©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 107675
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.107675
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.107675
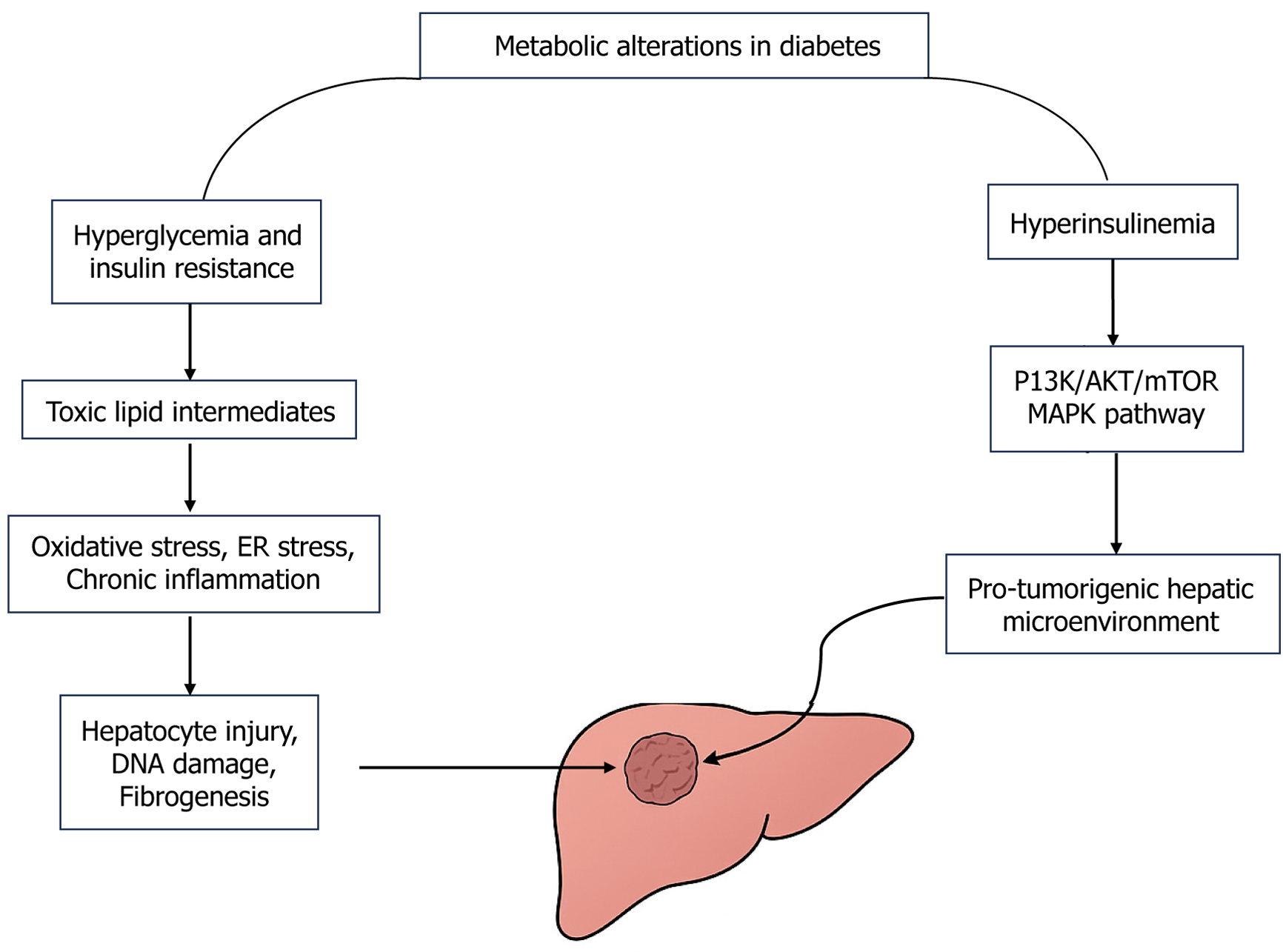
Figure 1 Metabolic alteration that leads to hepatocellular carcinoma.
PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Figure 2 Pathways relating diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Interleukin-6 from cancer-associated fibroblast leads to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) generation via signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway. The IGF-1 acts on liver cell by autocrine action. Hyperglycemia facilitates acetylation of β-catenin, promoting its nuclear entry and help to form lymphoid enhancer factor 1-β-catenin complexes, displacing transcription factor 7-like 2-corepressor complexes. Thereby Wnt gene transcription enhances. Acid-labile subunit binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and stabilizes it through deubiquitination. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma upregulates HMG-CoA synthase 2 that supress epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mutated p53 increases IGF-1 receptor expression. β-arrestin 2 translocates IGF-1 receptor to endoplasmic reticulum in hepatocellular carcinoma cell. IGF-1 interacts with sarco endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase which loads Ca into the ER and creates ER stress. Unfolded protein response sets in as an adaptive mechanism to restore ER homeostasis. Unfolded protein response facilitating cell survival. Activation of the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, leading to enhanced glycolysis. Mammalian target of rapamycin upregulates glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase which convert glucose-6-phosphate to 6 phosphogluconolactone. Pentose phosphate pathway results in DNA synthesis. Metformin activates adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase which inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin complex thereby inhibits cell anabolism and stimulatesglycogen synthase kinase 3 beta which inhibit glycolysis. IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; IL: Interleukin; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; GLUT: Glucose transporter; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; AMP: Adenosine monophosphate; PPP: Pentose phosphate pathway; SERCA2: Sarco endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; UPR: Unfolded protein response; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer factor; HMGCS2: HMG-CoA synthase 2; STAT3: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; G-6-P: Glucose-6-phosphate; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblast; IGFALS: Insulin-like growth factor acid labile subunit; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; TCF7 L2: Transcription factor 7-like 2.
- Citation: Giri S, Mukhuty A, Mondal SA, Sahoo J, Roy A, Kamalanathan S, Naik D. Link between type 2 diabetes mellitus and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(7): 107675
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i7/107675.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.107675