©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2015; 7(3): 498-506
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.498
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.498
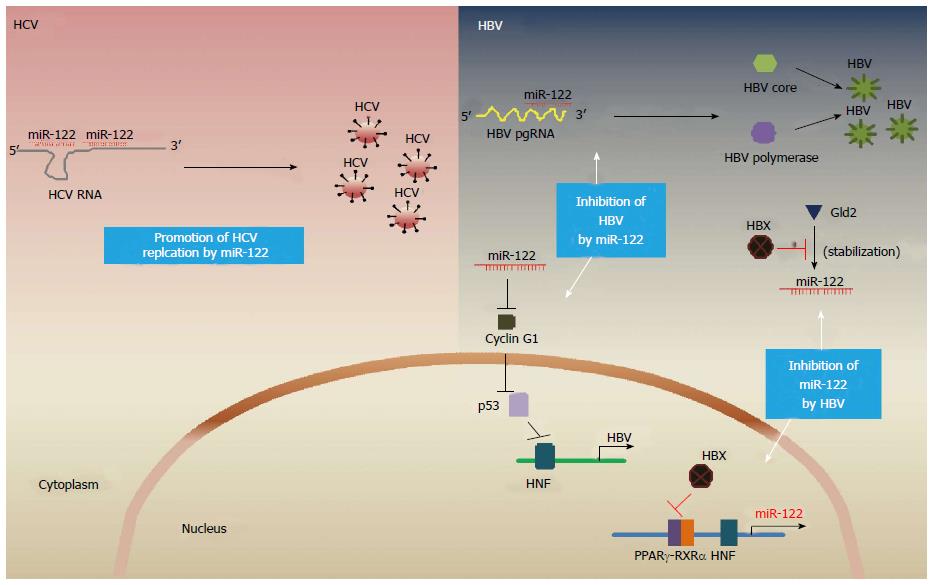
Figure 1 Emerging role of miR-122 in hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection.
Liver specific miR-122 binds to 5’UTR sites of HCV RNA and promotes their translation and replication. In contrast, miR-122 binds to highly conserved HBV pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) and modulating pgRNA stability, leading to inhibition of HBV production. miR-122 also positively regulates p53-mediated inhibition of HBV transcription through direct targeting cyclin G1. HBV infection affects miR-122 expression and stability. Hepatitis B viral X protein (HBX) binds to peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) and thereby inhibits miR-122 transcription. In addition, HBX also reduce the miR-122 levels through downregulating Gld2. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; miR-122: MicroRNA-122; Gld2: Germline development 2.
- Citation: Song K, Han C, Dash S, Balart LA, Wu T. MiR-122 in hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus dual infection. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(3): 498-506
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i3/498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.498