©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2025; 17(6): 106412
Published online Jun 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i6.106412
Published online Jun 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i6.106412
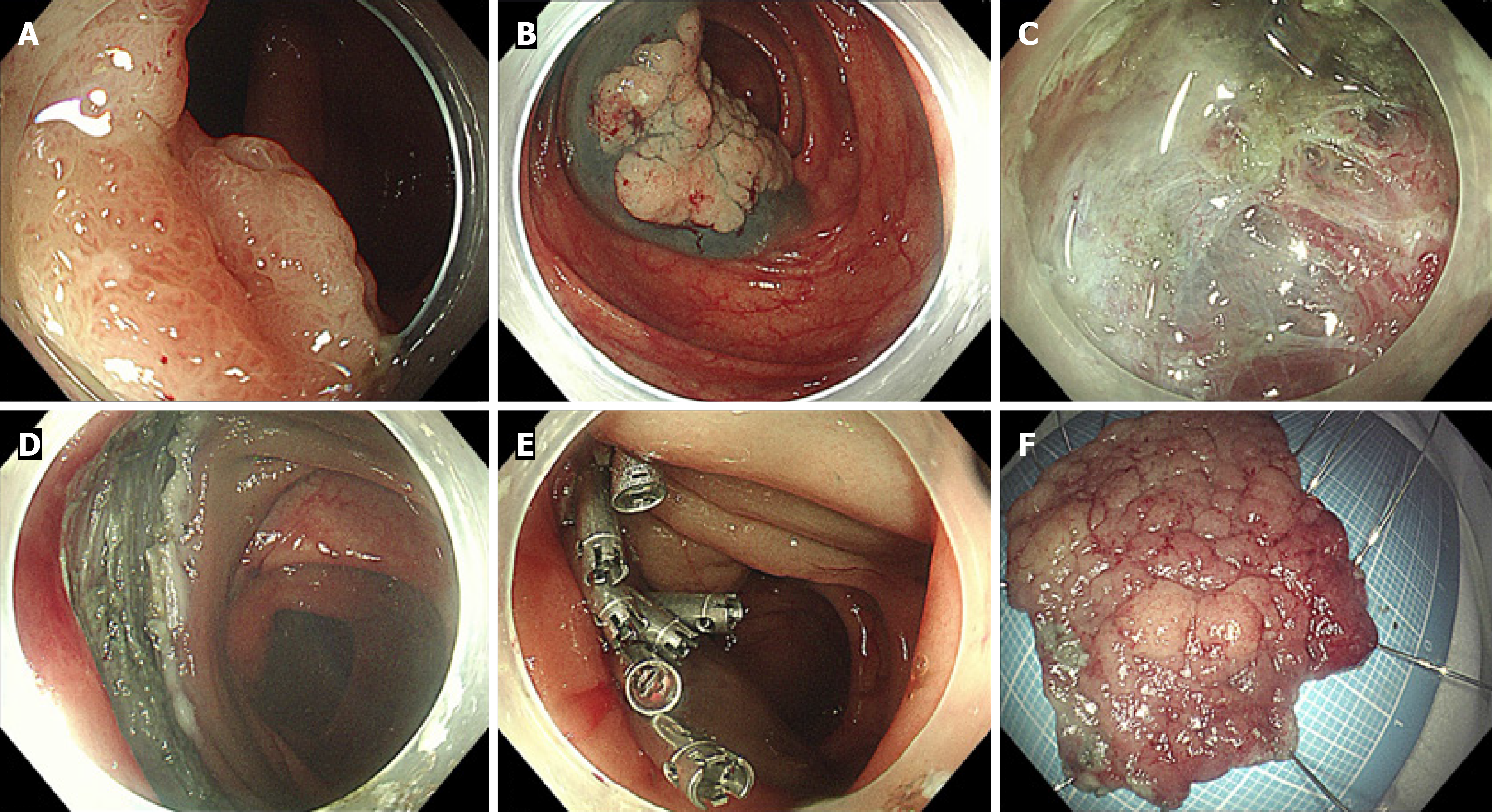
Figure 1 Laterally spreading tumors treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: 4.5 cm laterally spreading tumors in the ascending colon; B: Following injection of the lesion; C: Full circumstantial mucosal resection was performed; D: The mucosal wound after removal of the lesion; E: The wound was closed with titanium clips; F: The resected specimen.
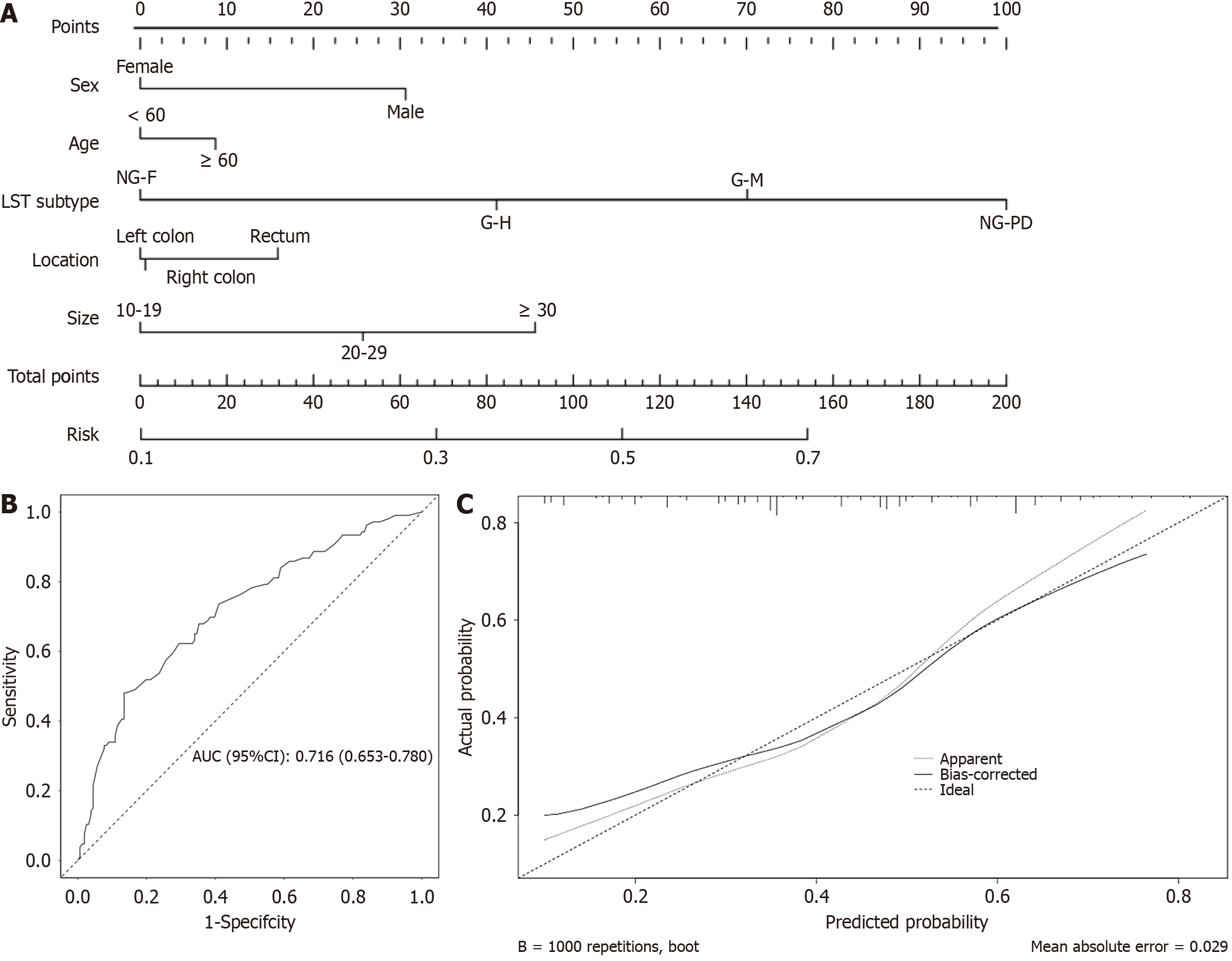
Figure 2 Nomogram model for the prediction of high-grade dysplasia/carcinoma.
A: Nomogram model predicting high-grade dysplasia/carcinoma in laterally spreading tumors; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve of the nomogram model predicting high-grade dysplasia/carcinoma in laterally spreading tumors; C: Calibration curve of the nomogram model; LST: Laterally spreading tumor; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Guo LH, Hu KF, Miao M, Ding Y, Zhang XJ, Ye GL. Endoscopic resection of colorectal laterally spreading tumors: Clinicopathologic characteristics and risk factors for treatment outcomes. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(6): 106412
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i6/106412.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i6.106412