Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i27.2757
Peer-review started: June 1, 2015
First decision: July 6, 2015
Revised: August 27, 2015
Accepted: November 13, 2015
Article in press: November 17, 2015
Published online: November 28, 2015
Processing time: 181 Days and 1.6 Hours
AIM: To investigate risk factors for development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with hepatitis C virus-related liver cirrhosis (LC-C).
METHODS: To evaluate the relationship between clinical factors including virological response and the development of HCC in patients with LC-C treated with interferon (IFN) and ribavirin, we conducted a multicenter, retrospective study in 14 hospitals in Japan. All patients had compensated LC-C with clinical or histological data available. HCC was diagnosed by the presence of typical hypervascular characteristics on computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging.
RESULTS: HCC was diagnosis in 50 (21.6%) of 231 LC-C patients during a median observation period of 3.8 years after IFN and ribavirin therapy. Patients who developed HCC were older (P = 0.018) and had higher serum levels of pretreatment alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) (P = 0.038). Multivariate analysis revealed the following independent risk factors for HCC development: history of treatment for HCC [P < 0.001, odds ratio (OR) = 15.27, 95%CI: 4.98-59.51], AFP levels of ≥ 10 ng/mL (P = 0.009, OR = 3.89, 95%CI: 1.38-11.94), and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) levels of ≥ 40 mAU/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy (P < 0.001, OR = 24.43, 95%CI: 4.11-238.67).
CONCLUSION: We suggested that the elevation of AFP and DCP levels at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy were strongly associated with the incidence of HCC irrespective of virological response among Japanese LC-C patients.
Core tip: Interferon (IFN)-based therapy reduces the rate of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. However, HCC development has frequently been reported in HCV-related liver cirrhosis (LC-C) patients who achieved sustained virological response. We conducted a multicenter, retrospective study to evaluate the relationship between clinical factors and HCC development in Japanese LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin therapy. We suggested that the elevation of Alpha-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin levels at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy were strongly associated with the incidence of HCC irrespective of virological response among Japanese LC-C patients.
- Citation: Shakado S, Sakisaka S, Chayama K, Okanoue T, Toyoda J, Izumi N, Matsumoto A, Takehara T, Ido A, Hiasa Y, Yoshioka K, Nomura H, Ueno Y, Seike M, Kumada H. Alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy-prothrombin at twenty-four weeks after interferon-based therapy predict hepatocellular carcinoma development. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(27): 2757-2764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i27/2757.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i27.2757
Chronically hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the commonest cause of liver cirrhosis in the world[1]. HCV-related liver cirrhosis (LC-C) patients are the high risk to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[2,3]. Many previous studies suggested that interferon (IFN)-based therapy reduces the rate of HCC development in patients with chronically HCV infection, especially those with sustained virological response (SVR)[4-8]. Non-SVR, male sex, older age, and advanced liver fibrosis have been shown to be risk factors for HCC development in patients treated with IFN[9-13]. Therapy with IFN and ribavirin has been used for LC-C patients, leading to significant effects including SVR. However, the development of HCC has frequently been reported in LC-C patients who achieved SVR[14,15]. The aim of this retrospective, multicenter study was to evaluate the relationship among pre- and post-treatment clinical factors, virological response, and HCC development in Japanese LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin to elucidate the predictive markers for HCC development.
We conducted a retrospective, multicenter study in 14 hospitals in Japan. All 290 patients with LC-C were treated with IFN plus ribavirin. A diagnosis of compensated LC-C was defined with the clinical or histological finding. We decided the presence of at least one of the following criteria: Liver biopsy demonstrating cirrhosis, multiple nodular appearance of liver surface on peritoneoscopy, liver stiffness greater than 12.5 kPa on transient elastography, presence of esophageal varices, or positive values of cirrhosis criteria[16-18].
Of the 290 patients, 59 developed HCC within 6 mo of completing IFN and ribavirin therapy and were excluded from the study. All analyses used data from the remaining 231 cases. Table 1 shows pretreatment clinical characteristics. Of 231 patients, 189 patients were infected with HCV genotype 1 and 80 patients (34.6%) had received treatment for HCC previously. Eighty patients were treated for HCC with hepatectomy, transcatheter chemoembolization, or radio frequency ablation therapy in each hospital. More detail of treatment history was not investigated in this study. The average follow-up period was 3.8 ± 2.2 years.
| All patients (n = 231) | Non HCC (n = 181) | HCC (n = 50) | P-value1 | |
| Sex (M:F) | 111:120 | 82:99 | 29:21 | NS |
| Age (yr) | 60.4 ± 9.2 | 59.6 ± 9.2 | 63.1 ± 9.1 | 0.018 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 3.4 | 23.7 ± 3.5 | 23.9 ± 2.9 | NS |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 1.4 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | NS |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | NS |
| Prothrombin (%) | 86.1 ± 15.2 | 86.1 ± 15.8 | 86.1 ± 13.2 | NS |
| ALT (IU/L) | 84.6 ± 64.4 | 86.6 ± 65.8 | 77.1 ± 59.6 | NS |
| GGT (IU/L) | 89.0 ± 124.0 | 89.0 ± 125.2 | 89.3 ± 122.1 | NS |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.2 ± 1.8 | 13.1 ± 1.9 | 13.5 ± 1.7 | NS |
| Platelets (104/mm3) | 12.1 ± 6.8 | 12.2 ± 7.2 | 11.7 ± 5.1 | NS |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 94.1 ± 916.1 | 24.2 ± 38.0 | 355.1 ± 1994.9 | 0.038 |
| DCP (mAU/mL) | 261.5 ± 2687.8 | 328.6 ± 3057.3 | 26.5 ± 18.1 | NS |
| IL28B (TT:non TT) | 161:70 | 130:51 | 31:19 | NS |
| Presence of EV | 74/191 (38.7%) | 60/146 (41.1%) | 14/45 (31.1%) | NS |
| HCC treatment history | 80 (34.6%) | 44 (24.3%) | 36 (72.0%) | NS |
| HCV genotype (1/2) | 189:42 | 147:34 | 42:8 | NS |
| IFN treatment (naive) | 208 (90.0%) | 162 (89.5%) | 46 (92%) | NS |
All 231 patients were treated with INF and ribavirin. Pegylated-IFN alpha-2b, pegylated-IFN alpha-2a or IFN alpha-2b were administered to 297 (85.3%), 19 (8.2%), 15 (6.5%), respectively.
Hepatic ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were performed every 3 to 6 mo during follow-up period for HCC surveillance. HCC was diagnosed on the basis of the presence of typical hypervascular characteristics of CT and/or MRI findings.
We conducted statistical analyze with Fisher’s exact test or Student’s t-test. Univariate and multivariate analysis were used with JMP version 9.0 for Macintosh (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). The odds ratio and 95%CI were also calculated.
HCC was diagnosed in 50 (21.6%) of 231 LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin during a median follow-up period of 3.8 years (0.6-11.9 years). Patients who developed HCC were older (P = 0.018) and had higher serum levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) (P = 0.038) than the non-HCC group (Table 1). In our study, no significant difference in HCC development was observed for male sex, platelet count, interleukin 28B genotype, presence of esophageal varices, HCV genotype, type of IFN or IFN treatment history (naive or non-naive).
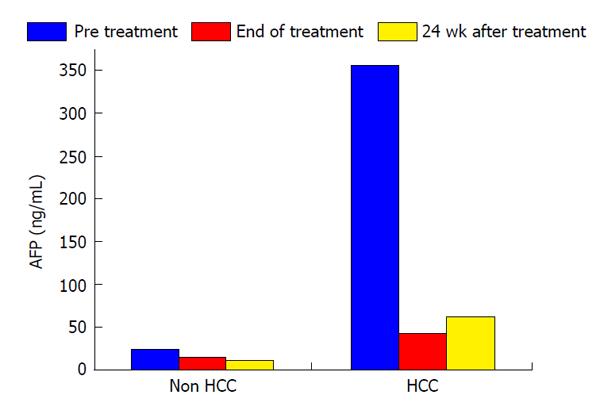
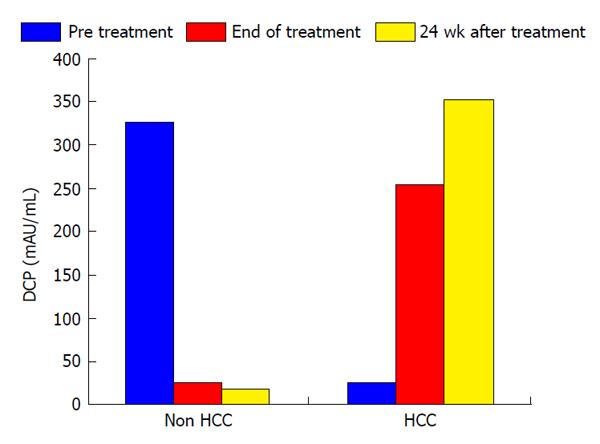
In this study, the duration of treatment with IFN and SVR were not associated with HCC development (Table 2). Serum levels of AFP and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) were focus to be risk factors for HCC development. Normal range of AFP and DCP were under 10 ng/mL and under 40 mAU/mL, respectively. In patients who developed HCC, serum levels of AFP decreased from 355.1 ng/mL to 42.8 ng/mL during the course of IFN therapy and then increased from 42.8 ng/mL to 63.2 ng/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy. In patients who did not develop HCC, serum AFP levels at the beginning, completion, and 24 wk after IFN and ribavirin therapy were 94.1, 15.5 and 11.5 ng/mL, respectively. In patients who did not develop HCC, serum DCP levels at the beginning, completion, and 24 wk after IFN and ribavirin therapy were 328.6, 25.6 and 18.4 mAU/mL, respectively. As with AFP, serum DCP levels were increased in patients who developed HCC. Serum levels of AFP and DCP were the greatest risk factors for HCC development at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy. In patients who did not develop HCC, albumin levels increased from 3.7 g/dL at the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy to 4.0 g/dL at 24 wk after the completion of treatment. A change of those tumor markers after IFN and ribavirin therapy was shown in Figures 1 and 2.
| Non HCC (n = 181) | HCC (n = 50) | P-value | |
| IFN treatment duration (wk) | 43.1 ± 21.5 | 44.1 ± 22.5 | NS |
| Sustained virological response | 63 (34.8%) | 12 (24%) | NS |
| Albumin levels at the end of IFN treatment (g/dL) | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | NS |
| Prothrombin levels at the end of IFN treatment (%) | 86.0 ± 21.5 | 83.5 ± 11.1 | NS |
| AFP levels at the end of IFN treatment (ng/mL) | 15.5 ± 34.9 | 42.8 ± 96.0 | 0.009 |
| DCP levels at the end of IFN treatment (mAU/mL) | 25.6 ± 47.2 | 255.6 ± 863.2 | 0.017 |
| Albumin levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (g/dL) | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 0.004 |
| Prothrombin levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (%) | 87.8 ± 17.9 | 86.6 ± 14.2 | NS |
| AFP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (ng/mL) | 11.5 ± 15.8 | 63.2 ± 193.2 | 0.002 |
| DCP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (mAU/mL) | 18.4 ± 12.7 | 354.0 ± 1887.5 | NS |
In our study, SVR was not associated to HCC development. And the levels of AFP and DCP were not associated with HCC development in patients with a SVR (Table 3).
| Patients with SVR (n = 75) | Non HCC (n = 63) | HCC (n = 12) | P-value1 | |
| AFP levels at pretreatment (ng/mL) | 16.1 ± 20.2 | 17.8 ± 22.2 | 12.6 ± 14.9 | NS |
| AFP levels at the end of IFN treatment (ng/mL) | 13.7 ± 47.8 | 17.9 ± 57.8 | 5.1 ± 1.8 | NS |
| AFP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (ng/mL) | 6.7 ± 10.0 | 5.8 ± 4.1 | 8.0 ± 15.1 | NS |
| Pre DCP levels at pretreatment (mAU/mL) | 93.7 ± 374.1 | 131.3 ± 481.4 | 40.3 ± 69.8 | NS |
| Post DCP levels at the end of IFN treatment (mAU/mL) | 140.0 ± 637.9 | 226.9 ± 864.2 | 42.1 ± 83.3 | NS |
| 24 wk DCP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment (mAU/mL) | 33.9 ± 52.6 | 28.9 ± 37.4 | 39.3 ± 66.5 | NS |
As shown in Table 4, the multivariate analysis revealed the following independent risk factors for HCC development after IFN and ribavirin therapy: History of treatment for HCC (P < 0.001, OR = 15.27, 95%CI: 4.98-59.51), AFP levels of ≥ 10 ng/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy (P = 0.009, OR = 3.89, 95%CI: 1.38-11.94), and DCP levels of ≥ 40 mAU/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy (P < 0.001, OR = 24.43, 95%CI: 4.11-238.67).
| Risk factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | OR | 95%CI |
| P-value | P-value | |||
| Age (over 60 yr) | 0.012 | Not significant | ||
| HCC treatment history | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | 15.27 | 4.98-59.51 |
| AFP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment ≥ 10 ng/mL | 0.003 | 0.009 | 3.89 | 1.38-11.94 |
| DCP levels at 24 wk after IFN treatment ≥ 40 mAU/mL | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | 24.43 | 4.11-238.67 |
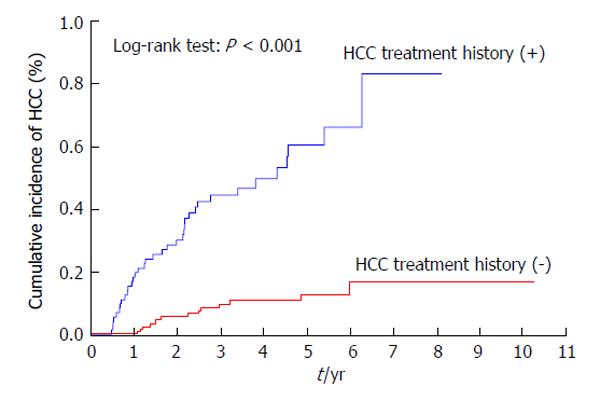
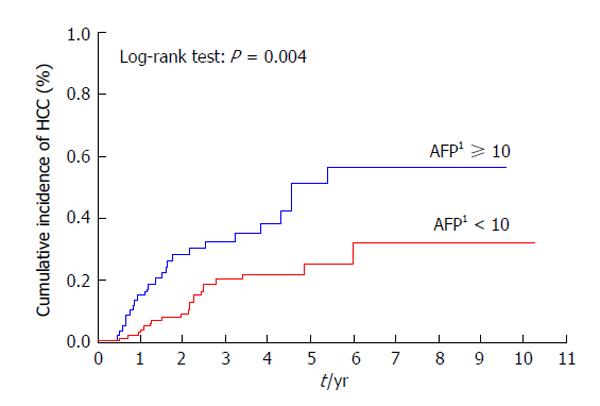
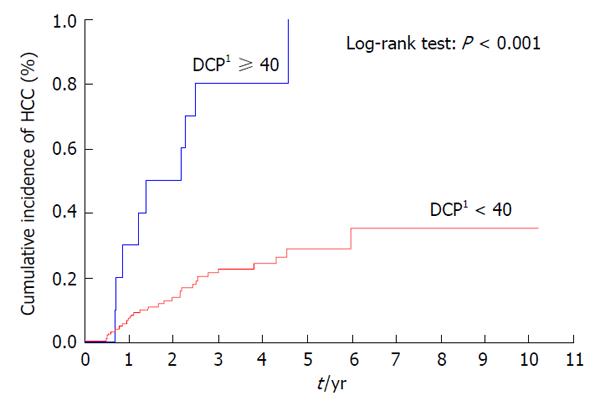
Patients with a previous history of treatment for HCC had a significantly higher cumulative incidence of HCC development after IFN and ribavirin therapy (P < 0.001) (Figure 3). The incidence of HCC was significantly lower in patients with AFP levels of < 10 ng/mL than in those with AFP levels of ≥ 10 ng/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy (P = 0.004) (Figure 4) as in patients with DCP levels of < 40 mAU/mL than in those with DCP levels of ≥ 40 mAU/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy (P < 0.001) (Figure 5).
In this retrospective, multicenter, cooperative study conducted in Japan, we evaluated risk factors of HCC development in LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin. A history of treatment for HCC was a strong risk factor for the development of HCC in our patients. Although HCC has a high recurrence rate, even after curative surgery, a suppressive effect of IFN on HCC recurrence after previous curative treatment has been reported in several studies[19-23]. Furthermore, particularly in Japan, IFN is used as an anti-cancer drug for the treatment of HCC[24-27]. Unfortunately, in LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin, most notably in those with a history of treatment for HCC, IFN therapy did not reduce recurrence rates in our study. Many studies reported that IFN-based therapy not only improves hepatic fibrosis and inflammation but also reduces the incidence of HCC, particularly in patients who achieve SVR[4-13]. In our study, a history of treatment for HCC was a stronger risk factor for HCC development than achieving SVR. In those patients receiving IFN and ribavirin therapy, long-term surveillance for HCC should be conducted even after antiviral therapy with SVR.
In our study, serum levels of AFP decreased after IFN and ribavirin therapy compared to baseline levels in both HCC and non-HCC groups. Serum levels of AFP were further decreased at 24 wk after IFN and ribavirin therapy in the non-HCC group. However, serum levels of AFP were increased at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy in patients who developed HCC. Therefore, serum AFP levels at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy may be a strong predictor of HCC development in LC-C patients treated with IFN and ribavirin. Serum levels of DCP were also increased at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy in patients who developed HCC. Both AFP and DCP serum levels at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy were more strongly associated with HCC development than those of pre- and/or post-IFN treatment.
Previous studies reported that a low or decreased AFP level during IFN therapy is associated with a reduced incidence of HCC[28-30]. Serum levels of AFP after IFN-based therapy are also informative, and a higher post-treatment AFP (≥ 6 ng/mL) was a risk factor for HCC development[11,31].
Recently, DCP was demonstrated as a tumor marker for the detection of HCC[32,33]. However, it was unclear whether DCP had value in detecting HCC in patients with LC-C who received IFN and ribavirin therapy. We demonstrated by multivariate analysis that elevated serum levels of AFP (≥ 10 ng/mL) and DCP (≥ 40 mAU/mL) at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy were independently associated with HCC development. In clinical practice, even in patients with SVR, careful surveillance for HCC is required in patients with LC-C with an AFP of ≥ 10 ng/mL or a DCP of ≥ 40 mAU/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy. A randomized controlled study demonstrated that the LC-C patients who were treated with long-term pegylated-IFN had a low risk of HCC development[34]. Therefore, LC-C patients with an AFP of ≥ 10 ng/mL or a DCP of ≥ 40 mAU/mL at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy should be considered for long-term maintenance treatment with pegylated-IFN, irrespective of whether SVR is achieved.
Recently, therapies with direct-acting antivirals without IFN have demonstrated great efficacy against HCV[35-38]. However, it is currently unknown whether serum AFP levels and HCC incidence are decreased in patients treated with IFN-free regimens using direct-acting antivirals.
Although this present study had some limitations, all included patients were diagnosed with well-established cirrhosis without chronic hepatitis. Thus, our findings provide valuable information.
In conclusion, we suggested that elevated serum levels of both AFP and DCP at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy are strongly associated with HCC development, irrespective of the virological response, among Japanese LC-C patients. In these patients, additional surveillance for the development of HCC may be required.
Chronically hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the commonest cause of liver cirrhosis in the world. HCV-related liver cirrhosis (LC-C) patients are the high risk to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Interferon (IFN)-based therapy reduces the rate of HCC development in patients with chronically HCV infection, especially those with sustained virological response (SVR). However, HCC development has frequently been reported in LC-C patients who achieved SVR. In those patients receiving IFN-based therapy, long-term surveillance for HCC should be conducted even after antiviral therapy with SVR. Knowing risk factors for HCC development is required in aged patients with LC-C treated with anti-viral agents.
Previous studies included chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. In this study, all included patients were diagnosed with well-established cirrhosis. SVR was not associated with HCC development in LC-C patients.
The authors suggested that elevated serum levels of both alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy are strongly associated with HCC incidence, irrespective of the virological response, among LC-C patients. In those patients, additional surveillance for the development of HCC may be required.
Serum levels of both AFP and DCP at 24 wk after the completion of anti-viral agent provide valuable information that can be used to clinical decisions.
The authors showed elevated serum levels of both AFP and DCP at 24 wk after the completion of IFN and ribavirin therapy are strongly associated with HCC incidence. This study has a certain clinical impact.
| 1. | Niederau C, Lange S, Heintges T, Erhardt A, Buschkamp M, Hürter D, Nawrocki M, Kruska L, Hensel F, Petry W. Prognosis of chronic hepatitis C: results of a large, prospective cohort study. Hepatology. 1998;28:1687-1695. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 444] [Cited by in RCA: 440] [Article Influence: 15.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Hu KQ, Tong MJ. The long-term outcomes of patients with compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis and history of parenteral exposure in the United States. Hepatology. 1999;29:1311-1316. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 208] [Cited by in RCA: 196] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Sangiovanni A, Prati GM, Fasani P, Ronchi G, Romeo R, Manini M, Del Ninno E, Morabito A, Colombo M. The natural history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: A 17-year cohort study of 214 patients. Hepatology. 2006;43:1303-1310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 433] [Cited by in RCA: 447] [Article Influence: 22.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 4. | Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, Nakatani S, Morimoto H, Takeda T, Nakajima S, Shiomi S, Seki S, Kobayashi K, Otani S. Randomised trial of effects of interferon-alpha on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic active hepatitis C with cirrhosis. Lancet. 1995;346:1051-1055. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 644] [Cited by in RCA: 607] [Article Influence: 19.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Moriyama M, Arakawa Y, Ide T, Sata M, Inoue O, Yano M, Tanaka M, Fujiyama S. Interferon therapy reduces the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma: national surveillance program of cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C in Japan. IHIT Study Group. Inhibition of Hepatocarcinogenesis by Interferon Therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:174-181. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 833] [Cited by in RCA: 781] [Article Influence: 28.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 6. | Imai Y, Kawata S, Tamura S, Yabuuchi I, Noda S, Inada M, Maeda Y, Shirai Y, Fukuzaki T, Kaji I. Relation of interferon therapy and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Osaka Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:94-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 234] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Serfaty L, Aumaître H, Chazouillères O, Bonnand AM, Rosmorduc O, Poupon RE, Poupon R. Determinants of outcome of compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27:1435-1440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 291] [Cited by in RCA: 278] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 8. | Shiratori Y, Ito Y, Yokosuka O, Imazeki F, Nakata R, Tanaka N, Arakawa Y, Hashimoto E, Hirota K, Yoshida H. Antiviral therapy for cirrhotic hepatitis C: association with reduced hepatocellular carcinoma development and improved survival. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:105-114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 226] [Cited by in RCA: 207] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Bruno S, Silini E, Crosignani A, Borzio F, Leandro G, Bono F, Asti M, Rossi S, Larghi A, Cerino A. Hepatitis C virus genotypes and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a prospective study. Hepatology. 1997;25:754-758. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 256] [Cited by in RCA: 247] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Cardoso AC, Moucari R, Figueiredo-Mendes C, Ripault MP, Giuily N, Castelnau C, Boyer N, Asselah T, Martinot-Peignoux M, Maylin S. Impact of peginterferon and ribavirin therapy on hepatocellular carcinoma: incidence and survival in hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2010;52:652-657. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 267] [Cited by in RCA: 255] [Article Influence: 15.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 11. | Oze T, Hiramatsu N, Yakushijin T, Miyazaki M, Yamada A, Oshita M, Hagiwara H, Mita E, Ito T, Fukui H. Post-treatment levels of α-fetoprotein predict incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma after interferon therapy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1186-1195. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Hung CH, Lee CM, Wang JH, Hu TH, Chen CH, Lin CY, Lu SN. Impact of diabetes mellitus on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon-based antiviral therapy. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:2344-2352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Tamaki N, Hirayama I, Tanaka T, Sato M, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, Ueda K, Kuzuya T. Effect of aging on risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 2010;52:518-527. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Ogawa E, Furusyo N, Kajiwara E, Takahashi K, Nomura H, Maruyama T, Tanabe Y, Satoh T, Nakamuta M, Kotoh K. Efficacy of pegylated interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin treatment on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a prospective, multicenter study. J Hepatol. 2013;58:495-501. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Yamashita N, Ohho A, Yamasaki A, Kurokawa M, Kotoh K, Kajiwara E. Hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C patients achieving a sustained virological response to interferon: significance of lifelong periodic cancer screening for improving outcomes. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:1504-1513. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, de Lédinghen V, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005;41:48-54. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1090] [Cited by in RCA: 1097] [Article Influence: 52.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, Le Bail B, Chanteloup E, Haaser M, Darriet M, Couzigou P, De Lédinghen V. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:343-350. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1796] [Cited by in RCA: 1861] [Article Influence: 88.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 18. | Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Tsubota A, Suzuki F, Arase Y, Murashima N, Chayama K, Kumada H. Distinction between chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Practical discriminant function using common laboratory data. Hepatol Res. 2000;18:252-266. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Primary liver cancer in Japan. Clinicopathologic features and results of surgical treatment. Ann Surg. 1990;211:277-287. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Nagasue N, Uchida M, Makino Y, Takemoto Y, Yamanoi A, Hayashi T, Chang YC, Kohno H, Nakamura T, Yukaya H. Incidence and factors associated with intrahepatic recurrence following resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:488-494. [PubMed] |
| 21. | Miyake Y, Takaki A, Iwasaki Y, Yamamoto K. Meta-analysis: interferon-alpha prevents the recurrence after curative treatment of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:287-292. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Shen YC, Hsu C, Chen LT, Cheng CC, Hu FC, Cheng AL. Adjuvant interferon therapy after curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a meta-regression approach. J Hepatol. 2010;52:889-894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Hsu YC, Ho HJ, Wu MS, Lin JT, Wu CY. Postoperative peg-interferon plus ribavirin is associated with reduced recurrence of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;58:150-157. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Sakon M, Nagano H, Dono K, Nakamori S, Umeshita K, Yamada A, Kawata S, Imai Y, Iijima S, Monden M. Combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-alpha therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major portal branches. Cancer. 2002;94:435-442. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 151] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Uka K, Aikata H, Takaki S, Miki D, Kawaoka T, Jeong SC, Takahashi S, Toyota N, Ito K, Chayama K. Pretreatment predictor of response, time to progression, and survival to intraarterial 5-fluorouracil/interferon combination therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:845-853. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Kasai K, Ushio A, Kasai Y, Sawara K, Miyamoto Y, Oikawa K, Kuroda H, Takikawa Y, Suzuki K. Therapeutic efficacy of combination therapy with intra-arterial 5-fluorouracil and systemic pegylated interferon α-2b for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous invasion. Cancer. 2012;118:3302-3310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Shakado S, Iwata K, Tsuchiya N, Kunimoto H, Yotsumoto K, Fukunaga A, Kuno S, Tanaka T, Sakurai K, Iwashita H. Pilot Study of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy with Interferon-beta and 5-fluorouracil: A New Chemotherapy for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014;61:557-562. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Nomura H, Kashiwagi Y, Hirano R, Tanimoto H, Tsutsumi N, Higashi M, Ishibashi H. Efficacy of low dose long-term interferon monotherapy in aged patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 and its relation to alpha-fetoprotein: A pilot study. Hepatol Res. 2007;37:490-497. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Chen TM, Huang PT, Tsai MH, Lin LF, Liu CC, Ho KS, Siauw CP, Chao PL, Tung JN. Predictors of alpha-fetoprotein elevation in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma, and its normalization after pegylated interferon alfa 2a-ribavirin combination therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:669-675. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Osaki Y, Ueda Y, Marusawa H, Nakajima J, Kimura T, Kita R, Nishikawa H, Saito S, Henmi S, Sakamoto A. Decrease in alpha-fetoprotein levels predicts reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus infection receiving interferon therapy: a single center study. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:444-451. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Nishimura T, Muraoka M, Suzuki Y, Tamaki N, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, Ueda K, Nakanishi H. α-fetoprotein levels after interferon therapy and risk of hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2013;58:1253-1262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 188] [Cited by in RCA: 213] [Article Influence: 16.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Ertle JM, Heider D, Wichert M, Keller B, Kueper R, Hilgard P, Gerken G, Schlaak JF. A combination of α-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin is superior in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion. 2013;87:121-131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Li C, Zhang Z, Zhang P, Liu J. Diagnostic accuracy of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin versus α-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol Res. 2014;44:E11-E25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Lok AS, Everhart JE, Wright EC, Di Bisceglie AM, Kim HY, Sterling RK, Everson GT, Lindsay KL, Lee WM, Bonkovsky HL. Maintenance peginterferon therapy and other factors associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:840-849; quiz e12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 146] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Poordad F, Lawitz E, Kowdley KV, Cohen DE, Podsadecki T, Siggelkow S, Heckaman M, Larsen L, Menon R, Koev G. Exploratory study of oral combination antiviral therapy for hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:45-53. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 238] [Cited by in RCA: 241] [Article Influence: 18.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Ikeda K, Toyota J, Karino Y, Chayama K, Kawakami Y, Ido A, Yamamoto K, Takaguchi K. Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1b infection. Hepatology. 2014;59:2083-2091. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 468] [Cited by in RCA: 453] [Article Influence: 37.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Lawitz E, Poordad FF, Pang PS, Hyland RH, Ding X, Mo H, Symonds WT, McHutchison JG, Membreno FE. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin in treatment-naive and previously treated patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection (LONESTAR): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2014;383:515-523. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 429] [Cited by in RCA: 443] [Article Influence: 36.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Ferenci P, Bernstein D, Lalezari J, Cohen D, Luo Y, Cooper C, Tam E, Marinho RT, Tsai N, Nyberg A. ABT-450/r-ombitasvir and dasabuvir with or without ribavirin for HCV. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1983-1992. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 571] [Cited by in RCA: 548] [Article Influence: 45.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
P- Reviewer: Enomoto H, Kanda T S- Editor: Gong XM L- Editor: A E- Editor: Liu SQ
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/