©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Aug 16, 2025; 17(8): 104238
Published online Aug 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i8.104238
Published online Aug 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i8.104238
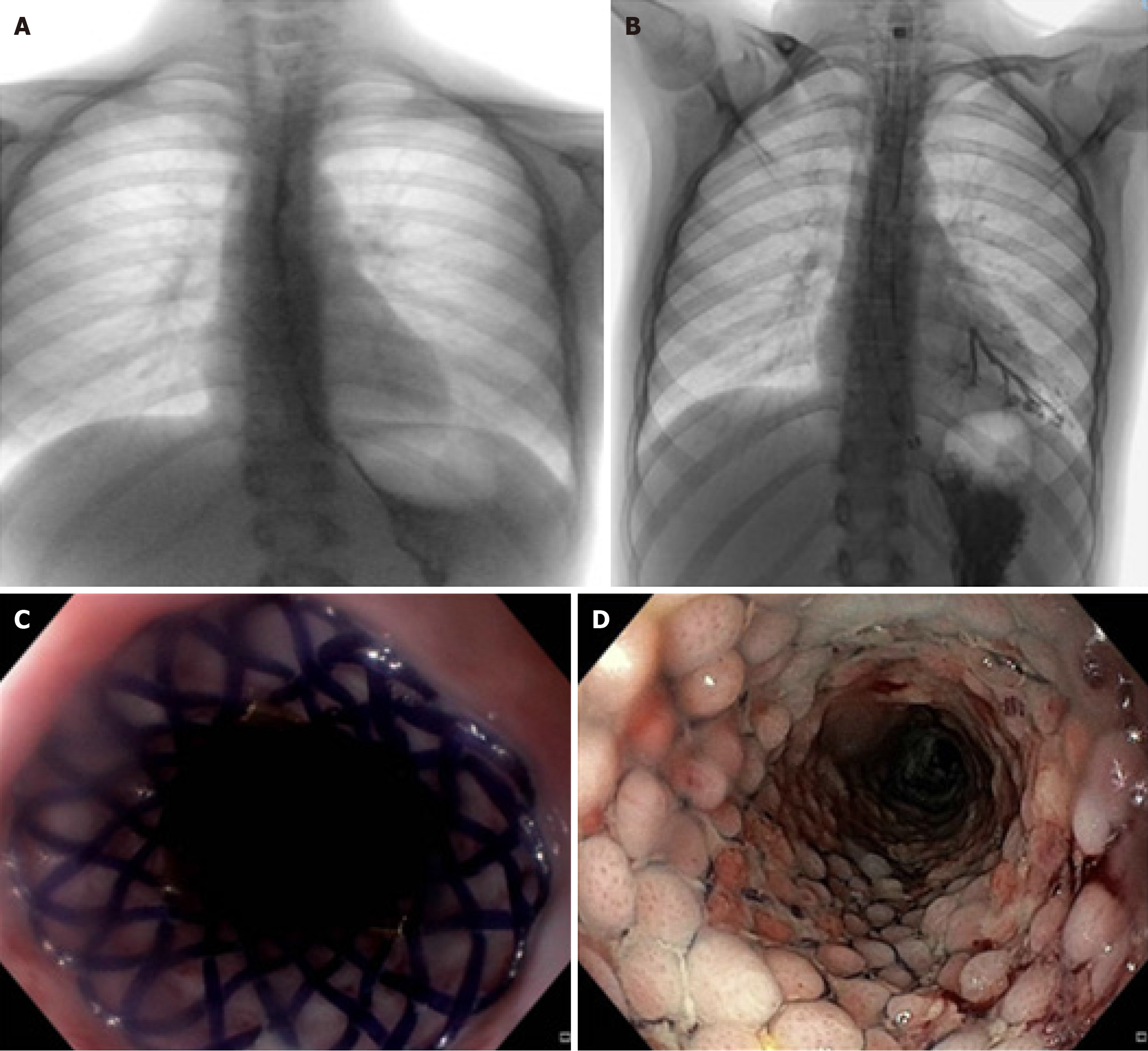
Figure 1 Reabsorbable stent after a complicated non-operative management for refractory esophageal strictures after corrosive ingestion.
A: Initial presentation of recurrent esophageal strictures; B: Tracheobronchial fistula after dilatations and dynamic stent placement; C: Absorbable stent placement; D: Esophageal restoration during stent re-absorption.
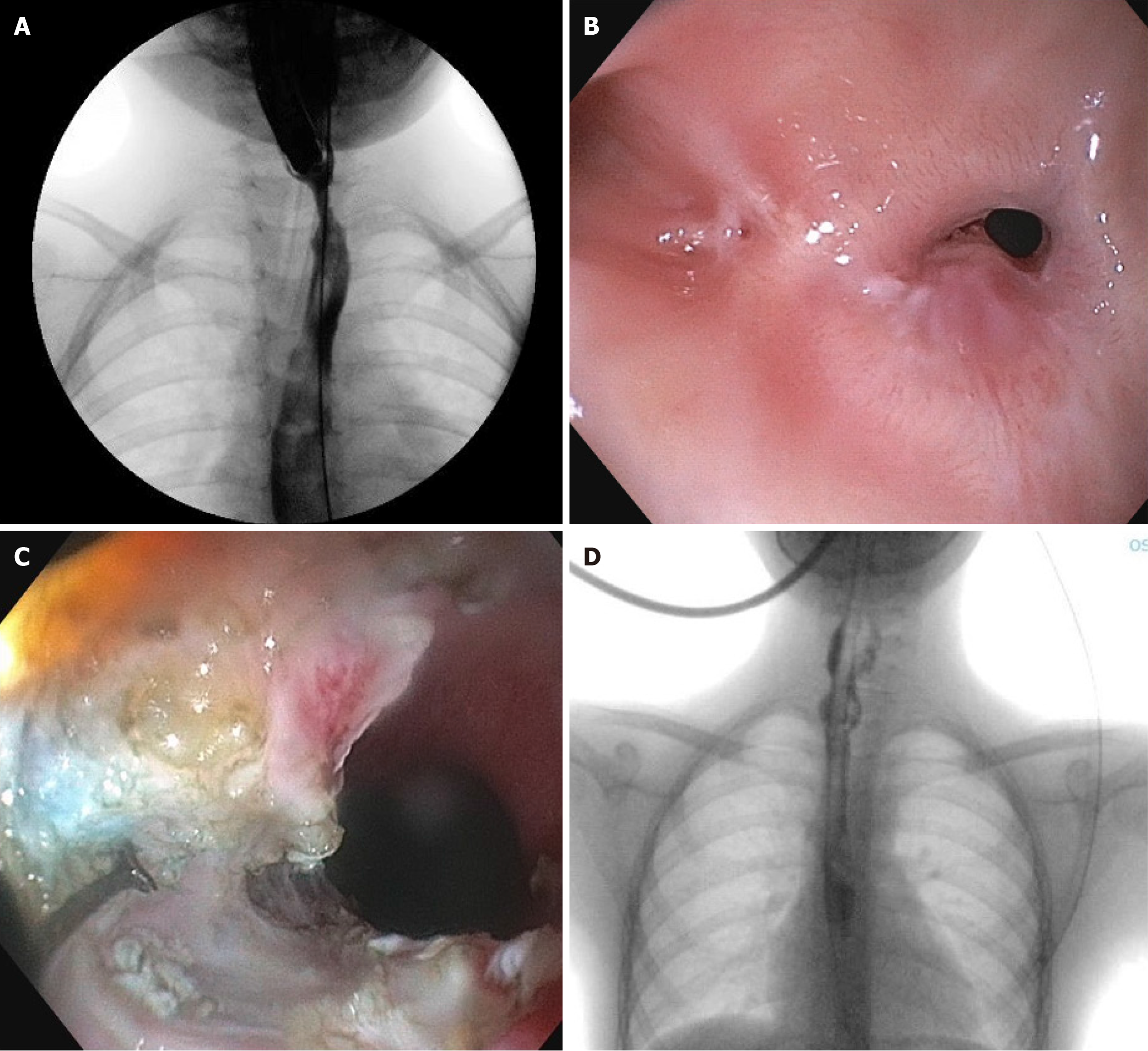
Figure 2 Peroral endoscopic tunneling for restoration of the esophagus for recurrent esophageal strictures after surgical resection for disk-bactery impaction.
A: Esophagram before treatment; B: Endoscopy before treatment showing the septum of the pseudodiverticulum; C: Esophageal lumen after recanalization with incisional therapy; D: Esophagram before refeeding.
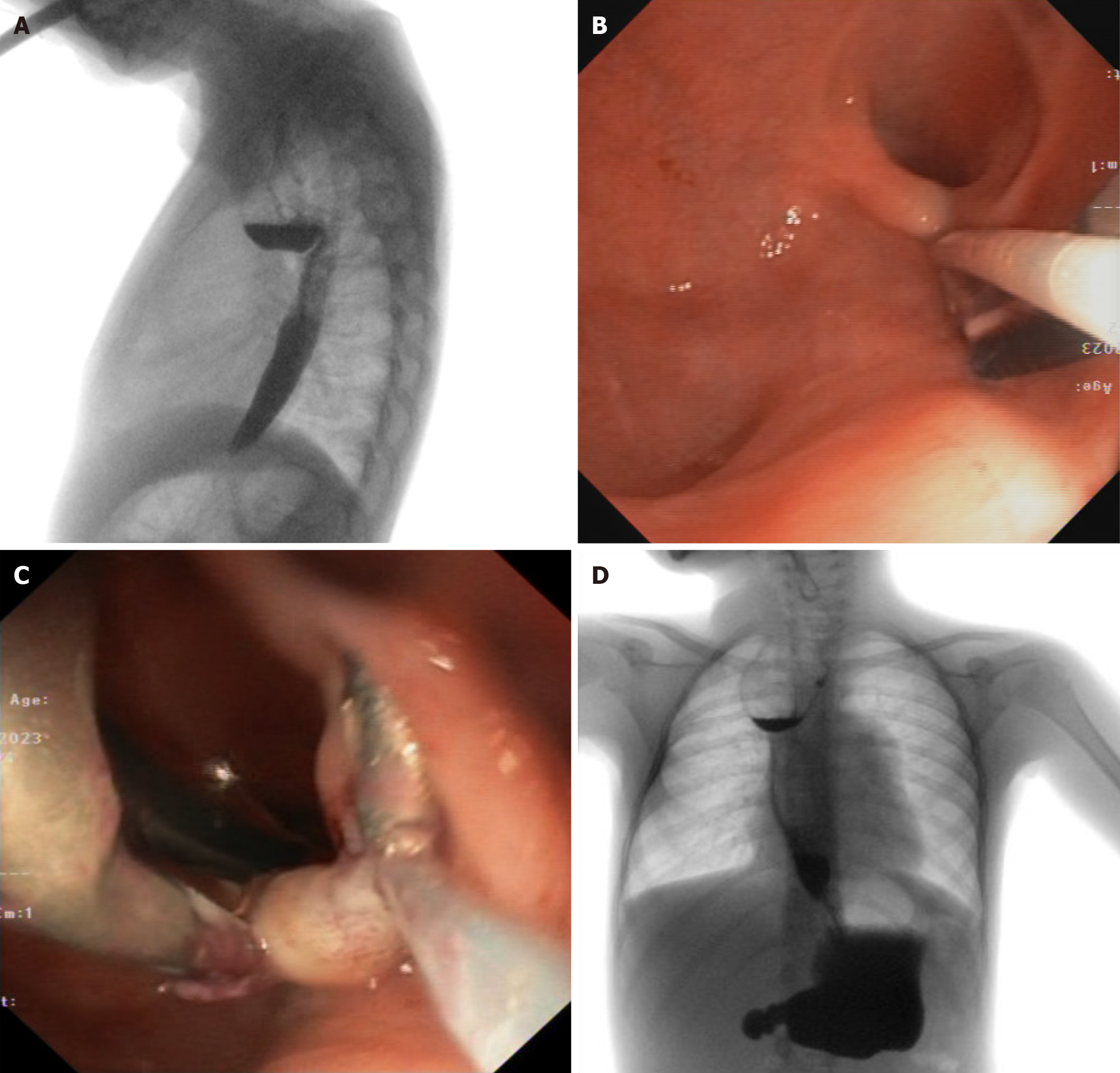
Figure 3 Transoral harmonic-scalpel assisted diverticulotomy for recurrent esophageal strictures after atresia repair.
A: Esophagram before treatment; B: Endoscopy and counter-traction placement with clip + snare technique; C: Harmonic scalpel application on the septum; D: Esophagram 1 year after treatment.
- Citation: Imondi C, Bartoli ME, Torroni F, Faraci S, Caldaro T, De Angelis P, Balassone V. Innovative endoscopic alternatives for the conservative management of recurrent/refractory esophageal strictures in children: A case series. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(8): 104238
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i8/104238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i8.104238