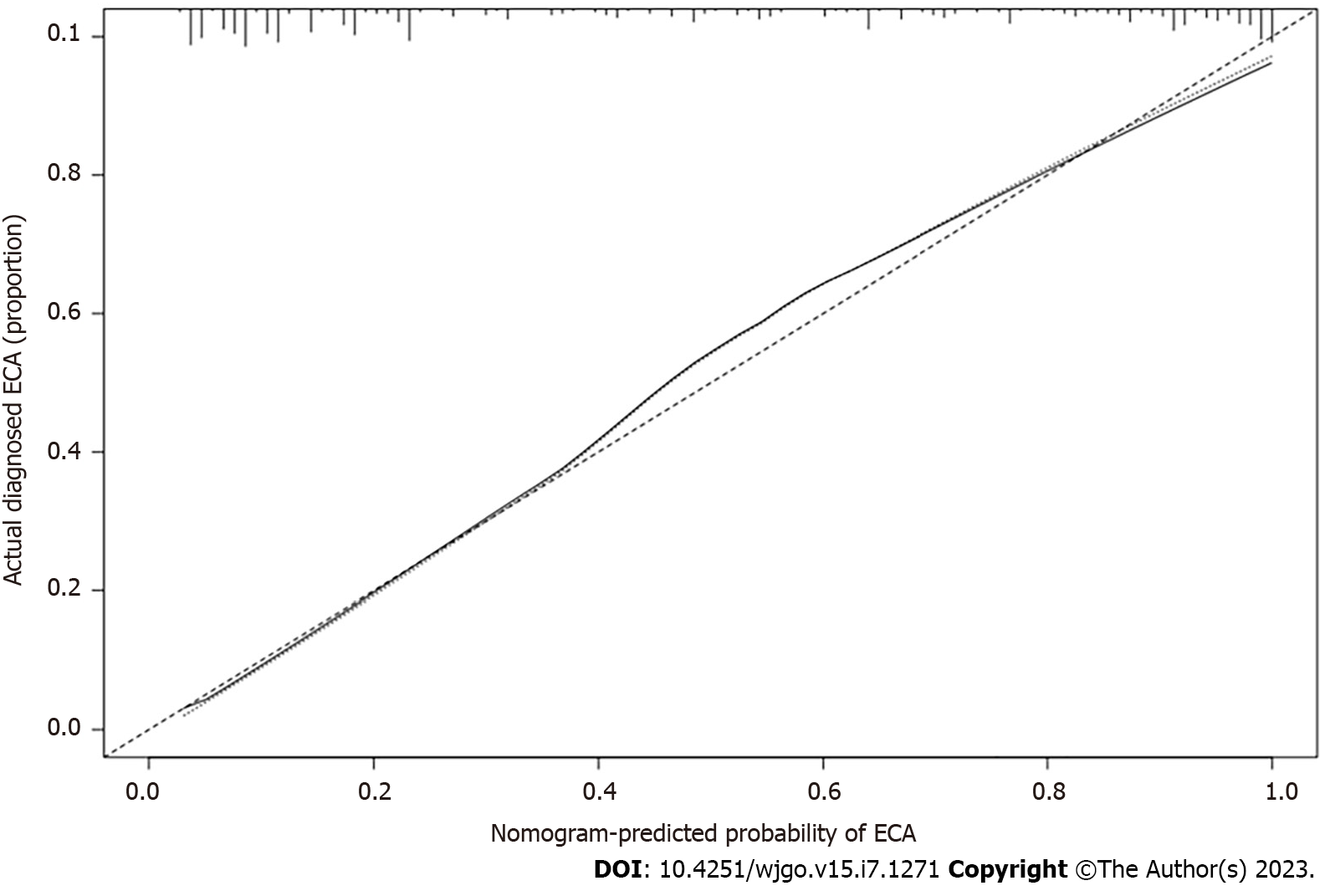
Figure 5 Calibration plot of the prediction.
The calibration curve shows good consistency between the predicted risk of early colorectal adenocarcinoma and the actual risk of pathological assessment using nomogram. ECA: Early colorectal adenocarcinoma.
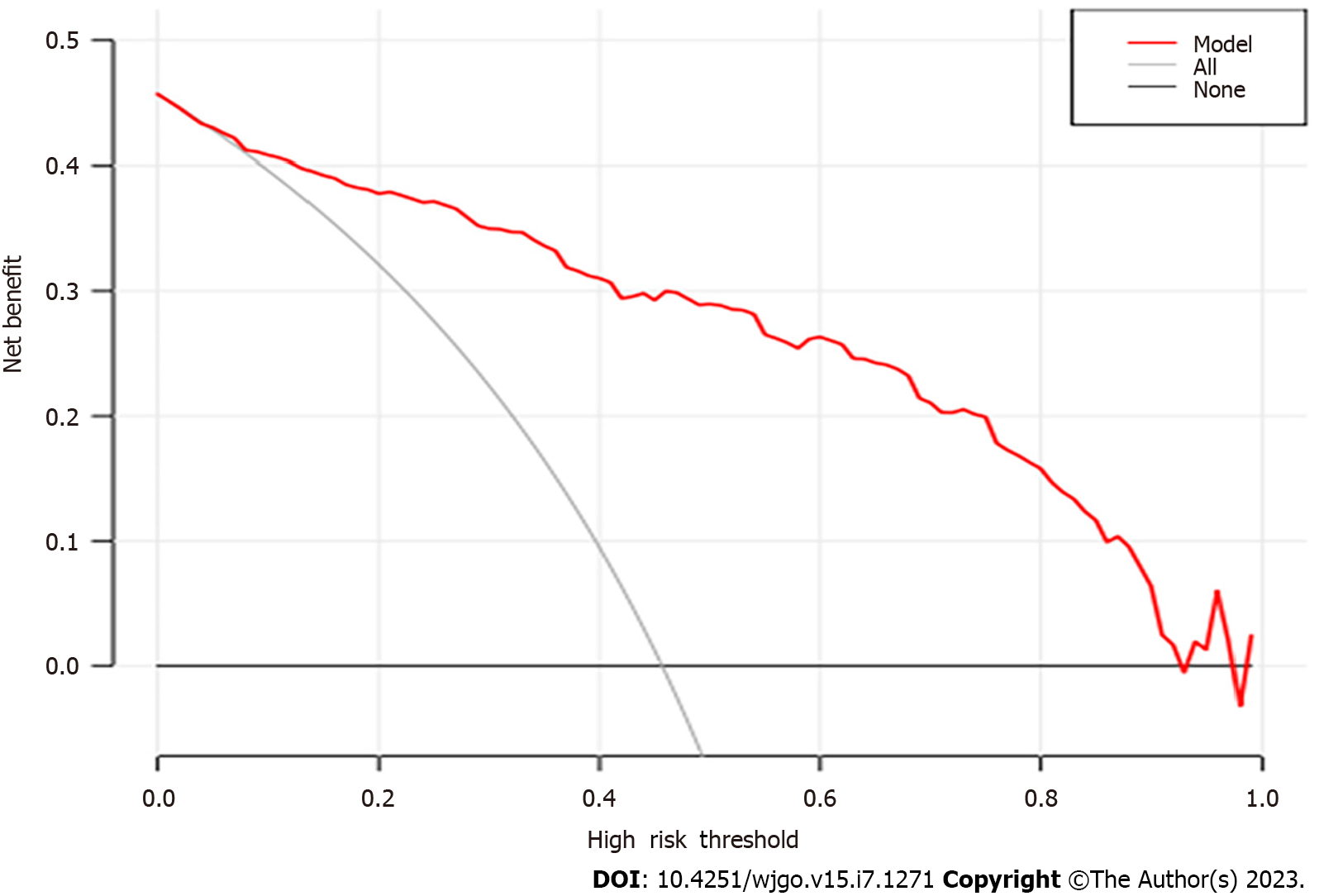
Figure 6 Decision curve analysis curve for the prediction model.
The Decision Curve Analysis curve indicated good clinical applicability of the calculator in predicting the pathological nature of colorectal tumor.
- Citation: Wang YD, Wu J, Huang BY, Guo CM, Wang CH, Su H, Liu H, Wang MM, Wang J, Li L, Ding PP, Meng MM. Development and validation of an online calculator to predict the pathological nature of colorectal tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(7): 1271-1282
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i7/1271.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1271