©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 100033
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.100033
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.100033
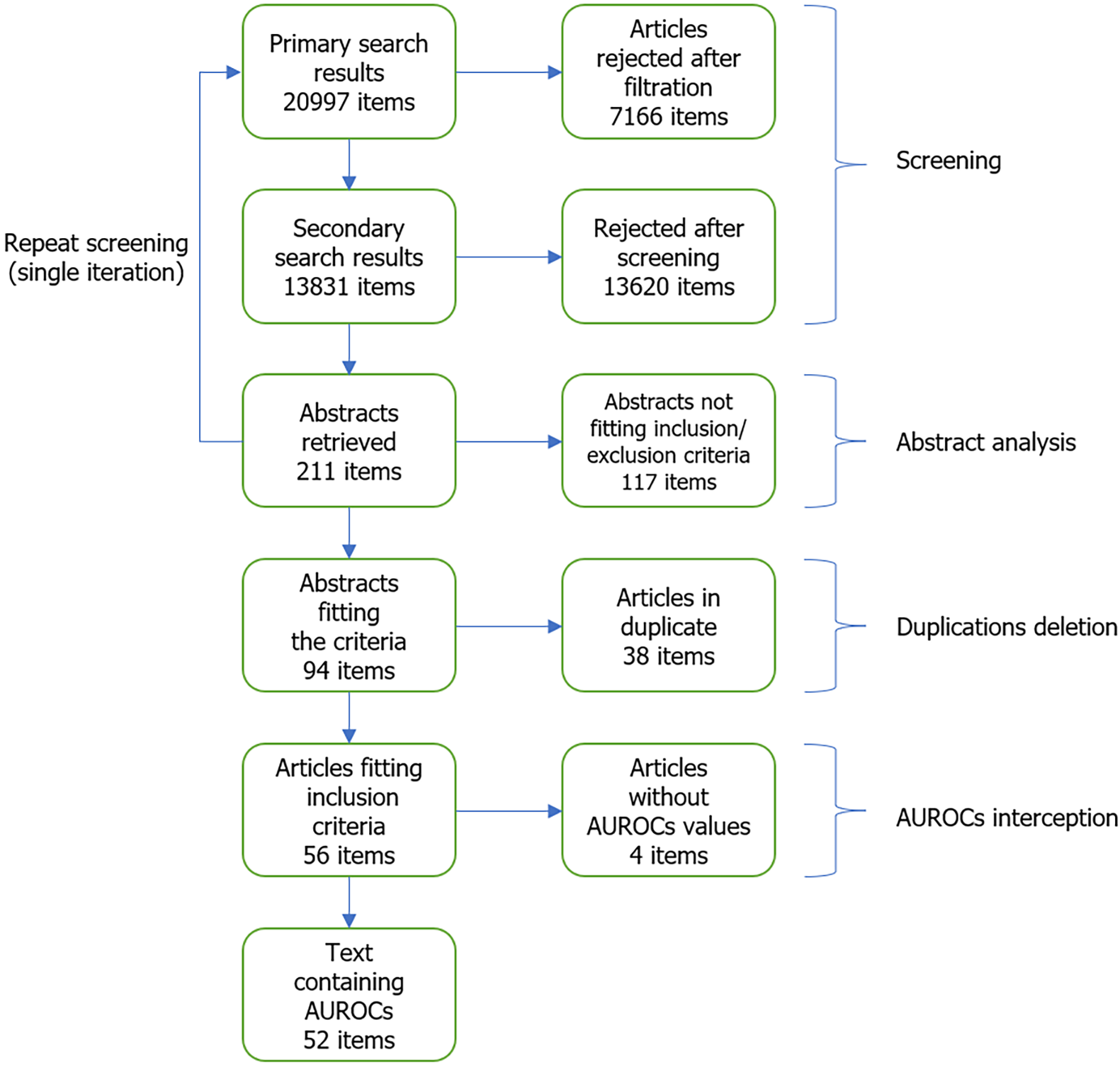
Figure 1 Flow diagram.
AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
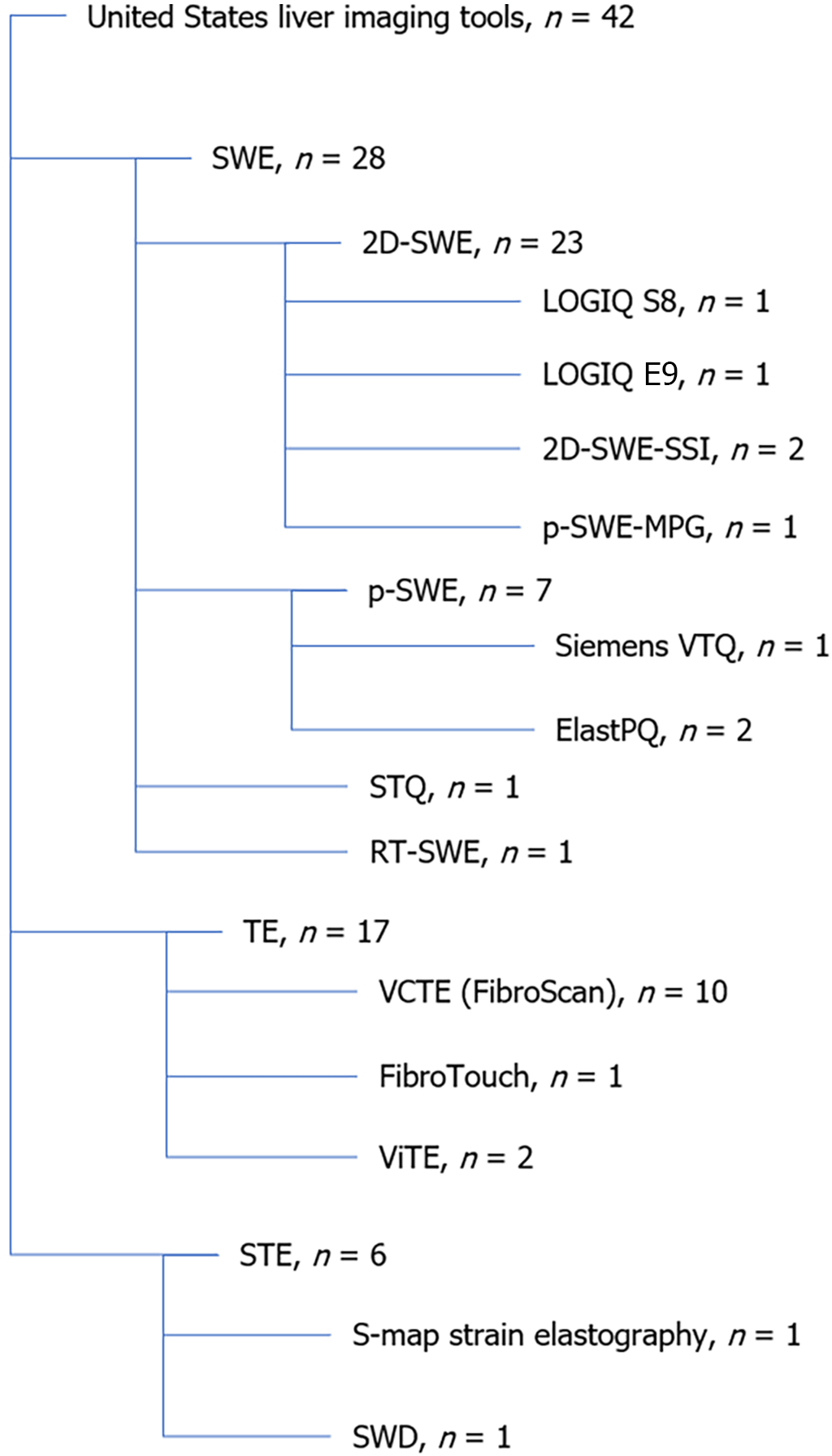
Figure 2 Ultrasound methods for liver fibrosis measurement.
SWE: Shear wave elastography; p-SWE: Point shear wave elastography; SSI: Supersonic imagine; MPG: Propagation map guidance; VTQ: Virtual TouchTM Quantification; STQ: Sound touch quantification; RT-SWE: Real-time shear wave elastography; TE: Transient elastography; VCTE: Vibration-controlled transient elastography; ViTE: Visual transient elastography; STE: Sound touch elastography; SWD: Shear wave dispersion.
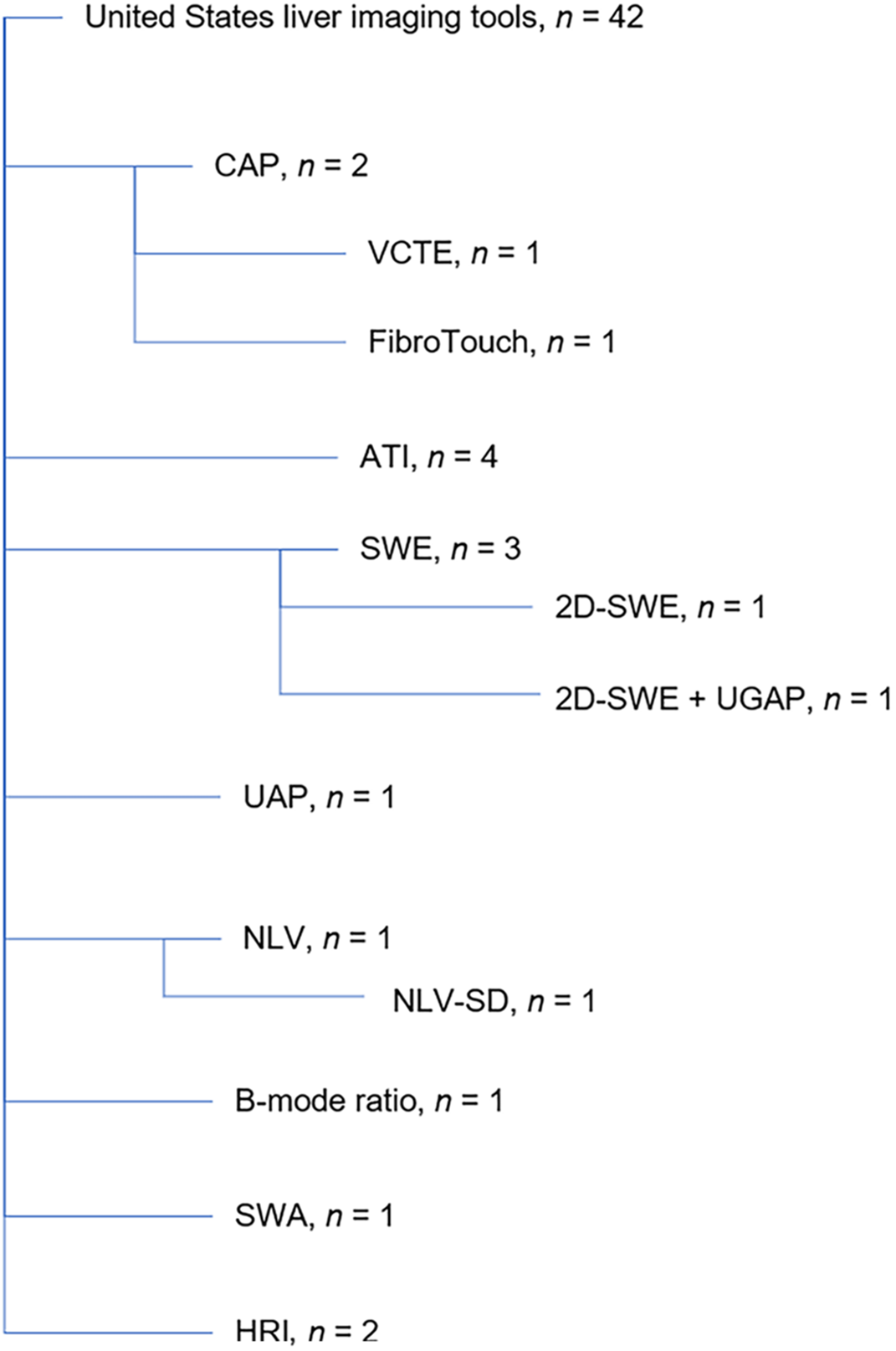
Figure 3 Ultrasound methods for liver fibrosis measurement.
CAP: Controlled attenuation parameter; SWE: Shear wave elastography; VCTE: Vibration-controlled transient elastography; ATI: Attenuation imaging; UGAP: Ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter; UAP: Ultrasound attenuation parameter; NLV: Normalized local variance; NLV-SD: Standard deviation of normalized local variance; SWA: Shear wave attenuation; HRI: Hepatic steatosis or fibrosis-related index.
- Citation: Pozowski P, Bilski M, Bedrylo M, Sitny P, Zaleska-Dorobisz U. Modern ultrasound techniques for diagnosing liver steatosis and fibrosis: A systematic review with a focus on biopsy comparison. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 100033
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/100033.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.100033