©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2015; 7(3): 362-376
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.362
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.362
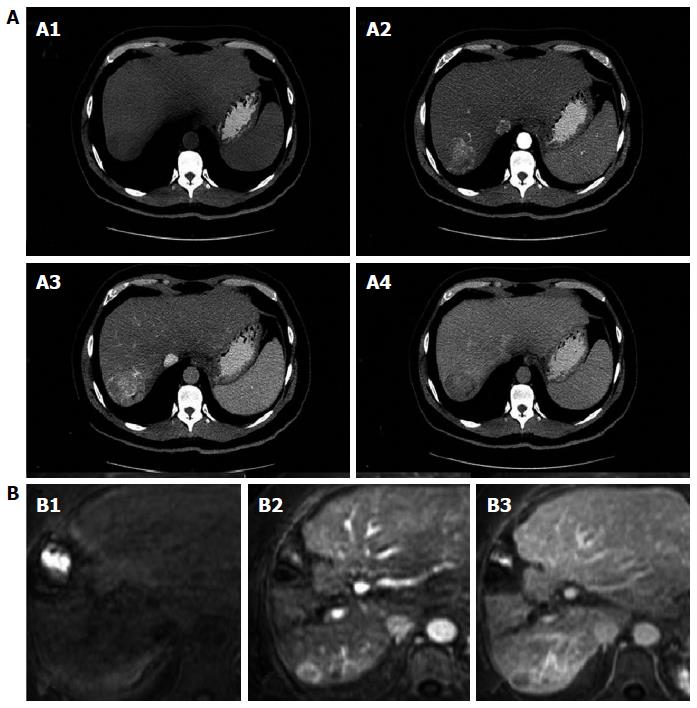
Figure 1 Contrast - enhanced computed tomography and Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Classical imaging pattern of hepatocellular carcinoma in contrast-enhanced computed tomography; A1: Simple phase, hypodense lesion in segment VII; A2: Arterial phase; A3: Enhanced portal; A4: 3 min late-phase washout; B: Diagnostic dynamic-contrast magnetic resonance imaging with classical pattern; B1: Simple phase; B2: Portal phase; B3: late-phase washout.
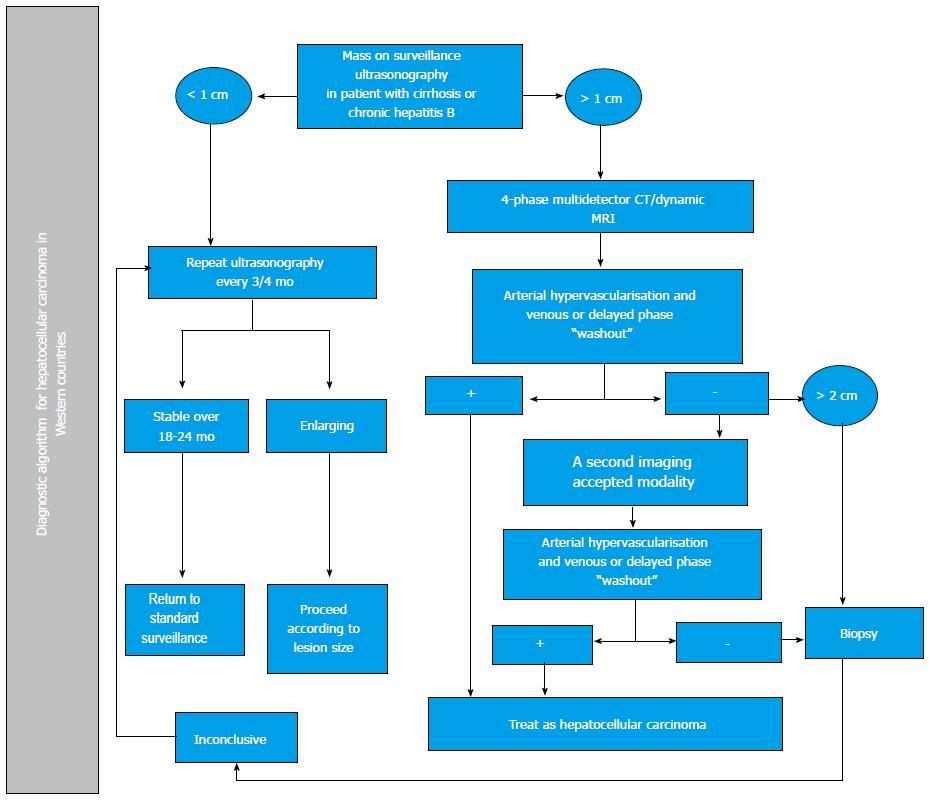
Figure 2 Diagnostic algorithm for hepatocellular carcinoma in Western countries.
Modified from Bruix et al[6], with permission of the author and John Wiley and Sons. CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
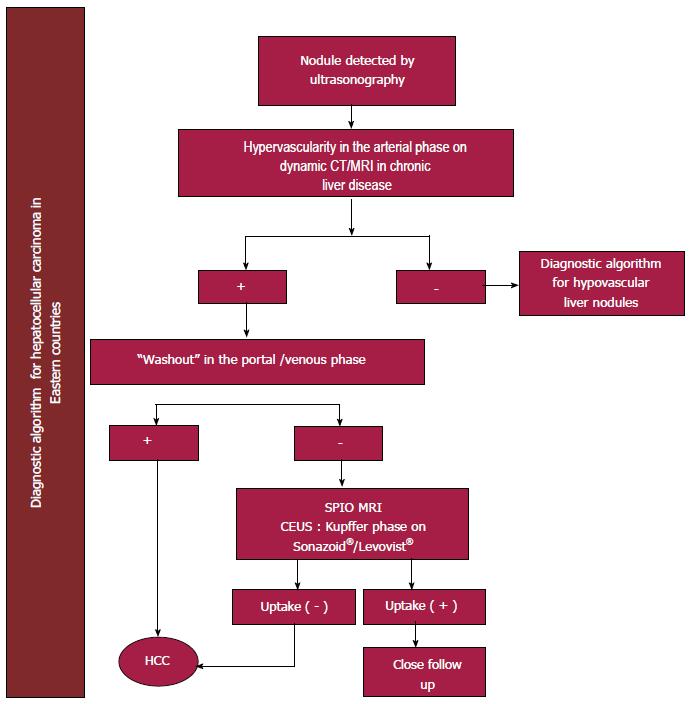
Figure 3 Diagnosis algorithm for hepatocellular carcinoma in Eastern countries.
Modified from Omata et al[51], with permission of the author and Springer. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; SPIO: Super paramagnetic iron oxide; CEUS: Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography.
Figure 4 Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system and treatment strategy.
- Citation: Tejeda-Maldonado J, García-Juárez I, Aguirre-Valadez J, González-Aguirre A, Vilatobá-Chapa M, Armengol-Alonso A, Escobar-Penagos F, Torre A, Sánchez-Ávila JF, Carrillo-Pérez DL. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(3): 362-376
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i3/362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.362