Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2025; 17(9): 107631
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.107631
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.107631
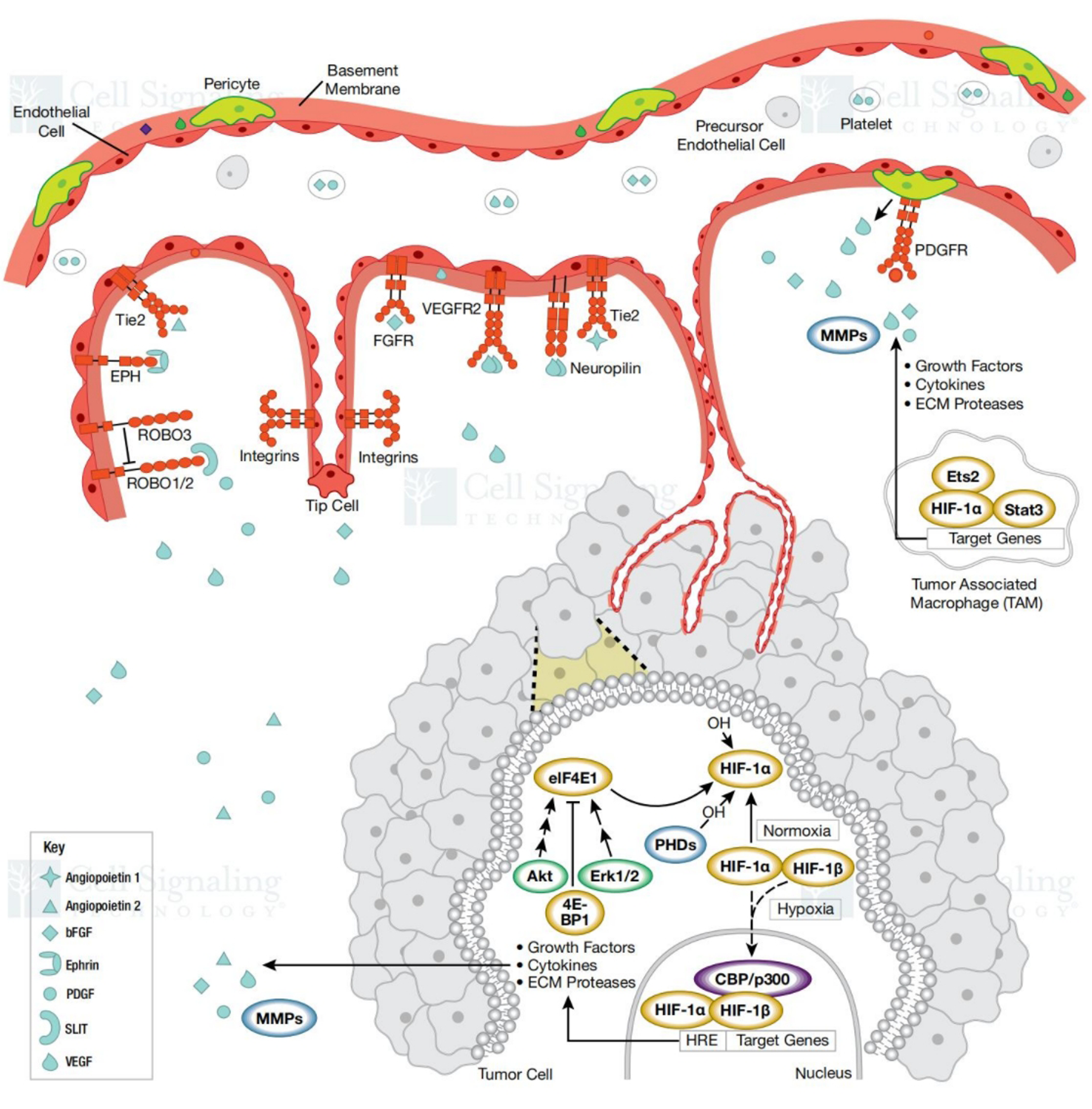
Figure 1 Mechanism of tumor angiogenesis.
Citation: Ilustration reproduced courtesy of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (www.cellsignal.com). The copyright license of Figure 1 is placed in the Supplementary material. Under tumor hypoxia, the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) dimer remains stable and activates multiple pro-angiogenic genes. This pathway stimulates tumor vascularization and progression through enhanced blood supply formation. Tie2: Tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and epidermal growth factor-like domains 2; EPH: Erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular; ROBO: Roundabout; FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; VEGFR2: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; Ets2: E26 transformation-specific 2; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1; Akt: Protein kinase B; Stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Erk: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; 4E-BP1: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; PHD: Prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein; CBP: CREB-binding protein; eIF4E1: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E1; HRE: Hypoxia-responsive element; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; SLIT: Slit guidance ligand; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
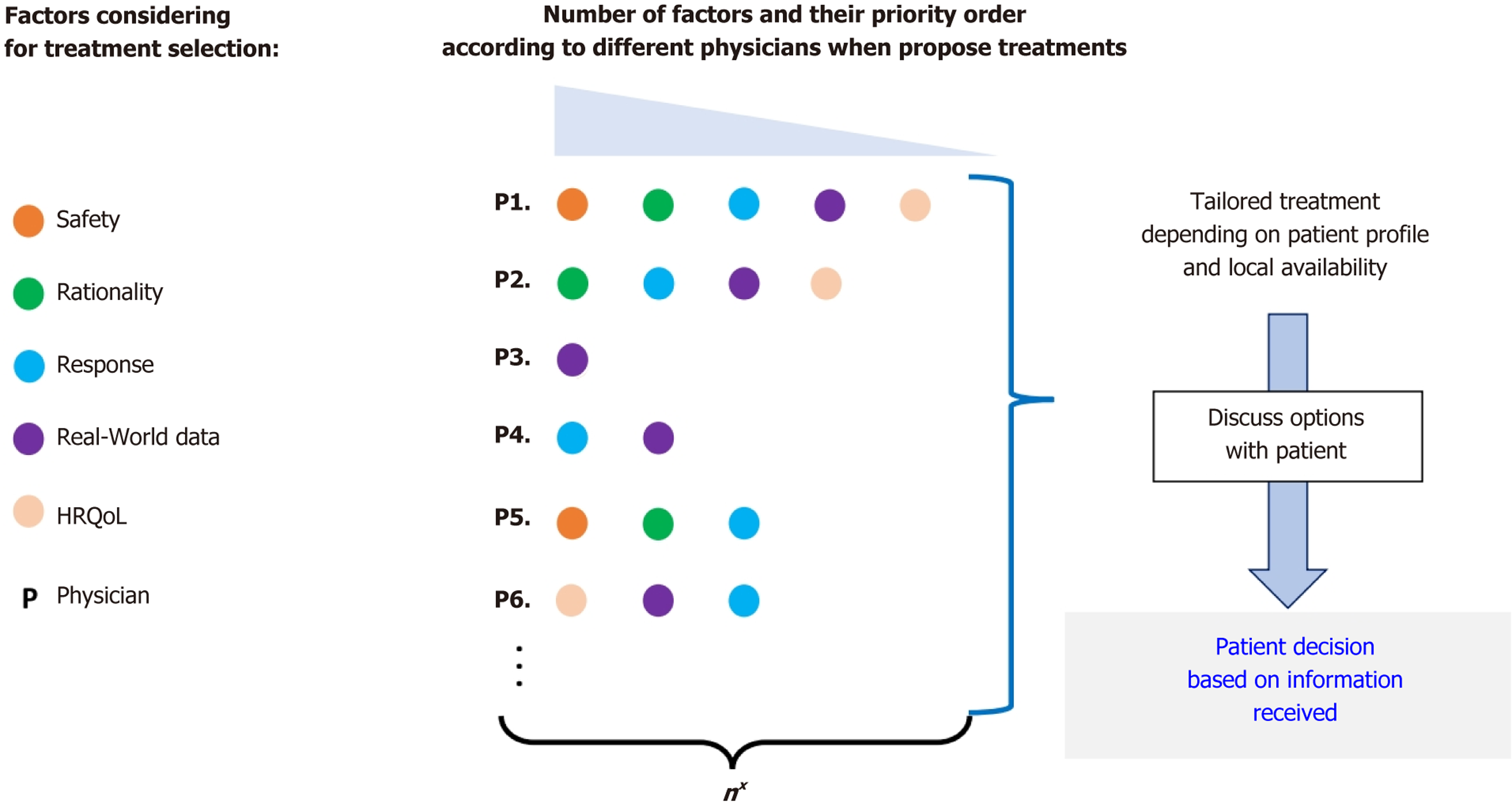
Figure 2 Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment options[30].
This schematic illustrates key clinical considerations influencing treatment selection and their relative prioritization among physicians. The left panel depicts decision factors (represented as spheres), with connecting lines indicating individual practitioners’ (P1, P2, ...Pn) priority sequences for hepatocellular carcinoma management. The bottom legend (nX) denotes the exponential growth of possible therapeutic combinations. The right panel demonstrates how final treatment plans emerge from integrated evaluations of clinical guidelines, patient-specific parameters, local resource availability, and health literacy considerations. Citation: Muñoz-Martínez S, Iserte G, Sanduzzi-Zamparelli M, Llarch N, Reig M. Current pharmacological treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2021; 60: 141-148. Copyright© The Authors 2025. Published by Elsevier Ltd. (https://s100.copyright.com/AppDispatchServlet?publisherName=ELS&contentID=S1471489221001028&orderBeanReset=true).
- Citation: Liu F, Zhang J, Li K. Postoperative adjuvant management in hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of therapeutic efficacy and prognostic outcomes. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(9): 107631
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i9/107631.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.107631