Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Aug 16, 2012; 4(8): 339-346
Published online Aug 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i8.339
Published online Aug 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i8.339
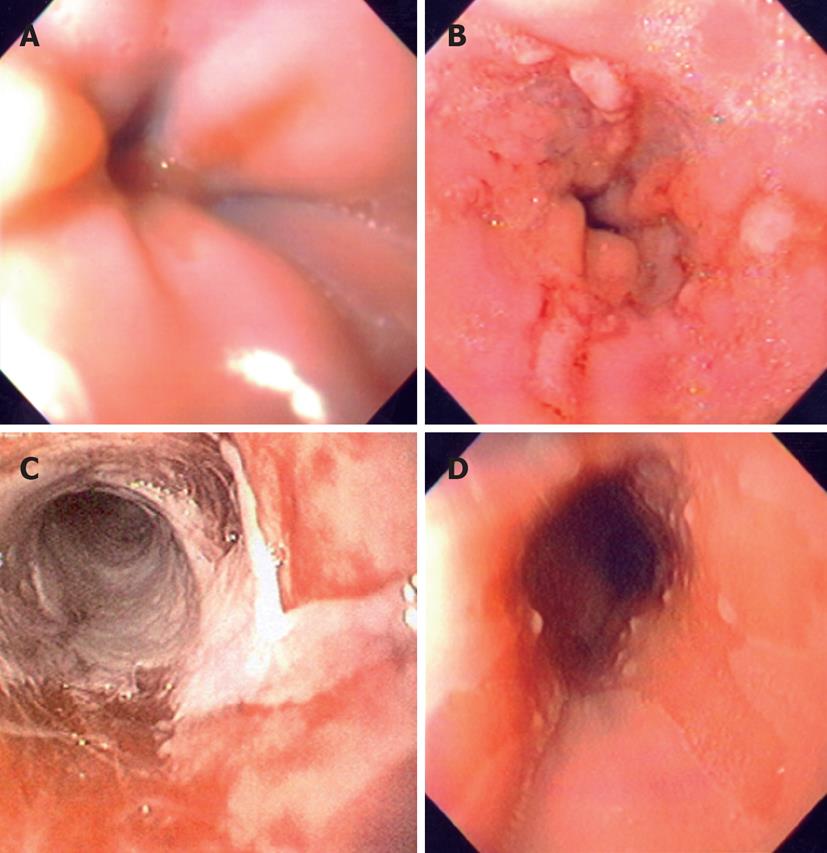
Figure 1 Endoscopy findings.
A: Endoscopy of a child with esophagitis Los Angeles grade A showing one mucosal break < 5 mm in length; B: Another child with Los Angeles grade B showing 3 mucosal breaks > 5 mm long not continuous between the tops of adjacent mucosal folds; C: Endoscopy of a child with esophagitis Los Angeles grade D with mucosal break that involves at least 75% of the luminal circumference; D: Another 14-year-old patient with Barrett esophagus showing an area of endoscopically suspected esophageal metaplasia.
- Citation: Goldani HA, Nunes DL, Ferreira CT. Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease in children: The role of endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2012; 4(8): 339-346
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v4/i8/339.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v4.i8.339