©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2018; 10(4): 96-102
Published online Apr 15, 2018. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i4.96
Published online Apr 15, 2018. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i4.96
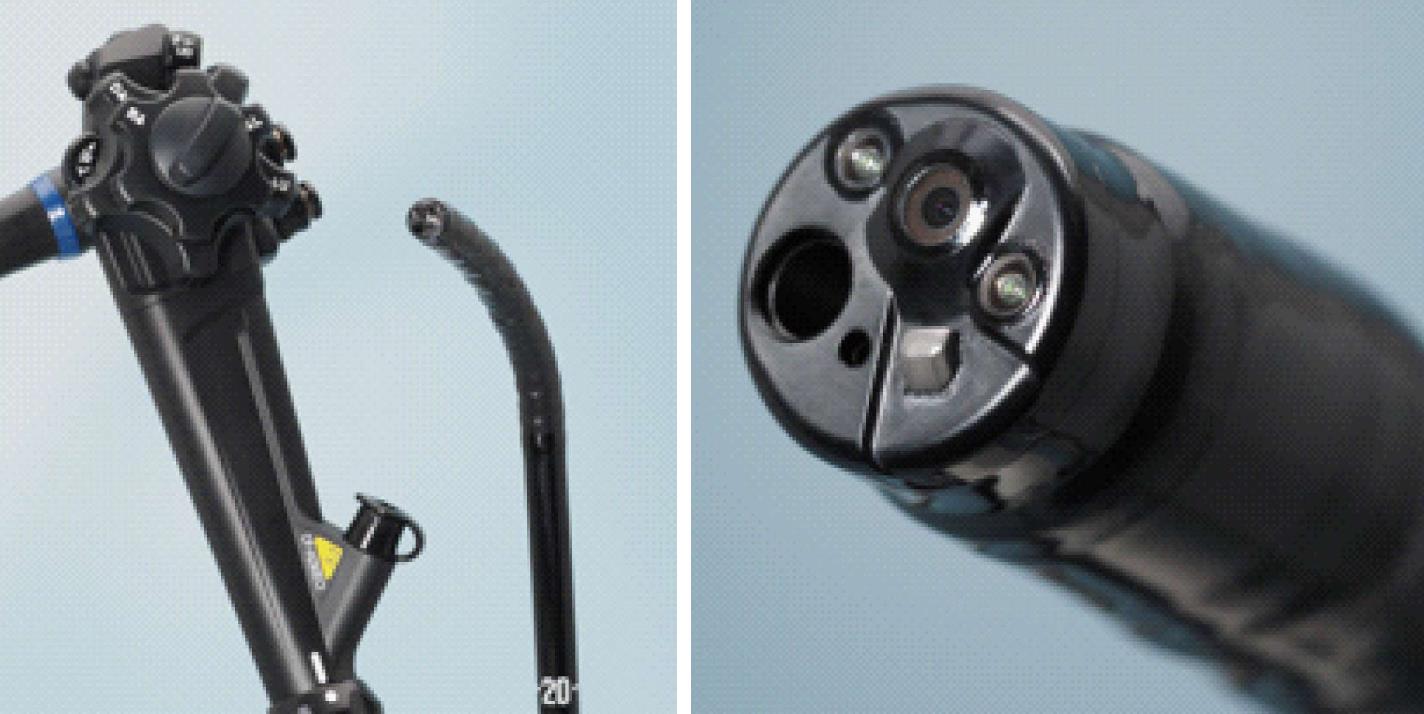
Figure 1 Technology of light contact microscopy, endocytoscope.
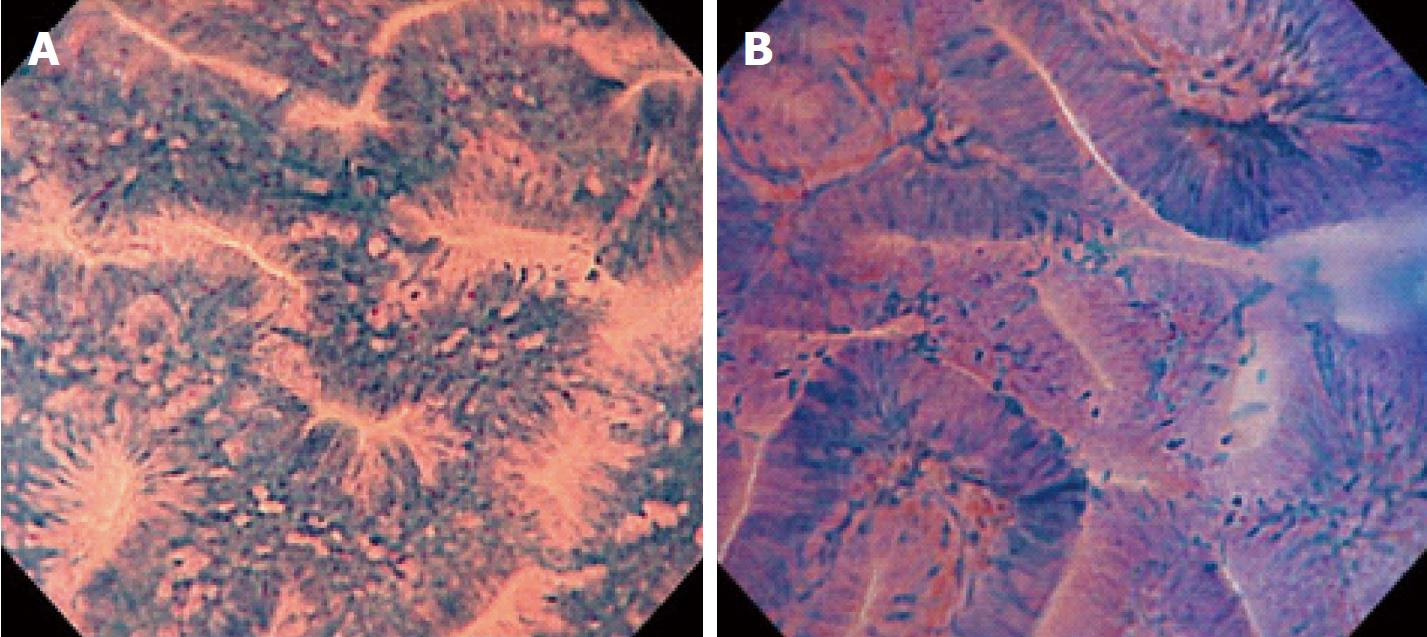
Figure 2 Typical images of endocytoscopic (EC) 1b and EC2.
A: EC1b shows narrow serrated lumina and small roundish nuclei; B: EC2 shows slit-like smooth lumina and uniform fusiform or roundish nuclei.
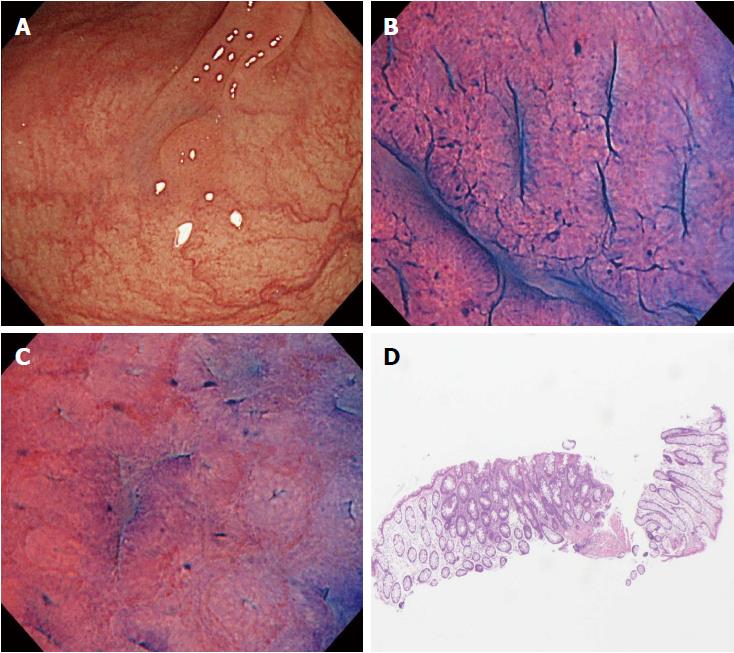
Figure 3 A case of disagreement between endocytoscopic (EC) 1b diagnosis and histopathologic diagnosis (adenoma).
A: Flat-type lesion (0-IIa) 3 mm in size; B: The polyp was located in the sigmoid colon. The EC images showed slit-like smooth lumina; C: The EC images showed roundish lumina; D: The nuclei were not clear due to inadequate staining. An endoscopist diagnosed the polyp as EC1b. Histologic examination revealed an adenomatous polyp.
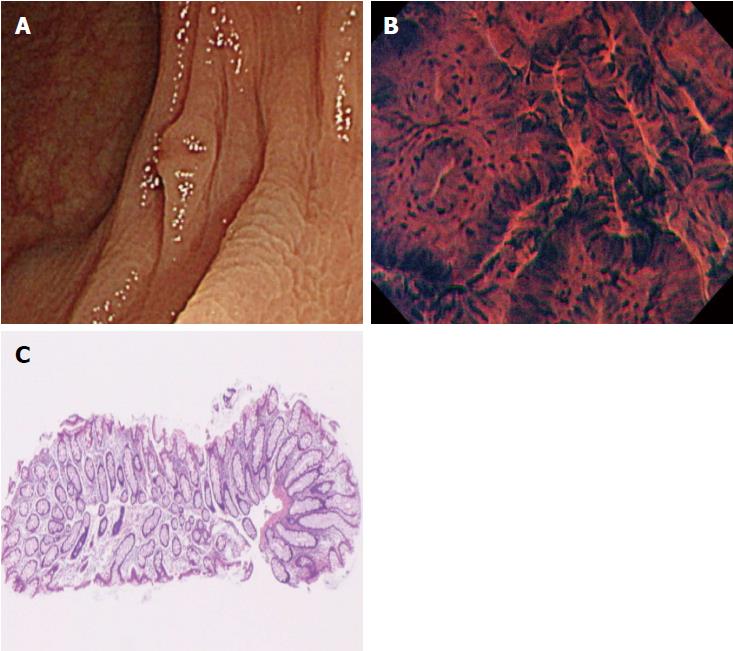
Figure 4 A case of disagreement between endocytoscopic (EC) 2 diagnosis and histopathologic diagnosis (hyperplastic polyp).
A: Flat-type lesion (0-IIa) with a shallow depressed area, 3 mm in size; B: The polyp was located in the transverse colon. Endoscopic imaging in the shallow depressed area showed typical EC2 features with slit-like smooth lumina and uniform fusiform and roundish nuclei; C: The polyp was diagnosed as EC2. Histologic examination revealed a hyperplastic polyp without a depressed area.
- Citation: Utsumi T, Sano Y, Iwatate M, Sunakawa H, Teramoto A, Hirata D, Hattori S, Sano W, Hasuike N, Ichikawa K, Fujimori T. Prospective real-time evaluation of diagnostic performance using endocytoscopy in differentiating neoplasia from non-neoplasia for colorectal diminutive polyps (≤ 5 mm). World J Gastrointest Oncol 2018; 10(4): 96-102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v10/i4/96.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v10.i4.96