Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Mar 8, 2016; 8(7): 376-384
Published online Mar 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i7.376
Published online Mar 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i7.376
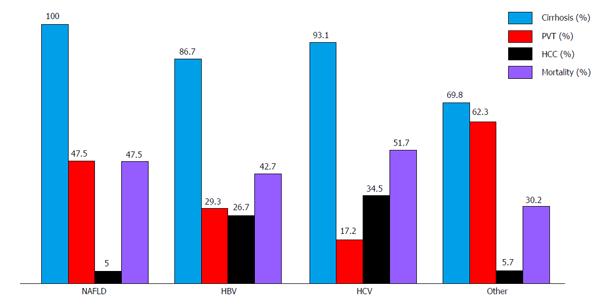
Figure 1 Incidence of portal vein thrombosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular cancer, in addition to mortality rate in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and other liver-related diseases (others).
PVT: Portal vein thrombosis; HCC: Hepatocellular cancer; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
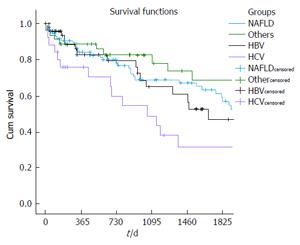
Figure 2 Survival functions in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and other liver-related diseases (others).
Of the patients, 50.0% with NAFLD, 33.3% with hepatitis B, 26.3% with hepatitis C, and 58.3% with other diseases were alive at the end of the 5-year period with a significant difference according to the Kaplan-Meier log Rank test (P = 0.040). NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Basaranoglu M, Najjar SM, Demirbag AE, Senturk H. Significant cohort of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with portal vein thrombosis in transplant waiting list. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(7): 376-384
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i7/376.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i7.376