©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Apr 28, 2015; 7(6): 831-845
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.831
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.831
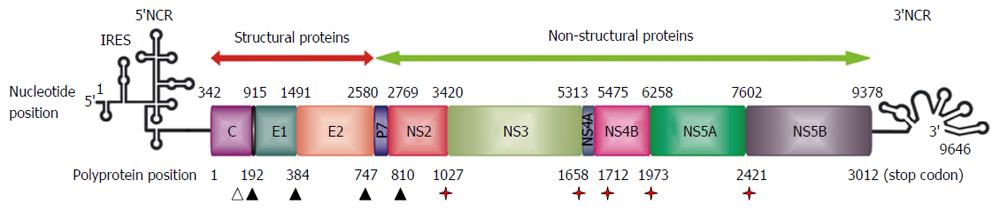
Figure 1 Organisation of hepatitis C virus genome and hepatitis C virus polyprotein processing.
Schematic representation of the 9.6 kb positive-stranded RNA genome. Simplified RNA secondary structures in the 5’ and 3’ non-coding regions (NCRs) are shown. Internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-mediated translation produces a polyprotein precursor that is processed into the mature structural and non-structural proteins. Nucleotide positions are shown by numbers on the upper part of the scheme. Amino acid positions are shown by numbers in the lower part of the scheme. The coding region is depicted by rectangles showing the corresponding encoded proteins. Solid arrowheads denote cleavages by the endoplasmic reticulum signal peptidase. The open arrowhead indicates further C-terminal processing of the core protein by signal peptide peptidase. Red stars indicate cleavages by the hepatitis C virus NS2 and NS3-4A proteases.
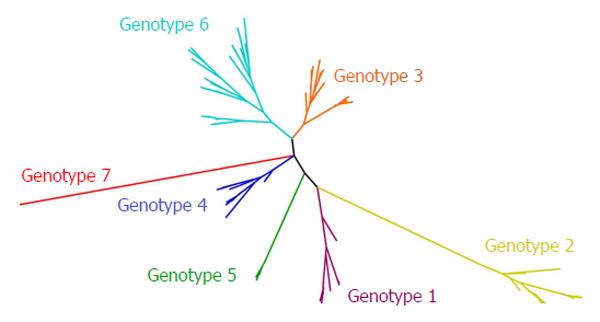
Figure 2 Evolutionary tree of the seven genotypes and all known subtypes of hepatitis C virus.
The tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood method using GTR + I + G (general time-reversible substitution model considering invariable sites and gamma distribution) as the nucleotide substitution model that best fitted the data using a 307-nucleotide sequence from the NS5B-coding region. Sequences used for the construction of this phylogenetic tree were extracted from Yusim et al[155].
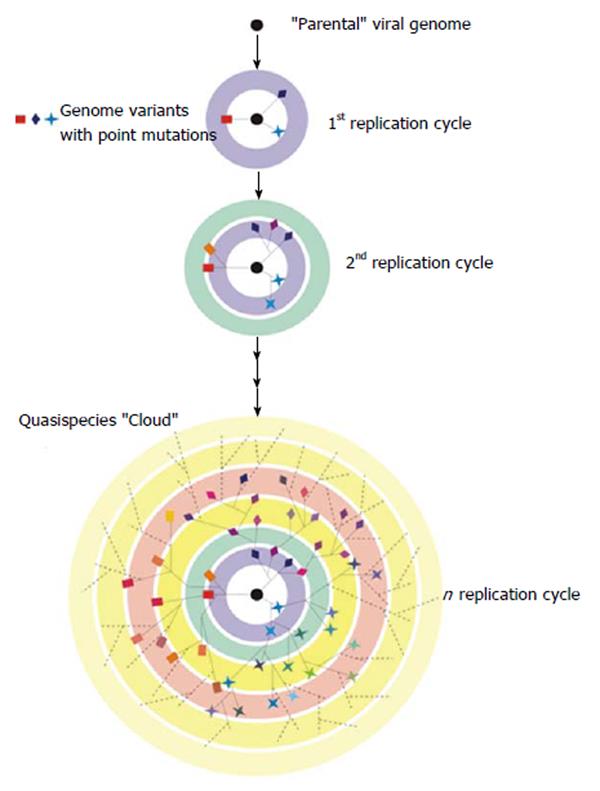
Figure 3 Viral quasispecies.
A virus replicating with a high mutation rate will generate a diverse mutant repertoire over the course of a few generations. In this schematic representation, a “parental” viral genome (black filled circle) gives rise to different variants (coloured squares, prisms and stars), each linked to another one by a point mutation. The concentric circles represent replication cycles. The resulting distribution is often referred to as quasispecies “Cloud”.
- Citation: Echeverría N, Moratorio G, Cristina J, Moreno P. Hepatitis C virus genetic variability and evolution. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(6): 831-845
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i6/831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.831