©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Nov 18, 2016; 8(32): 1402-1413
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1402
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1402
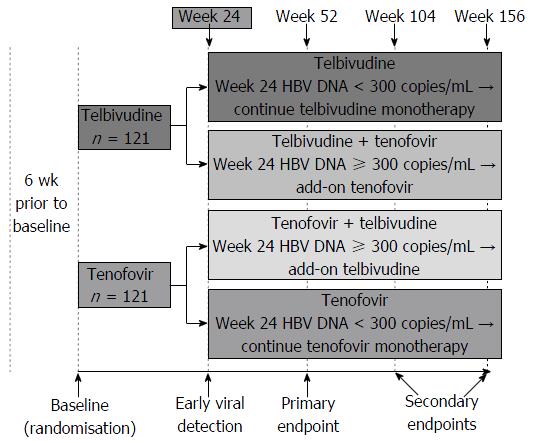
Figure 1 Study design.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
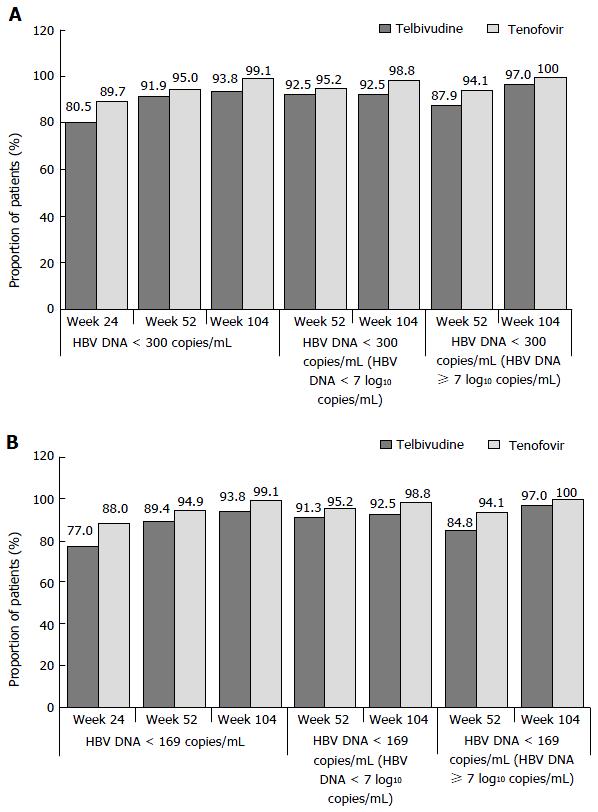
Figure 2 Proportions of patients achieving hepatitis B virus DNA < 300 (A) or < 169 copies/mL (B), by visit and by baseline hepatitis B virus DNA levels (< 7 or ≥ 7 log10 copies/mL), roadmap intent-to-treat population.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
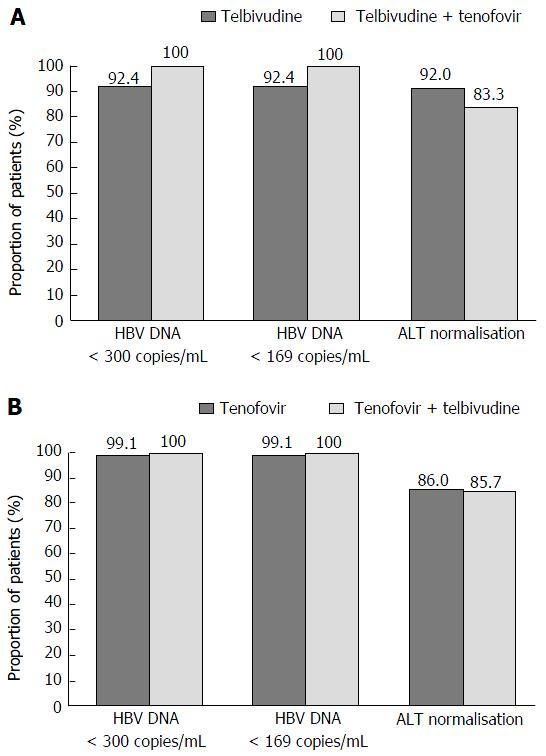
Figure 3 Intensification with tenofovir (A) or telbivudine (B), virologic response and aminotransferase normalisation at week 104, roadmap intent-to-treat population.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
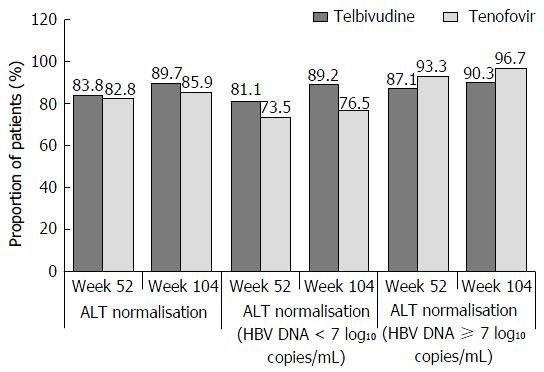
Figure 4 Proportions of patients achieving aminotransferase normalisation, by visit and by baseline hepatitis B virus DNA levels (< 7 or ≥ 7 log10 copies/mL), roadmap intent-to-treat population.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
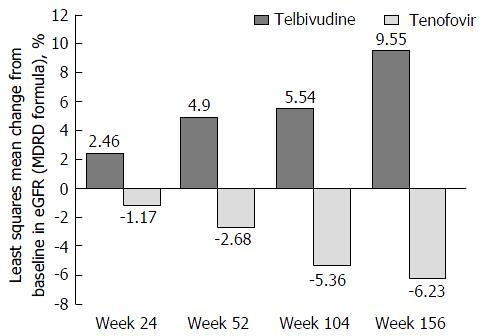
Figure 5 Changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate over time with telbivudine and tenofovir, safety population.
eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; MDRD: Modification of diet in renal disease.
- Citation: Krastev Z, Petrova D, Kotzev I, Celen MK, Mendelson M, Chandra R, Pandey P, Hamed K. Telbivudine vs tenofovir in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients: OPTIMA roadmap study. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(32): 1402-1413
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i32/1402.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1402