©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 10, 2015; 7(6): 593-605
Published online Jun 10, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i6.593
Published online Jun 10, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i6.593
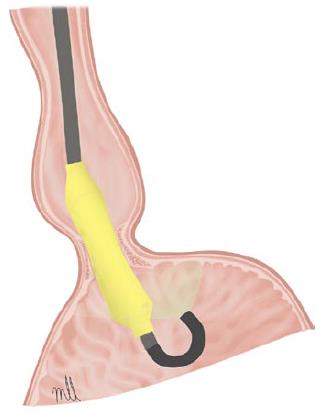
Figure 1 Witzel dilator.
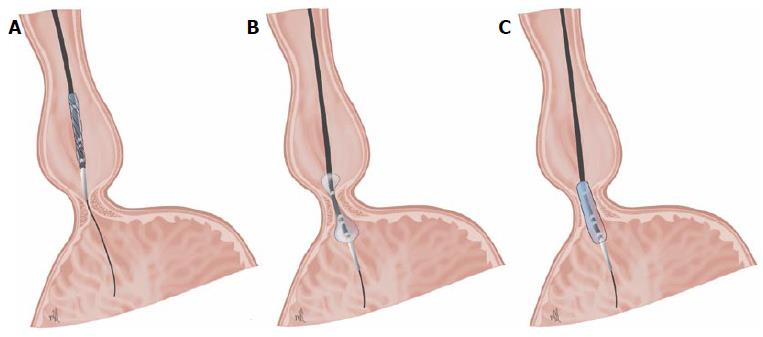
Figure 2 Dilation with Rigiflex balloon positioned at the level of the lower oesophageal sphincter.
A: Step 1: positioning the balloon in the esophagogastric junction (EGJ); B: Step 2: deflated balloon in the EGJ; C: Step 3: inflated balloon in the EGJ.
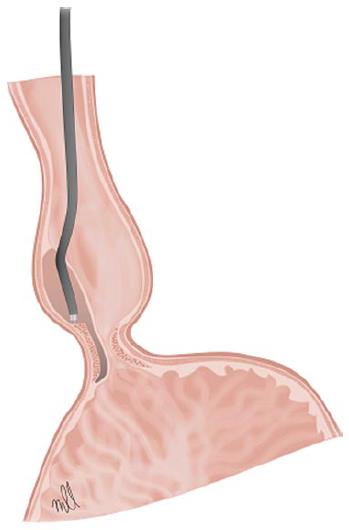
Figure 3 Peroral endoscopic myotomy.
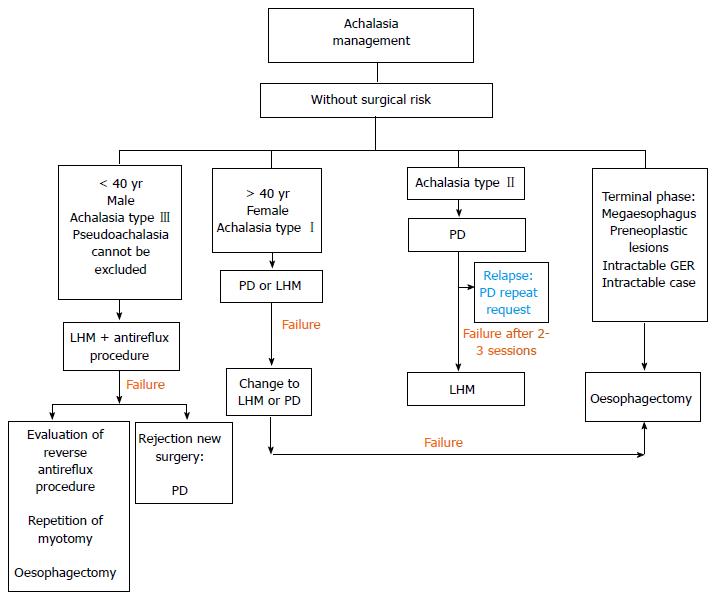
Figure 4 Management algorithm in patients without surgical risk.
PD: Pneumatic dilation; LHM: Laparoscopic Heller myotomy.
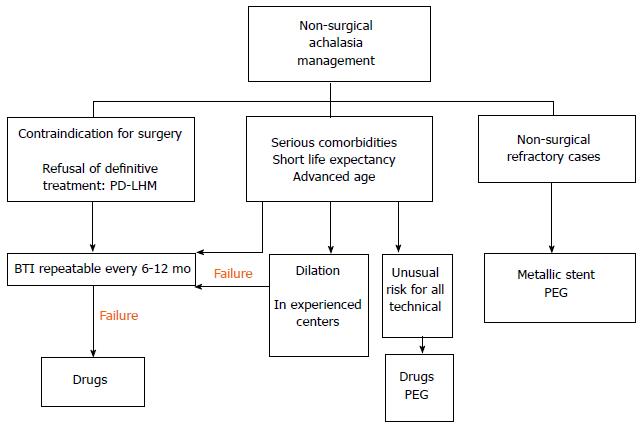
Figure 5 Non-surgical management algorithm.
PEG: Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy; BTI: Botulinum toxin injection; PD: Pneumatic dilation; LHM: Laparoscopic Heller myotomy.
- Citation: Luján-Sanchis M, Suárez-Callol P, Monzó-Gallego A, Bort-Pérez I, Plana-Campos L, Ferrer-Barceló L, Sanchis-Artero L, Llinares-Lloret M, Tuset-Ruiz JA, Sempere-Garcia-Argüelles J, Canelles-Gamir P, Medina-Chuliá E. Management of primary achalasia: The role of endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(6): 593-605
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i6/593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i6.593