©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2023; 15(6): 943-958
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.943
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.943
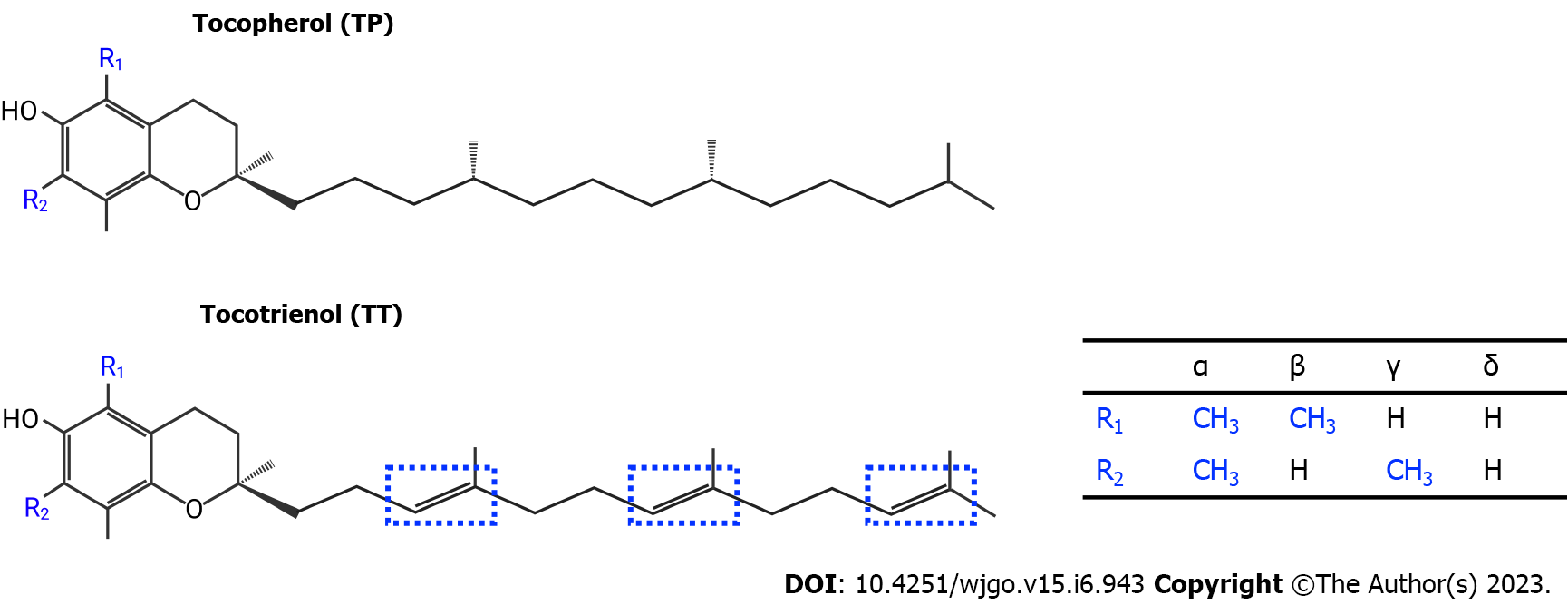
Figure 1 Chemical structure of vitamin E homologues, namely tocopherol, and tocotrienol.
TP has a saturated phytyl side chain, while tocopherol has three double bonds (indicated in blue line dotted box) on the side chain. The α-, β-, γ-, δ-isomers differ in the position of the methyl group on the chromanol ring (R1 and R2).
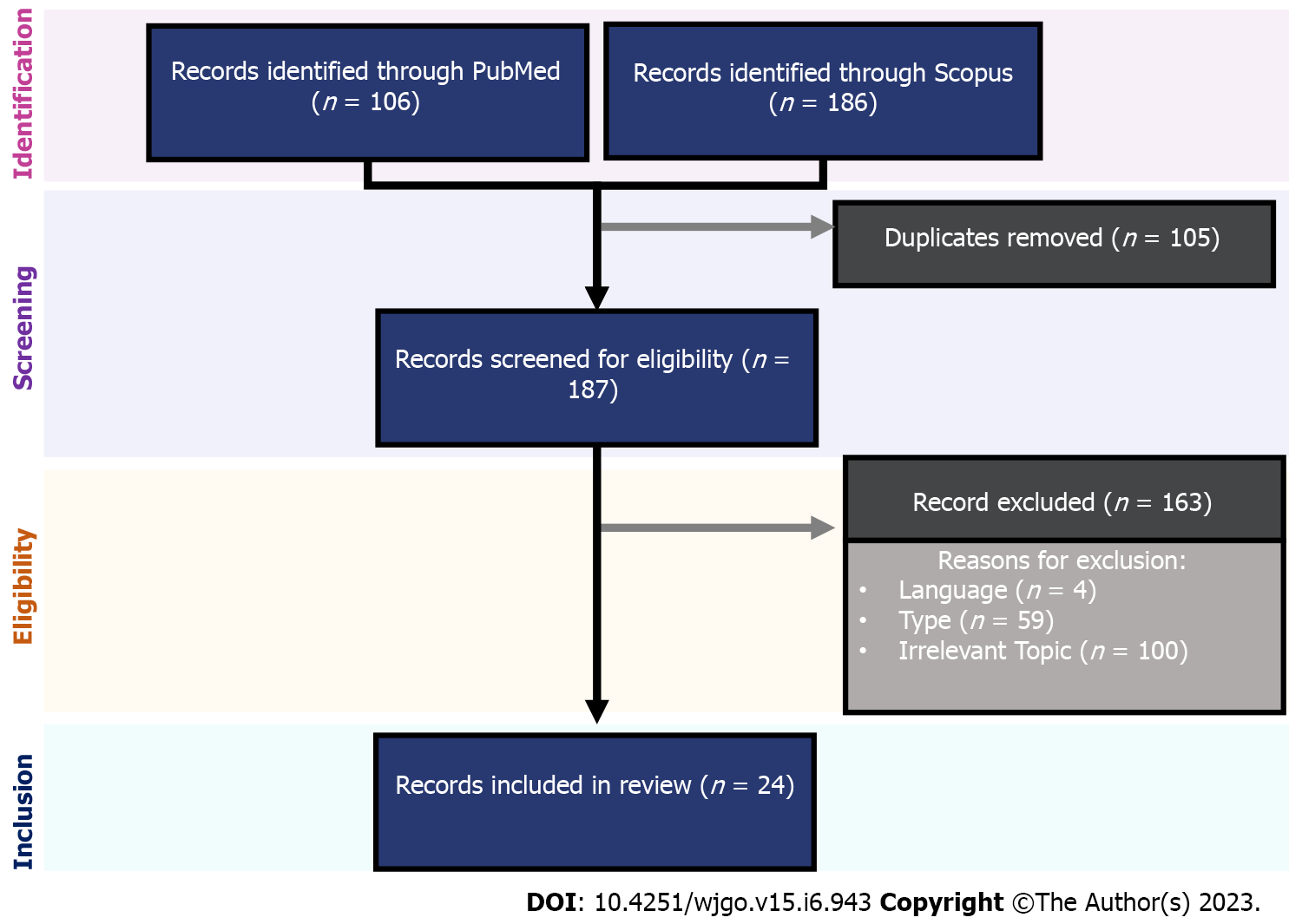
Figure 2 Process of article selection in this scoping review.
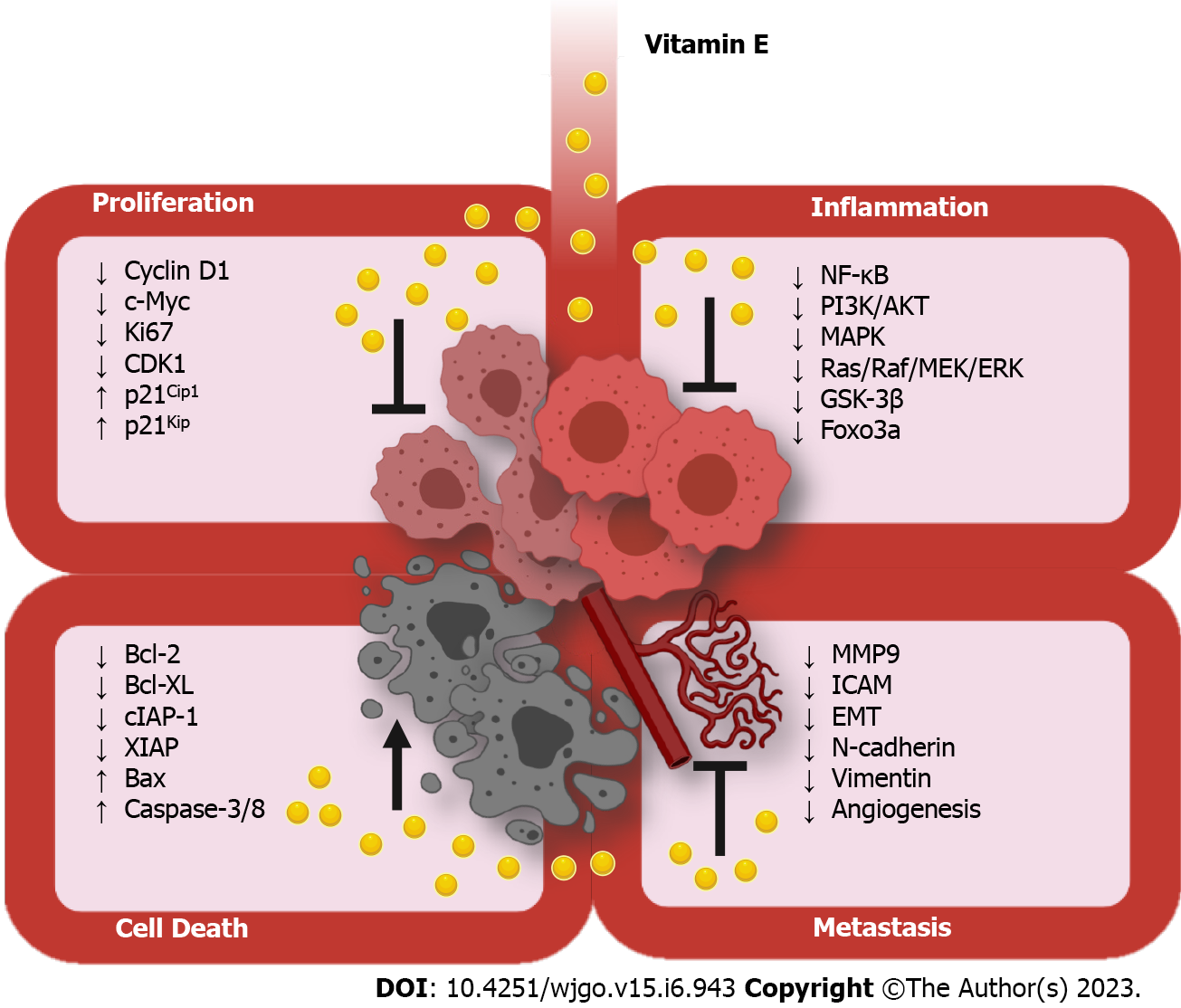
Figure 3 Role of vitamin E in modulating proliferation, cell death, inflammation and metastasis in pancreatic cancer.
c-Myc: Cellular myelocytomatosis; CDK1: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-xL: B-cell lymphoma-extra-large; cIAP-1: Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1; XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; Bax: Bcl-2 associated X protein; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, Protein kinase B; MAPKL Microtubule-associated protein kinase; Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK: Rat sarcoma virus/rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; Foxo3a: Forkhead box transcription factor-3a; MMP9: Matrix metalloproteinase 9; ICAM-1, Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; EMT: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal tumor transition. The figure is created by author and generated using Biorender.com.
- Citation: Ekeuku SO, Etim EP, Pang KL, Chin KY, Mai CW. Vitamin E in the management of pancreatic cancer: A scoping review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(6): 943-958
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i6/943.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.943