Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2019; 11(5): 404-415
Published online May 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i5.404
Published online May 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i5.404
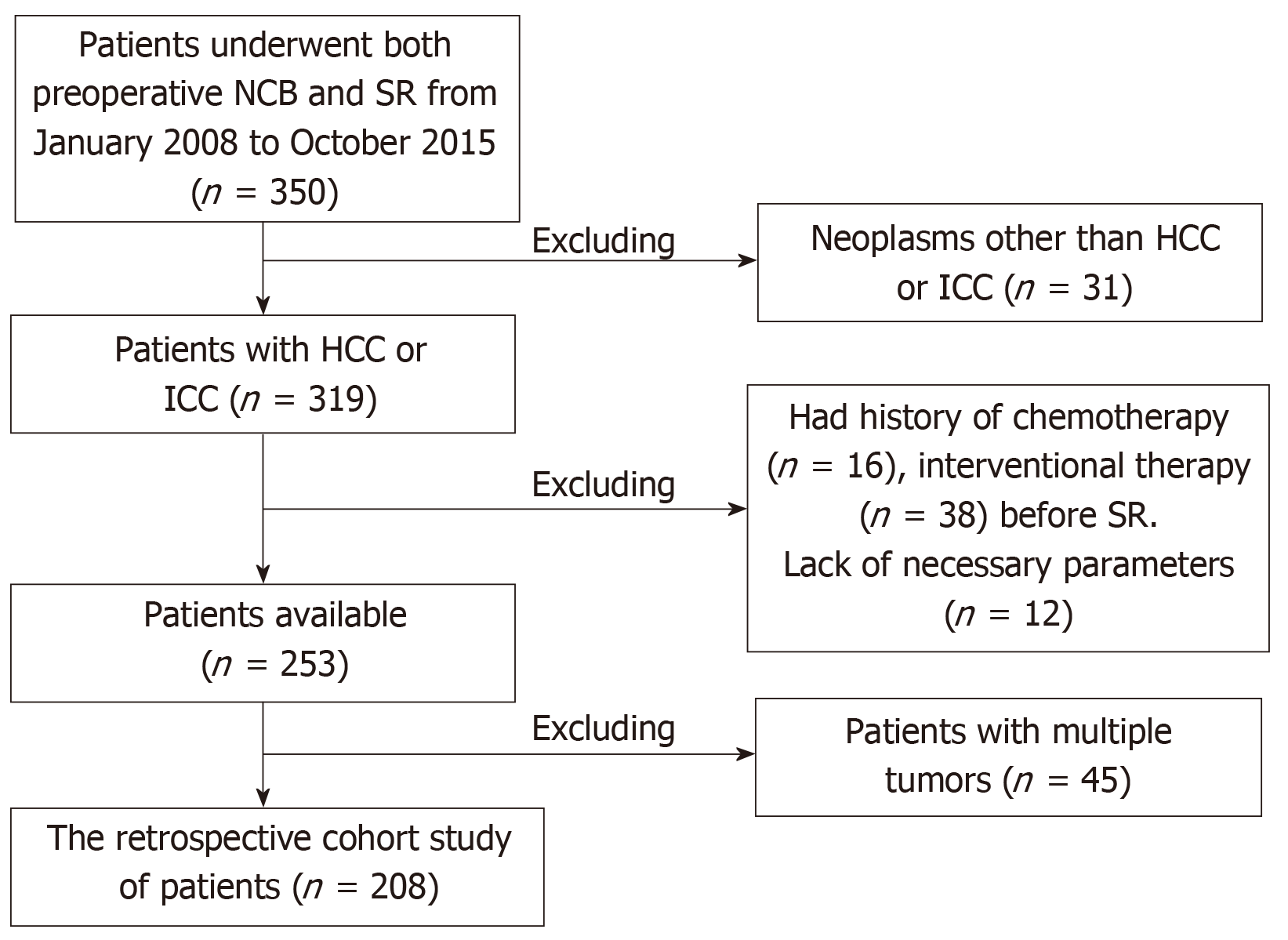
Figure 1 Schematic of the patient selection procedures.
NCB: Needle core biopsy; SR: Surgical resection; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ICC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
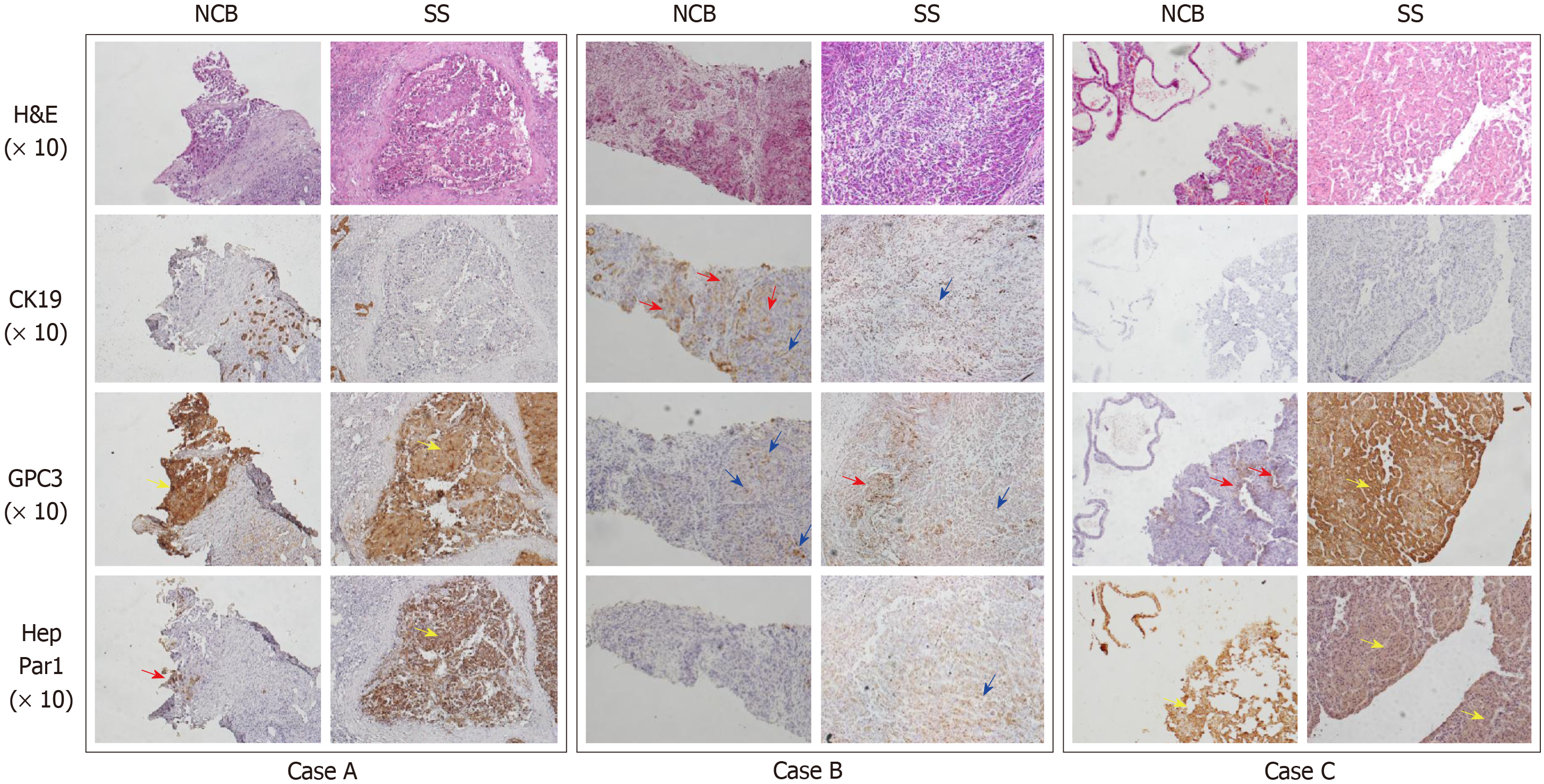
Figure 2 The four-tier score method for interpretation of the IHC staining of the three markers.
NCB: Needle core biopsy; SS: Surgical specimen; H&E: Haematoxylin and eosin; CK: Cytokeratin; GPC3: Glypican 3; HepPar1: Hepatocyte paraffin-1; Blue arrow: Scattered positive cells; Red arrow: One positive cluster; Yellow arrow: Numerous positive clusters or massive positive staining.
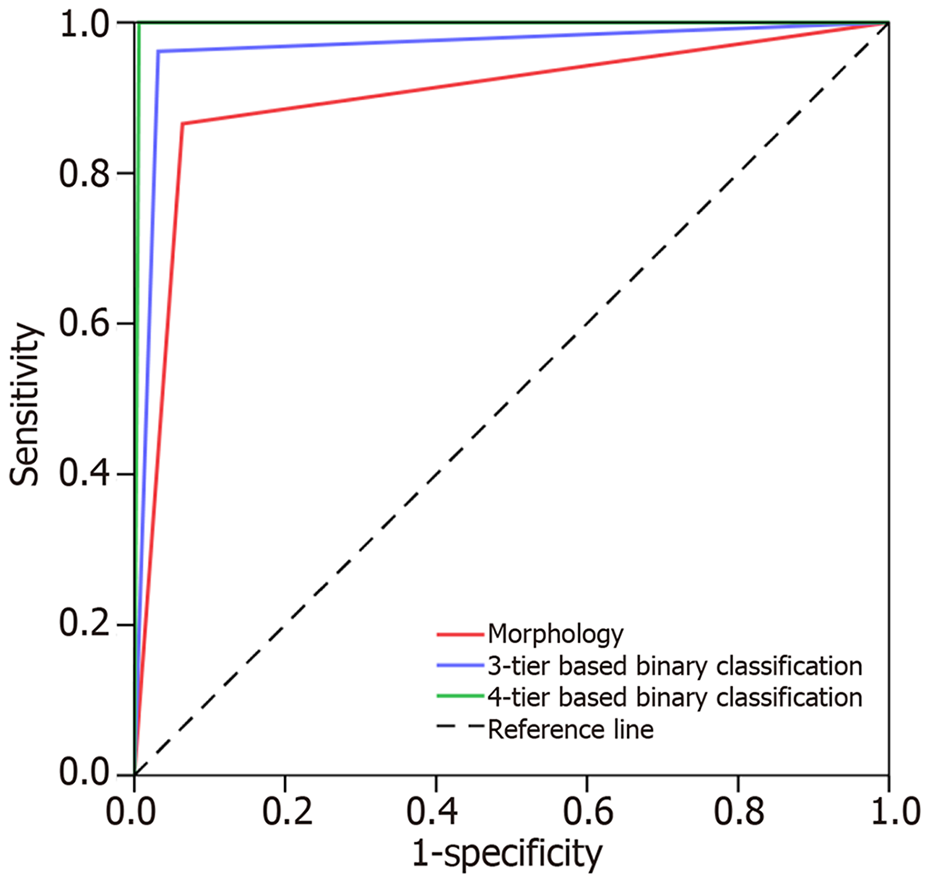
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic showing the accuracy of needle core biopsy diagnosis.
- Citation: Wu JS, Feng JL, Zhu RD, Liu SG, Zhao DW, Li N. Histopathological characteristics of needle core biopsy and surgical specimens from patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(5): 404-415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i5/404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i5.404