©2010 Baishideng.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2010; 2(6): 239-242
Published online Jun 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i6.239
Published online Jun 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i6.239
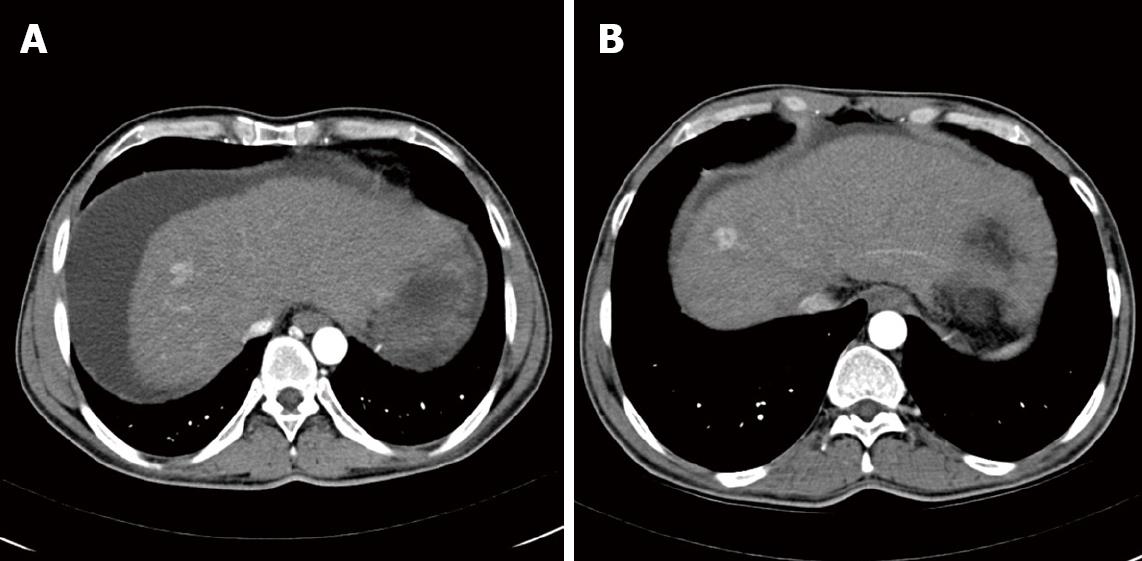
Figure 1 Computed tomography (CT)-scans: Axial IV contrast enhanced CT.
Arterial phase image showing the reference lesion at the indicated time points. Size of this lesion remained stable between 2007 and 2009. A: CT liver November, 2007; B: CT liver December, 2009.
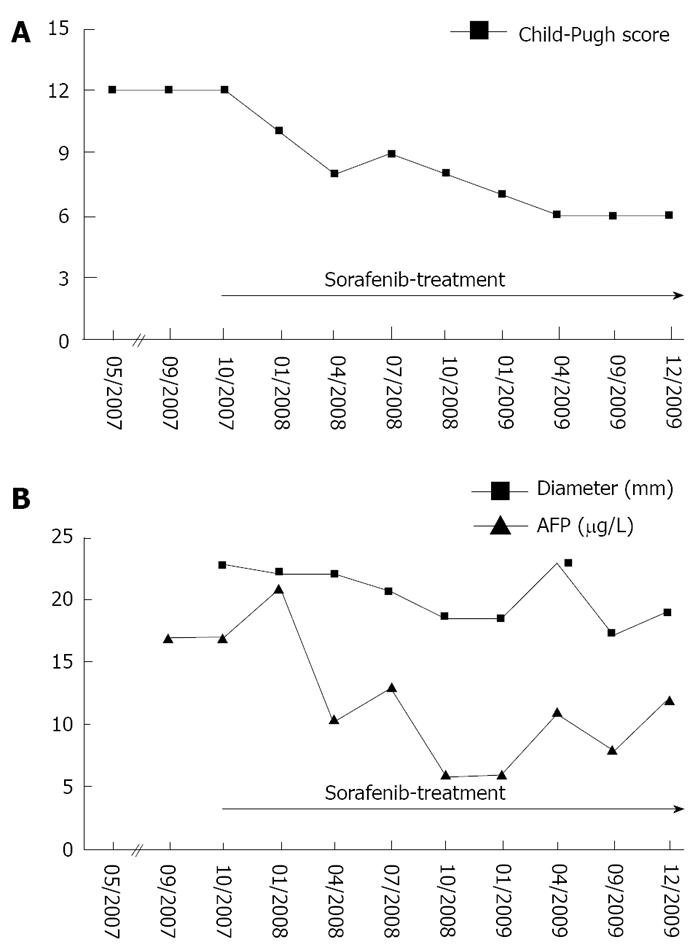
Figure 2 Clinical course of the patient.
Therapy evaluation was performed by physical examination, complete blood count and creatinine, ALT, AST, AP, GGT, INR and assessment of adverse events as well as CT scans of the abdomen. A: Child-Pugh score; B: Serum AFP levels and the diameter of the reference lesion at the time-points indicated. ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; AP: alkaline phosphatase; GGT: gamma glutamyltransferase; INR: international normalized ratio; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Roderburg C, Bubenzer J, Spannbauer M, O ND, Mahnken A, Ludde T, Trautwein C, Tischendorf JJ. Long-term survival of a HCC-patient with severe liver dysfunction treated with sorafenib. World J Hepatol 2010; 2(6): 239-242
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v2/i6/239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v2.i6.239