©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2012; 4(6): 191-195
Published online Jun 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i6.191
Published online Jun 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i6.191
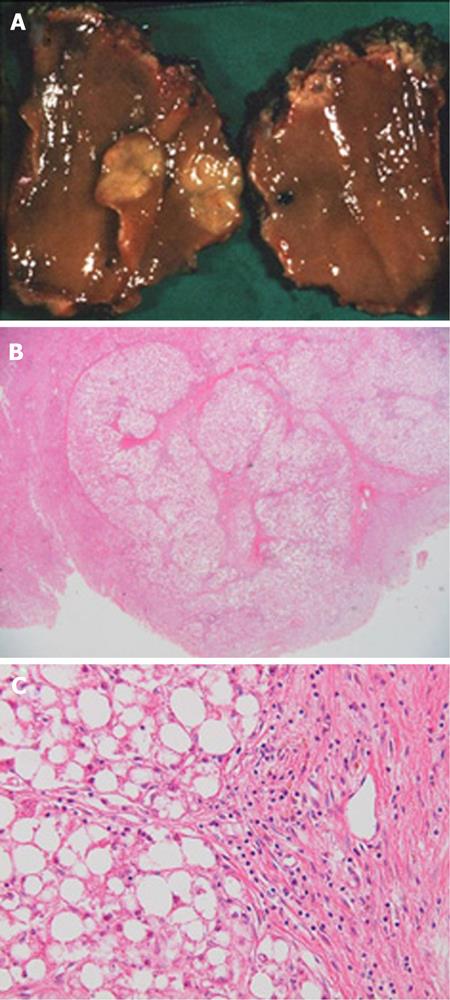
Figure 1 Initial surgery for focal nodular hyperplasia at the age of 18 years.
A: Resected specimen; B: A central scar and fibrous partition in the nodule [hematoxylin and eosin stain (HE × 4)]; C: Markedly vacuolated cells, without atypical cells, in the nodule and central vein in the central scar (HE × 400).
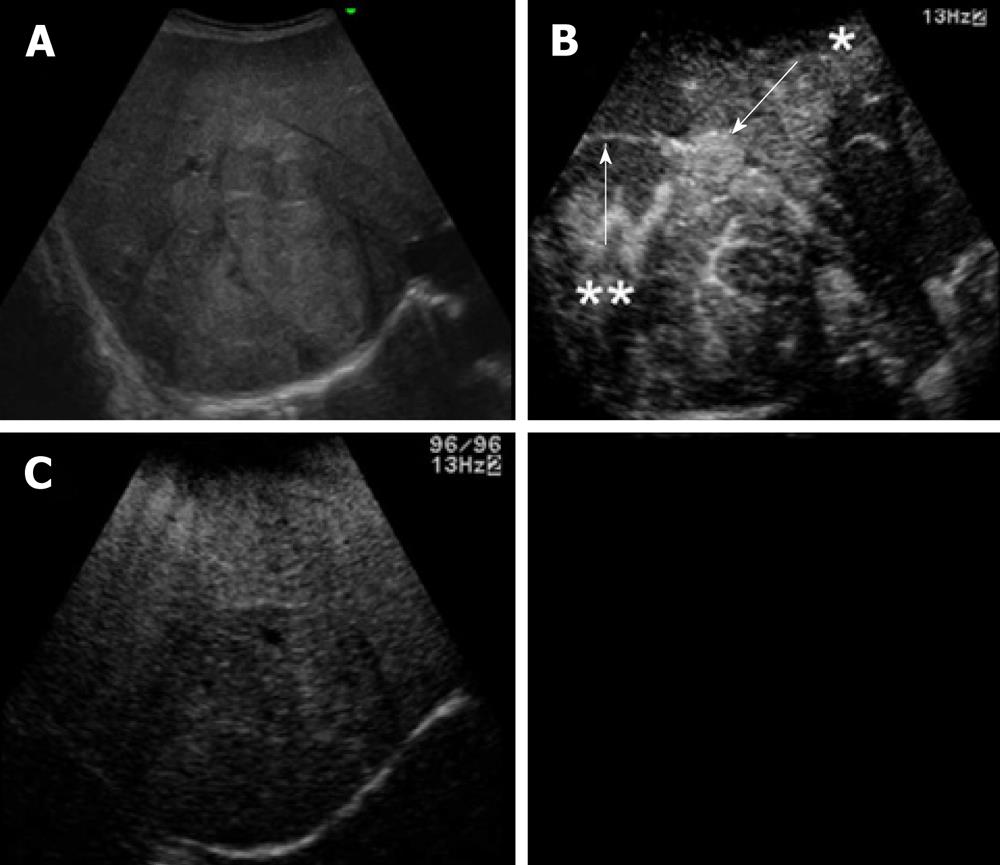
Figure 2 Ultrasonography.
A: A heterogeneous echoic mass with a capsule of 10 cm in diameter; B: The tumor with many satellite nodules (arrow, star) around the capsule (arrow, double star) was highly enhanced in the early phase with the perflubutane microbubble contrast agent; C: The wash-out effect was not obvious in the Kupffer phase, which was an atypical finding inconsistent with hepatocellular carcinoma.
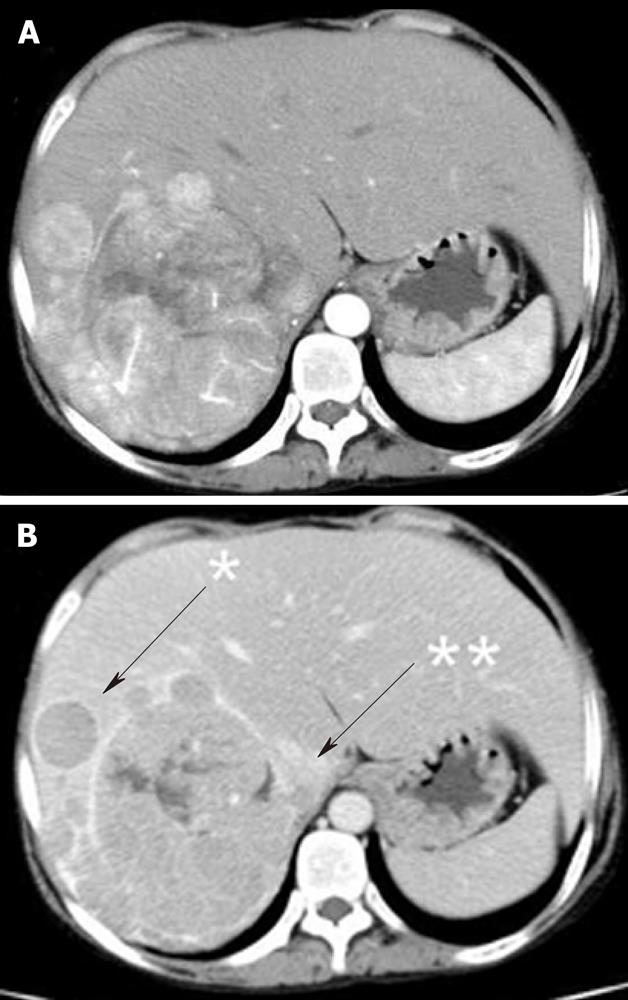
Figure 3 Dynamic computer tomography.
A: A highly-enhanced tumor measuring 10 cm in the early phase; B: An iso- to low-density tumor in the late phase. It had satellite nodules (arrow, star) and a partially torn capsule (arrow, double star).
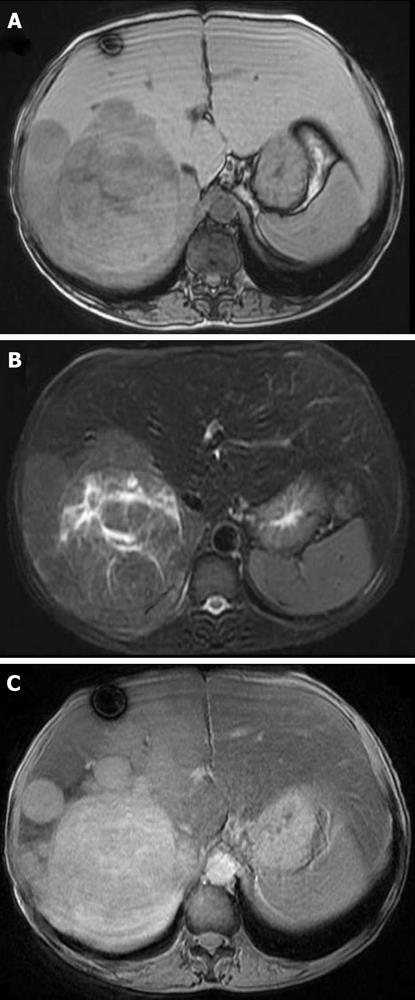
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging.
A: A low-intensity tumor in a T1WI; B: A high-intensity tumor in a T2WI; C: A tumor with low enhancement after resovist administration.
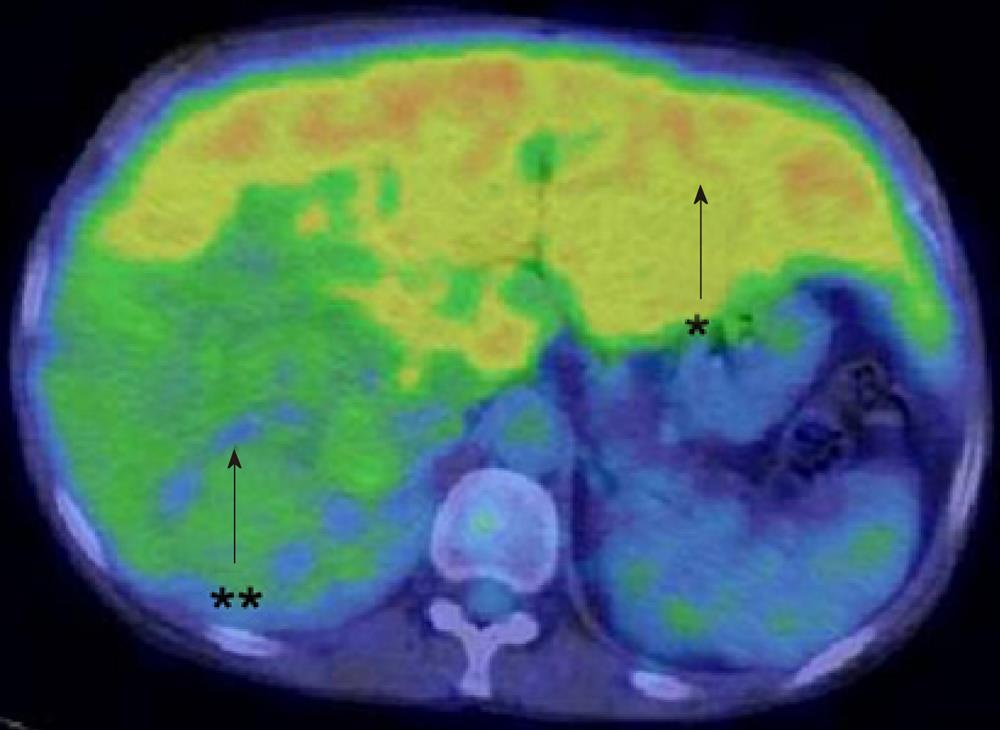
Figure 5 Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computer tomography.
High levels of FDG accumulation with a SUVmax of 4.2 in the non-tumorous liver (arrow, star) and relatively low uptake of FDG with a SUVmax of 2.7 in the tumor (arrow, double star). FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography.
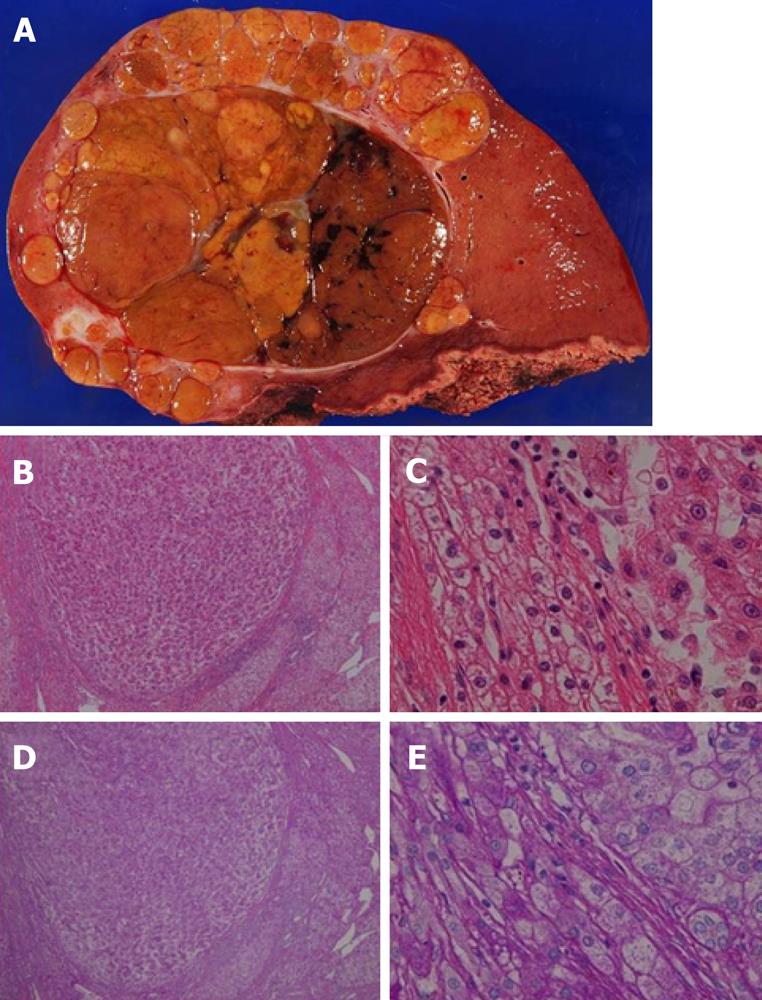
Figure 6 Giant tumor in the right lobe.
A: Resected specimen showed a giant tumor of 10 cm in diameter on the cut surface. The tumor contained septums and hemorrhagic regions; B: hematoxylin and eosin stain (HE) staining revealed the capsule with some extracapsular invasions (HE × 4); C: Histology of the tumor revealed moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with intrahepatic metastases, whereas no adenomatous components were observed (HE × 400); D: Cells with enlarged clear endoplasmic reticula were observed in the non-tumorous region [periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain × 4]. E: PAS staining revealed a PAS-positive area in accordance with a clear area (PAS × 400).
- Citation: Mikuriya Y, Oshita A, Tashiro H, Amano H, Kobayashi T, Arihiro K, Ohdan H. Hepatocellular carcinoma and focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver in a glycogen storage disease patient. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(6): 191-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i6/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i6.191