©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2025; 17(10): 112380
Published online Oct 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i10.112380
Published online Oct 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i10.112380
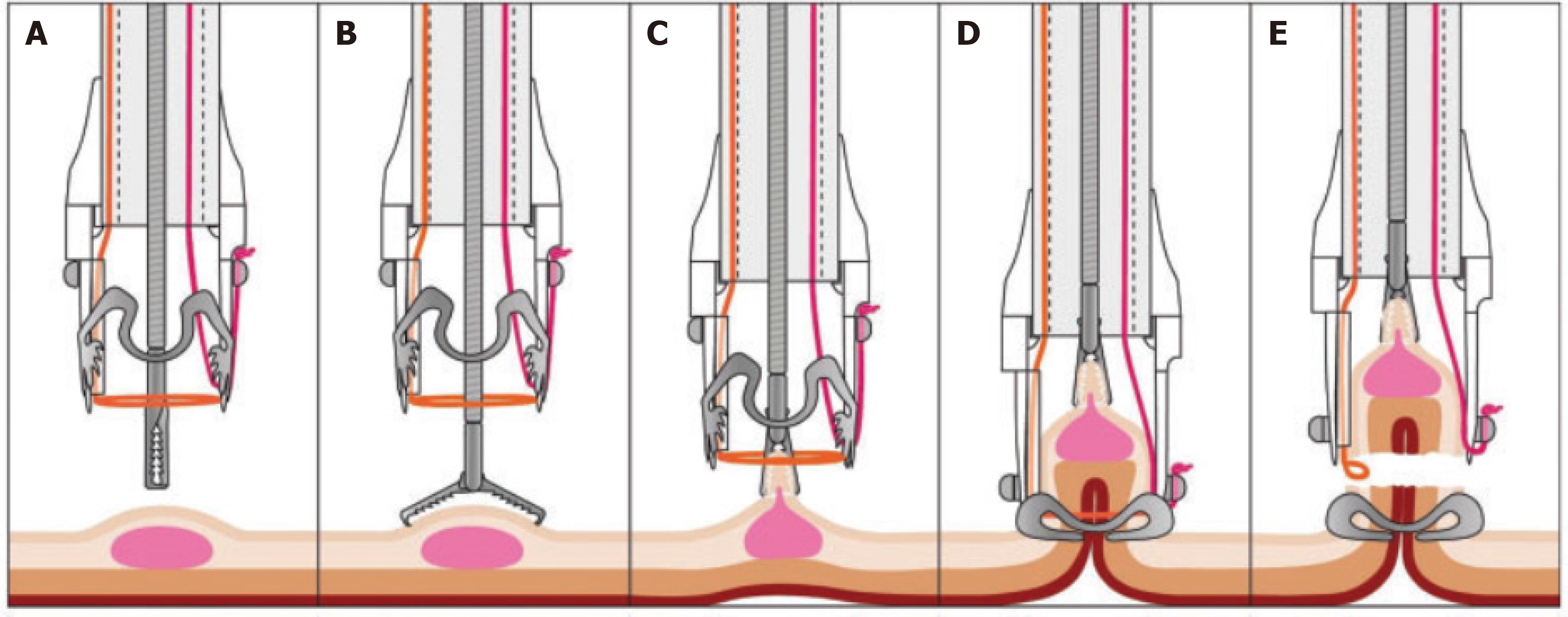
Figure 1 Description of the full-thickness resection device and its application[10].
Schematic description of the full-thickness resection device (FTRD) technique (https://ovesco.com/ftrd-system/). A: Components of the FTRD: The clip is mounted on the tip of the endoscope. The snare is integrated in the tip of the cap. A grasping forceps is advanced through the working channel of the endoscope; B: The target lesion is grasped with the forceps; C: The target lesion is pulled into the cap; D: The over-the-scope-clip is deployed and creates a full-thickness duplication of the colonic wall; E: The pseudopolyp above the clip is resected using the preloaded snare. Citation: Albrecht H, Raithel M, Braun A, Nagel A, Stegmaier A, Utpatel K, Schäfer C. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Tech Coloproctol 2019; 23: 957-963. Copyright© Ovesco Endoscopy AG 2019. Published by Ovesco (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Albrecht H, Schaefer C, Stegmaier A, Gschossmann J, Hagel A, Raithel M. Real-world topographical efficacy, procedural outcome and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection in colon segments. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(10): 112380
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i10/112380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i10.112380