©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Jun 28, 2015; 7(12): 1652-1659
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1652
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1652
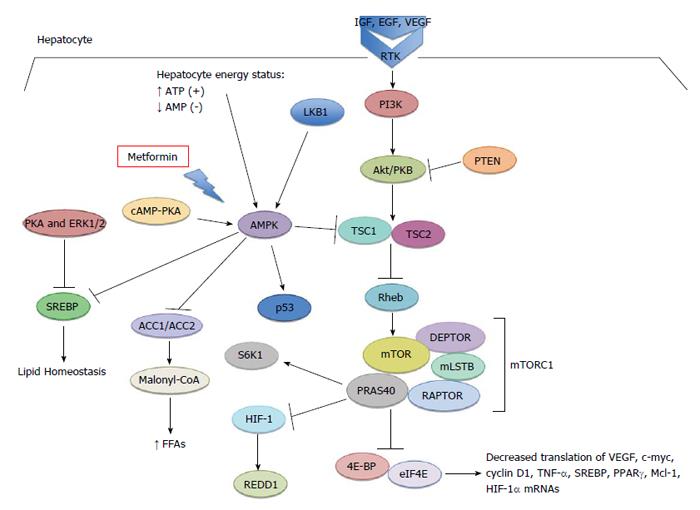
Figure 1 Effects of metformin on hepatocyte energy status and the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, in turn affecting metabolism and inflammation.
4E-BP: 4 eukaryotic-binding protein; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; PKB: Protein kinase B; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate kinase; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DEPTOR: DEP domain-containing mTOR interacting protein; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; eIF4E: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; FFAs: Free fatty acids; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha; IGF: Insulin growth factor; LKB1: Liver kinase B1; mLSTB: Mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositol 3 kinase; PKA: Protein kinase A; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PRAS40: Proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa; RAPTOR: Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; Rheb: Ras homolog enriched in brain; RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinase; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; TSC: Tumor suppressor complex; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Bhat A, Sebastiani G, Bhat M. Systematic review: Preventive and therapeutic applications of metformin in liver disease. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(12): 1652-1659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i12/1652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1652