©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2026; 18(2): 116475
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.116475
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.116475
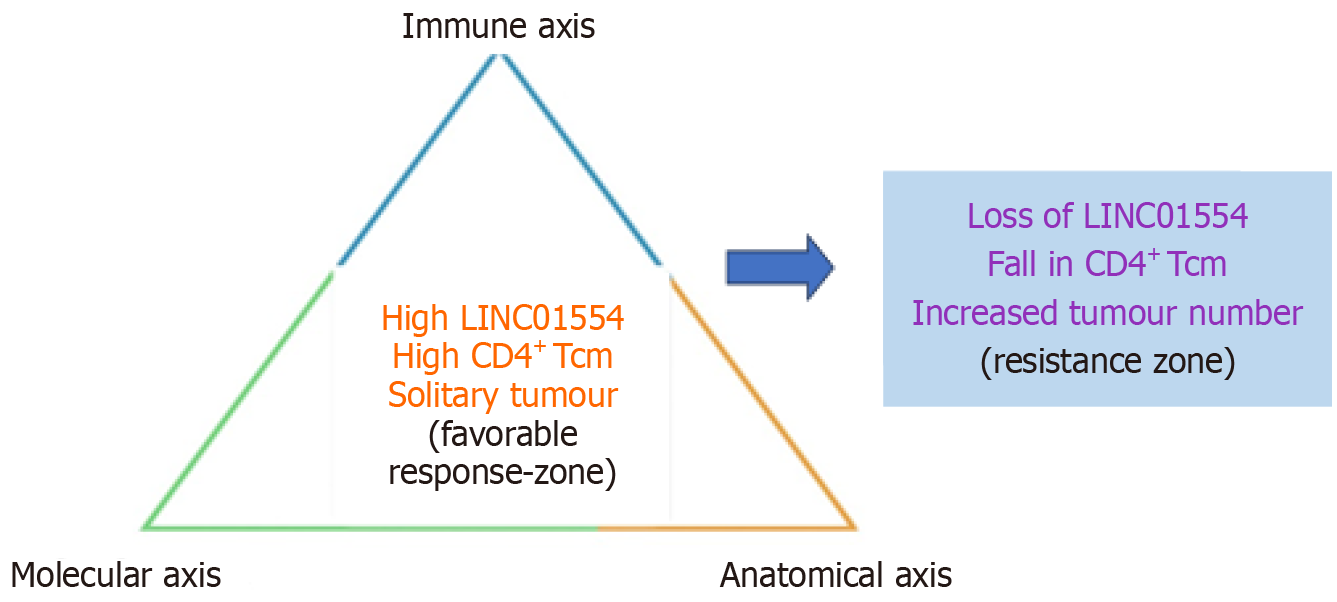
Figure 1 Tri-axial biomarker model for response to sintilimab plus lenvatinib in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
This schematic illustrates how molecular (LINC01554 expression), immune (CD4+ central memory T cell infiltration), and anatomical (tumour morphology) axes interact to define therapeutic outcomes. Tumours characterised by high LINC01554, high CD4+ memory T-cell, and solitary morphology cluster within a favourable response zone, whereas loss of these features such as reduced LINC01554 expression, declining CD4+ memory T-cell, or increased tumour number progressively shifts the disease toward a resistance zone, reflecting transition from biological sensitivity to refractoriness.
- Citation: Kashiv P, Saxena K, Balwani MR, Kute VB. Integrating molecular and immune biomarkers for precision therapy in hepatitis B: Associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2026; 18(2): 116475
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v18/i2/116475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.116475