©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Oct 8, 2015; 7(22): 2411-2417
Published online Oct 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2411
Published online Oct 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2411
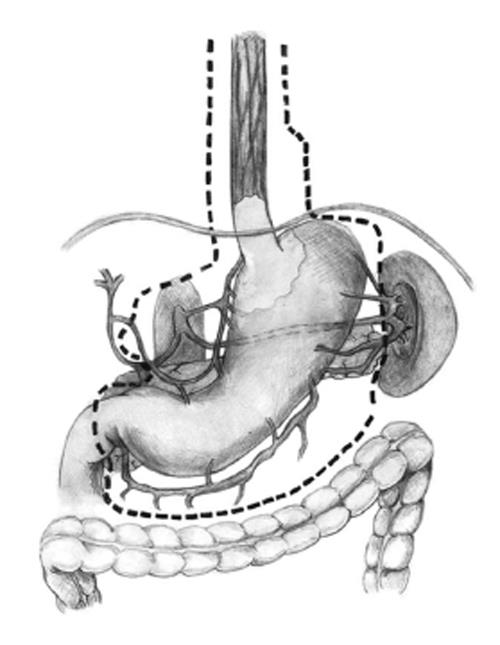
Figure 1 Lymph node dissection when performing total esophagogastrectomy.
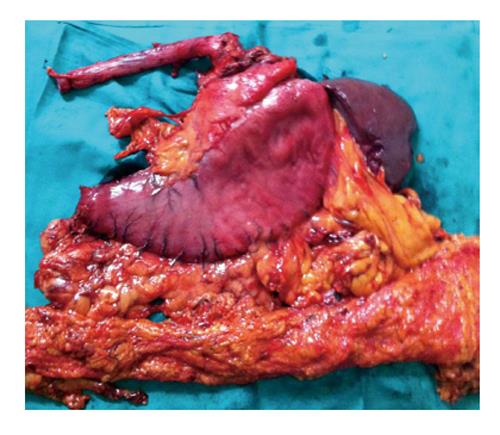
Figure 2 Surgery specimen, which was dissected in the operating room after surgery.
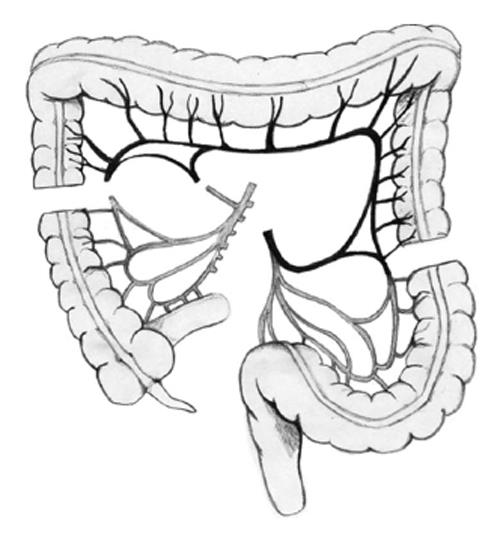
Figure 3 Colon section at the origin of middle colic artery, preserving the marginal arcade.
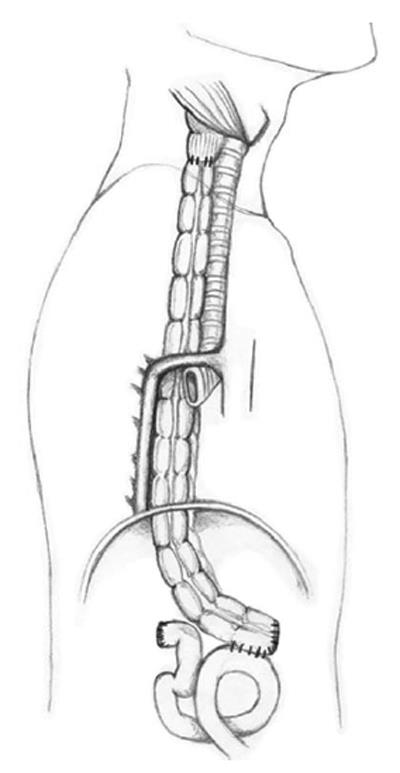
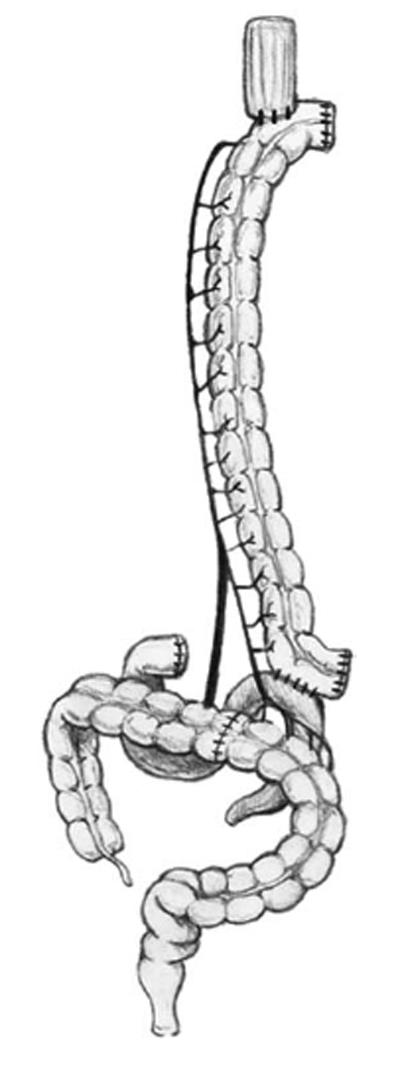
Figure 4 Transverse colon interposition through the posterior mediastinum.
Coloesophageal anastomosis and colojejunal anastomosis are shown lateral view.
Figure 5 Transverse colon interposition through the posterior mediastinum.
Coloesophageal anastomosis and colojejunal anastomosis are shown front view.
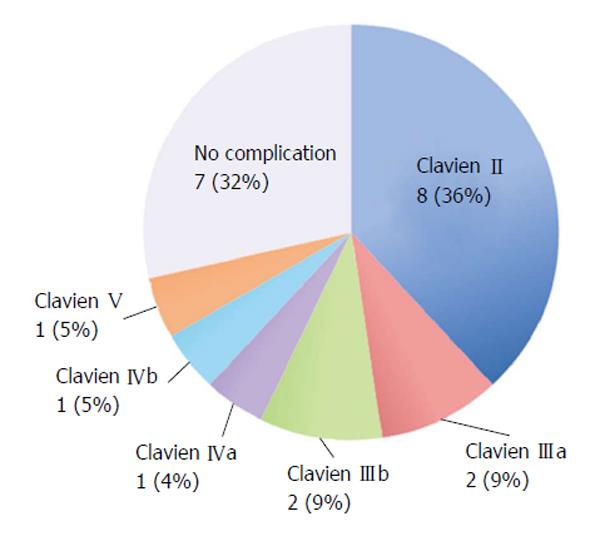
Figure 6 Complications observed according to Clavien Dindo classifications.
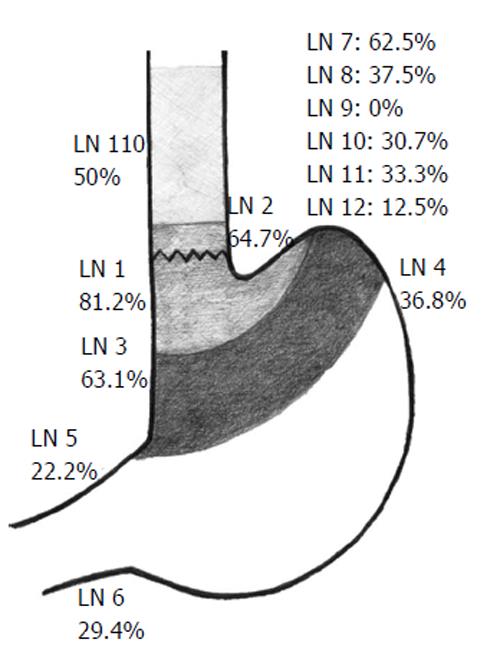
Figure 7 Lymph node metastasis distribution.
Only patients with esophagogastric junction cancer are considered. LN: Lymph node according to the Japanese classifications.
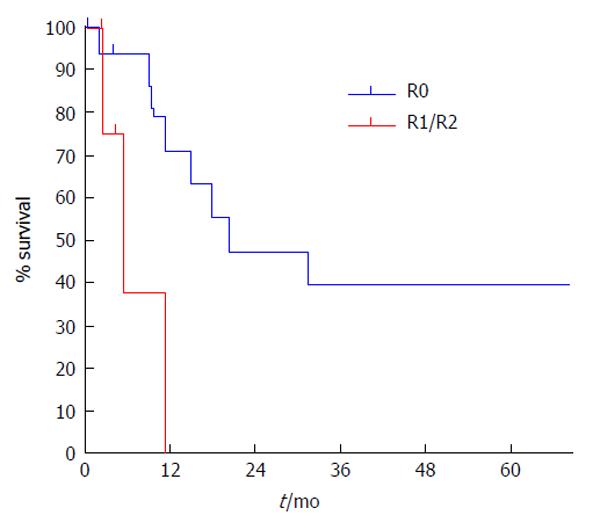
Figure 8 Cancer specific survival at 5 years, according to residual tumors.
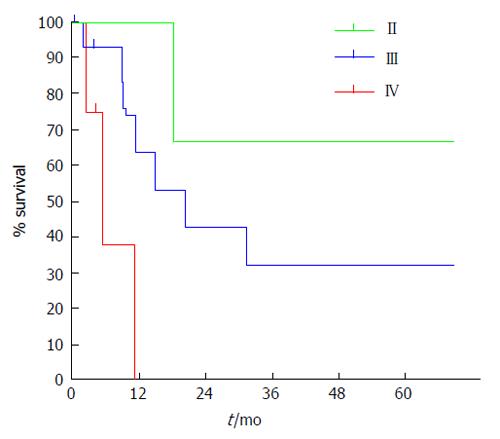
Figure 9 Five year survival follow-up by tumor stage according to the TNM classifications.
- Citation: Ceroni M, Norero E, Henríquez JP, Viñuela E, Briceño E, Martínez C, Aguayo G, Araos F, González P, Díaz A, Caracci M. Total esophagogastrectomy plus extended lymphadenectomy with transverse colon interposition: A treatment for extensive esophagogastric junction cancer. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(22): 2411-2417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i22/2411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2411