©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 113660
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113660
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113660
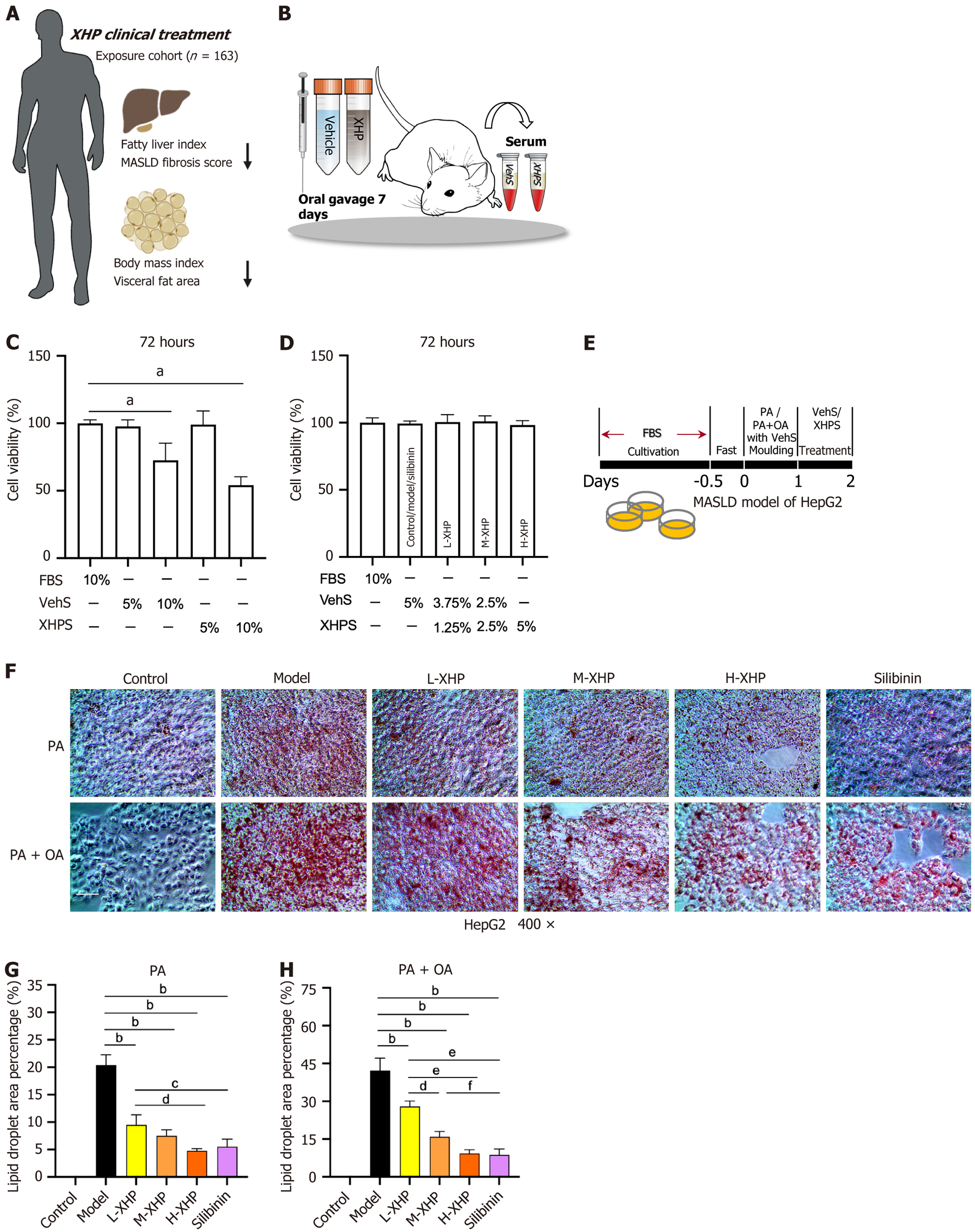
Figure 1 Xietu Hemu prescription inhibits metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-associated lipid accumulation in vivo and in vitro.
A: Xietu Hemu prescription (XHP) clinical treatment inhibits lipid accumulation of the liver and visceral adipose tissue; B: Flow chart of the preparation of XHP-containing serum (XHPS); C and D: Cell activity assay after intervention with different concentrations of XHPS (n = 3); E: Schematic diagram of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease model construction with the HepG2 cell line by XHPS intervention; F-H: Oil red O staining of HepG2 cells after XHPS intervention with different concentrations and statistics of differences in lipid droplet area occupation (n = 3). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. 400 ×, 25 μm. aP < 0.001 vs control; bP < 0.001 vs model; cP < 0.05 vs low dose of XHP (L-XHP); dP < 0.01 vs L-XHP; eP < 0.001 vs L-XHP; fP < 0.05 vs medium dose of XHP. XHP: Xietu Hemu prescription; XHPS: Xietu Hemu prescription-containing serum; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; L-XHP: Low dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; M-XHP: Medium dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; H-XHP: High dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; VehS: Vehicle serum; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; PA: Palmitic acid; OA: Oleic acid.
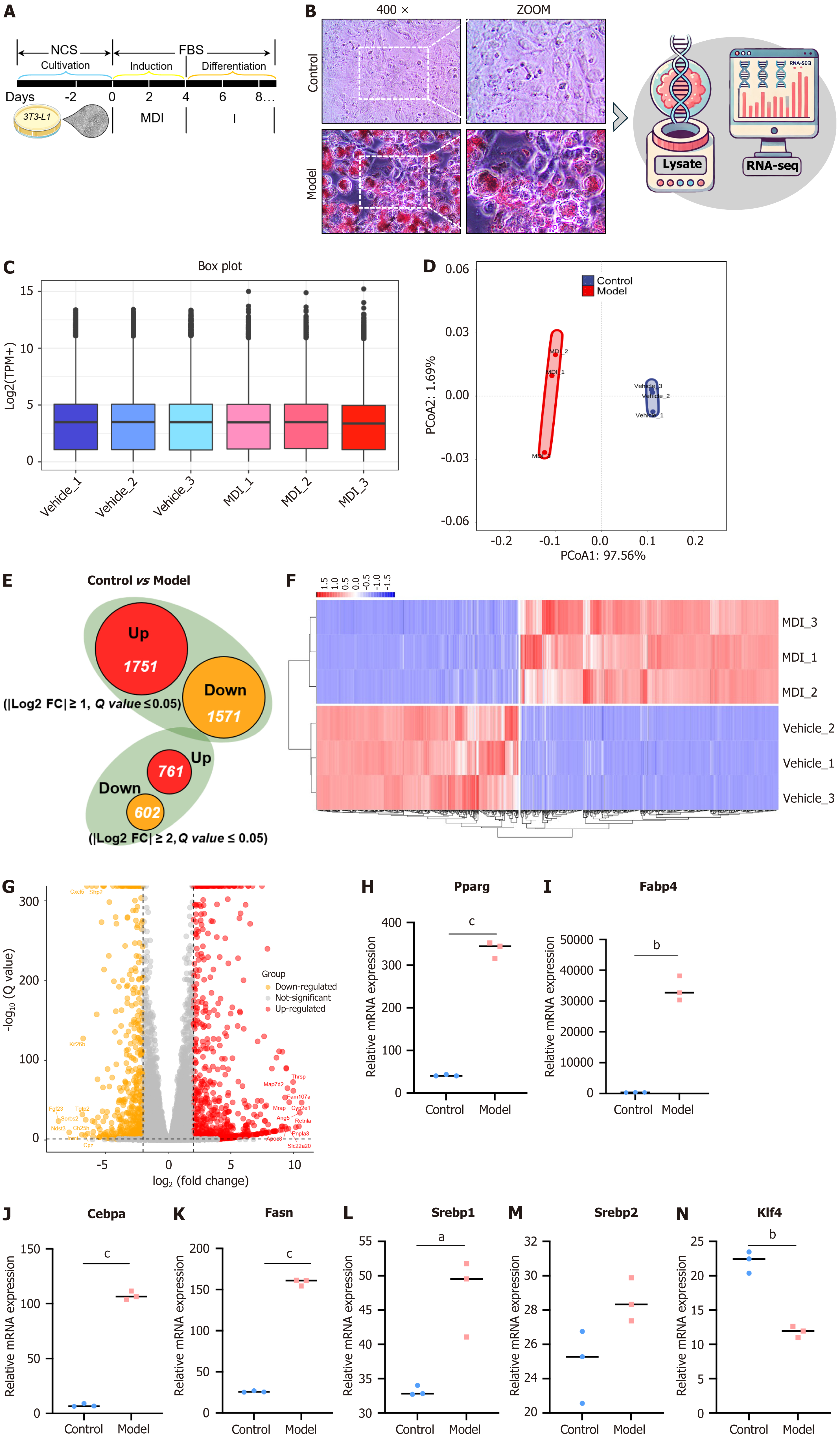
Figure 2 RNA sequencing analysis of the differences in 3T3-L1 cell differentiation.
A: Schematic diagram of 3T3-L1 cell culture and differentiation process; B: Oil red O staining images in the control group vs model group on day 6; C: Box plot of gene expression of samples (n = 3); D: Principal coordinate analysis plot of gene expression of samples (n = 3); E: The number of up-regulated or down-regulated differential genes between control and model groups (n = 3); F and G: Heatmap (F) and volcano plot (G) of differential gene expression for genes demonstrating significant differences based on the screening criteria of |Log2FC| ≥ 2 and q value ≤ 0.05 (n = 3); H-N: Comparison expression of key genes for lipid droplet accumulation and differentiation in control and model groups. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. 400 ×, 25 μm. aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.005 vs control; cP < 0.001 vs control. PCoA: Principal coordinate analysis; NCS: Newborn calf serum; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; MDI: 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, dexamethasone, and insulin; TPM: Transcripts per million.
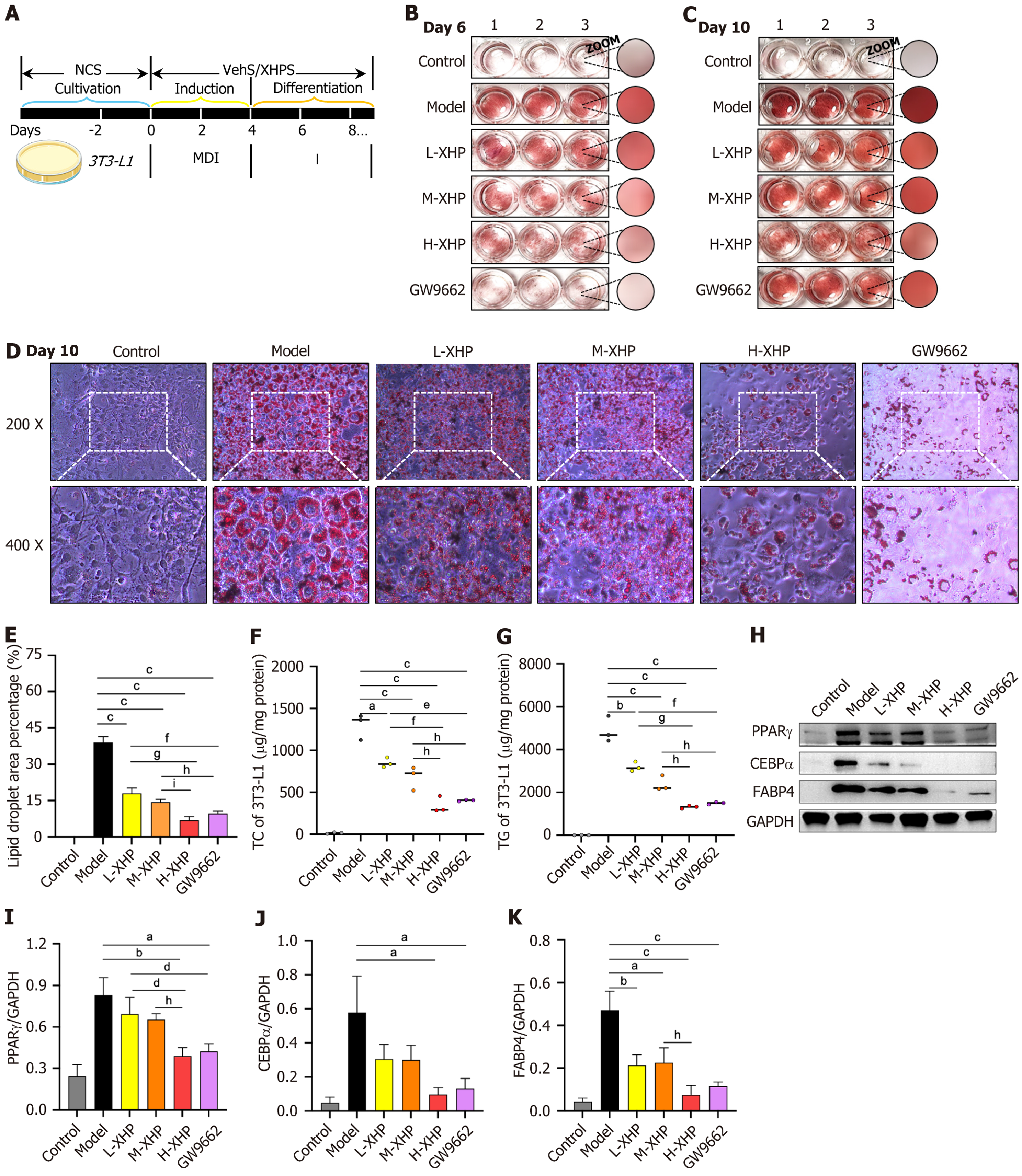
Figure 3 Xietu Hemu prescription restrains lipid synthesis during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells.
A: Schematic diagram of the differentiation process of 3T3-L1 cells by Xietu Hemu prescription (XHP)-containing serum intervention; B and C: Photos of oil red O staining of 3T3-L1 cell differentiation on day 6 and 10; D and E: Oil red O staining micro camera and statistics of difference in lipid droplet area occupation on day 10; F and G: Detection of intracellular lipid levels on day 10 (n = 3); H-K: Detection and quantitative statistics of intracellular lipid synthesis-related protein levels on day 10 (n = 3). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. 200 ×, 50 μm; 400 ×, 25μm. aP < 0.01 vs model; bP < 0.005 vs model; cP < 0.001 vs model; dP < 0.05 vs low dose of XHP (L-XHP); eP < 0.01 vs L-XHP; fP < 0.005 vs L-XHP; gP < 0.001 vs L-XHP; hP < 0.05 vs medium dose of XHP (M-XHP); iP < 0.005 vs M-XHP. XHPS: Xietu Hemu prescription-containing serum; L-XHP: Low dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; M-XHP: Medium dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; H-XHP: High dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; VehS: Vehicle serum; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride.
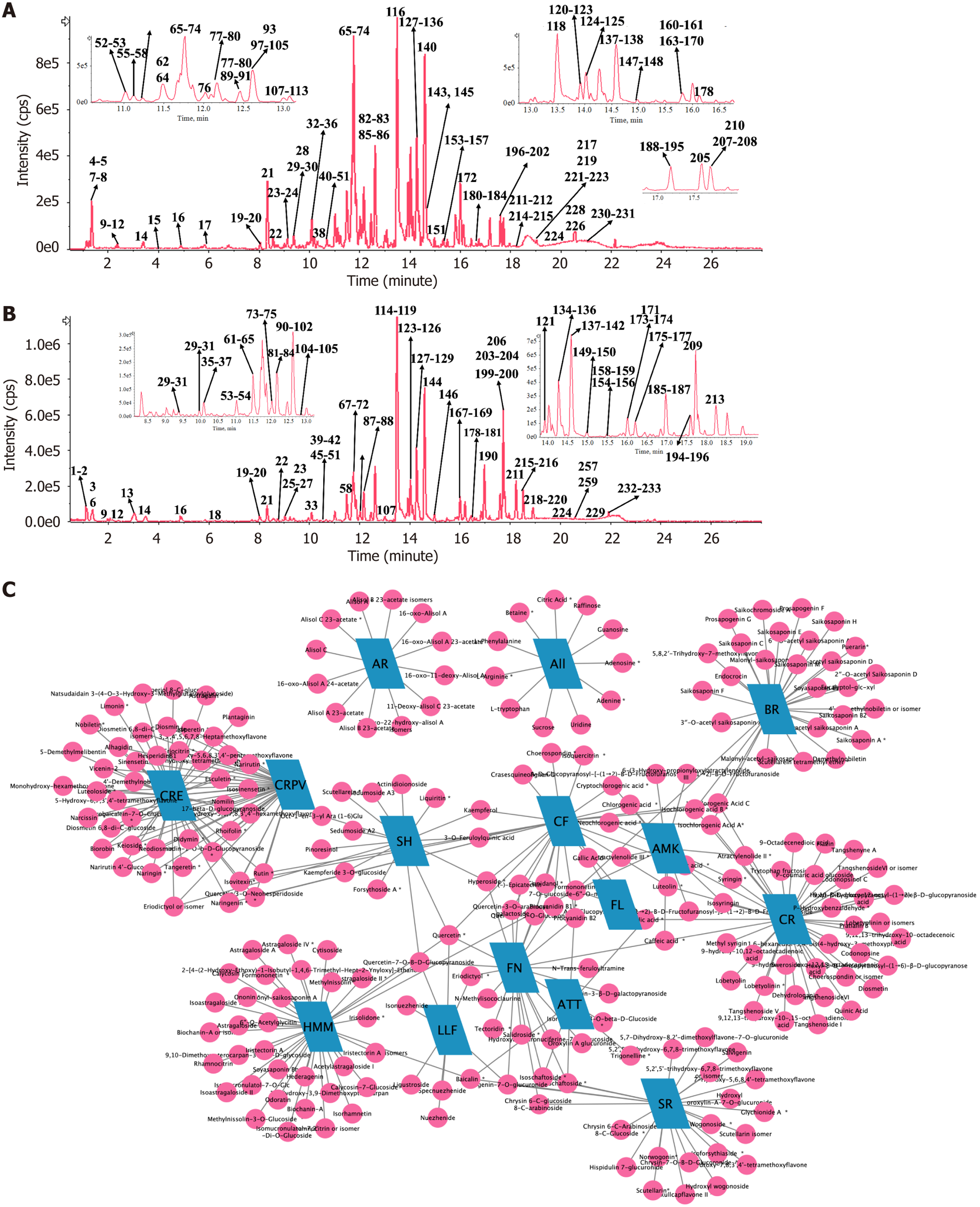
Figure 4 Xietu Hemu prescription component identification.
A and B: Ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time of flight mass analyzer-tandem mass spectrometry of Xietu Hemu prescription (XHP); C: The relationship of metabolites and botanical drugs of XHP.
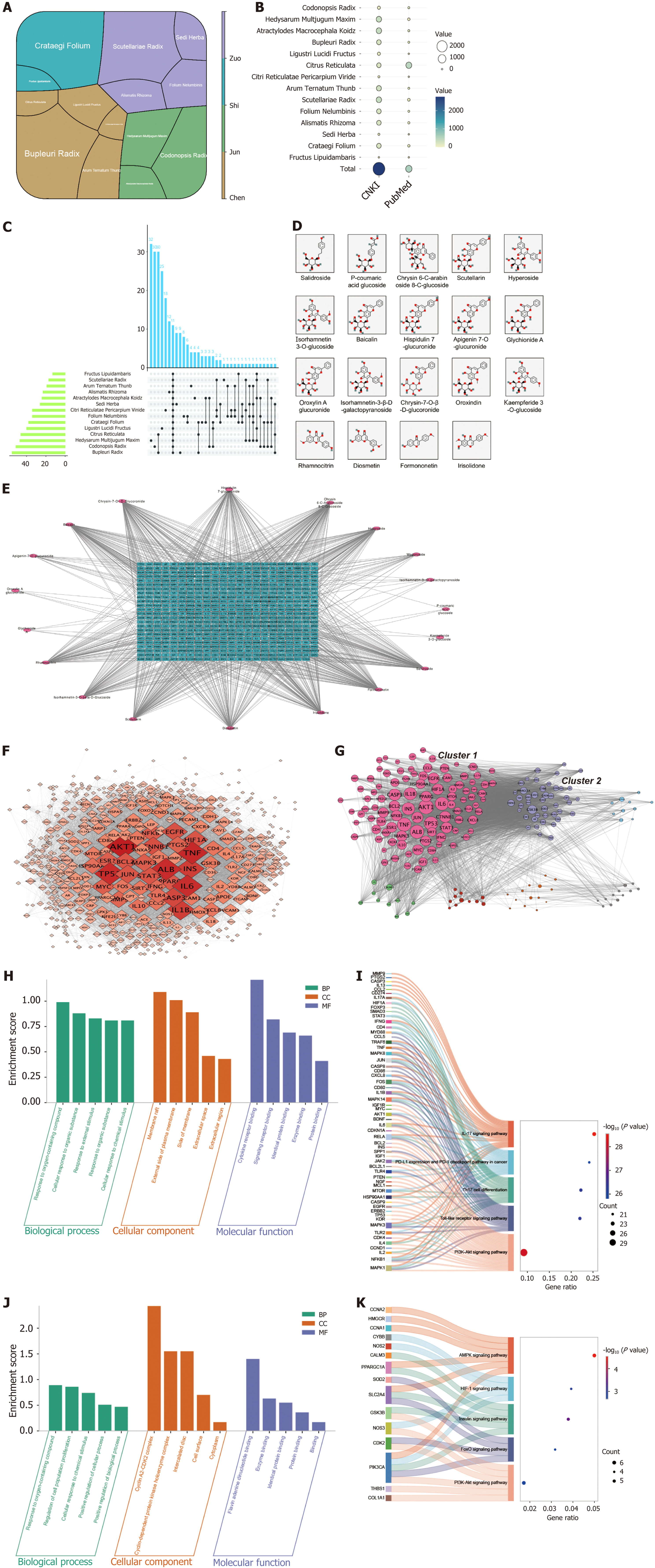
Figure 5 The correlation assessment of Xietu Hemu prescription and obesity.
A: Composition of Xietu Hemu prescription (XHP) by “JUN-CHEN-ZUO-SHI”; B: The strength of the correlation between each XHP botanical drug with obesity was obtained from the literature search; C: Number of exclusive metabolites or overlap metabolites of each botanical drug in XHP; D: The structure of representative metabolites in XHP serum; E: Network of XHP serum metabolites with related targets; F: Protein-protein interaction network of the targets in E; G: Model decomposition of F into 7 sub-networks; H-K: Functional analysis of the sub-networks. H and I are the Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of cluster 1, while J and K are the KEGG pathway and GO enrichment analyses of cluster 2. XHP: BP: Biological processes; CC: Cellular components; MF: Molecular functions.
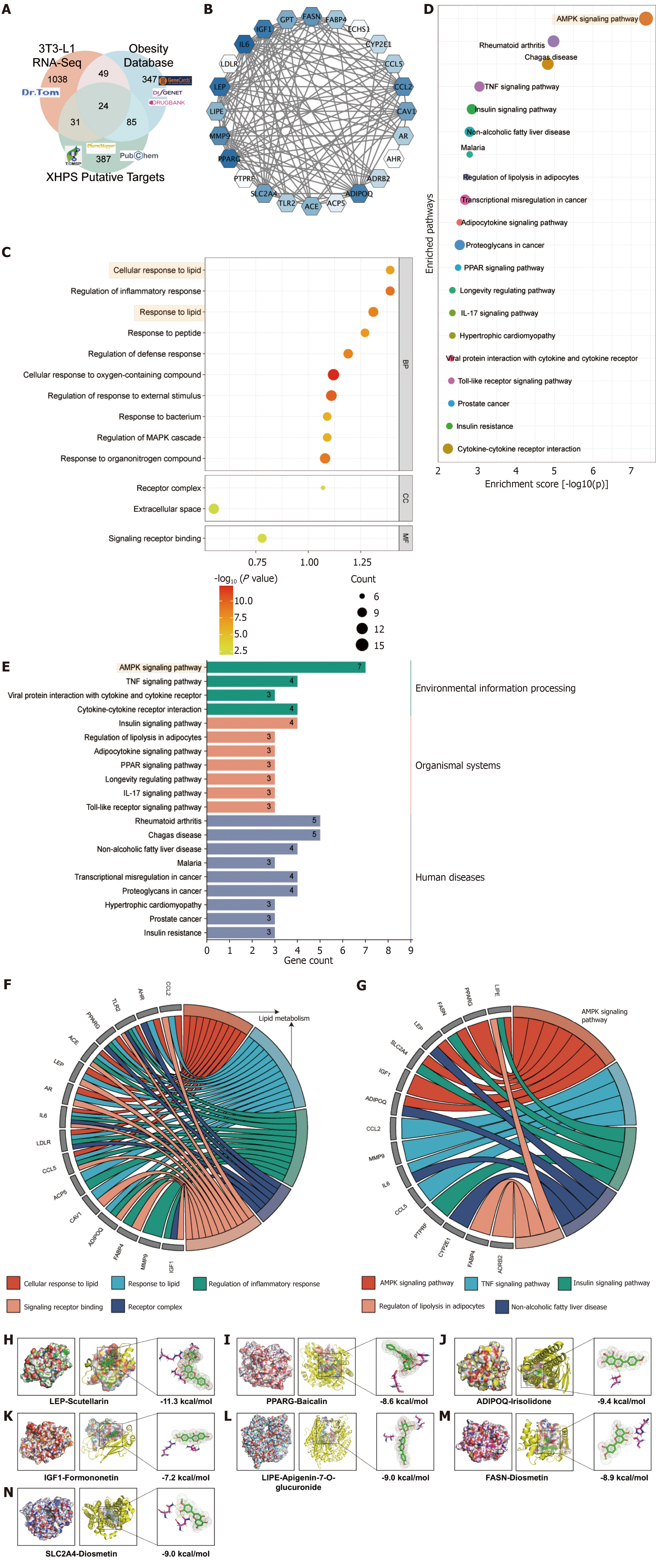
Figure 6 Mechanism prediction of Xietu Hemu prescription therapy in obesity hints leptin is the hub-target and the adenosine mono
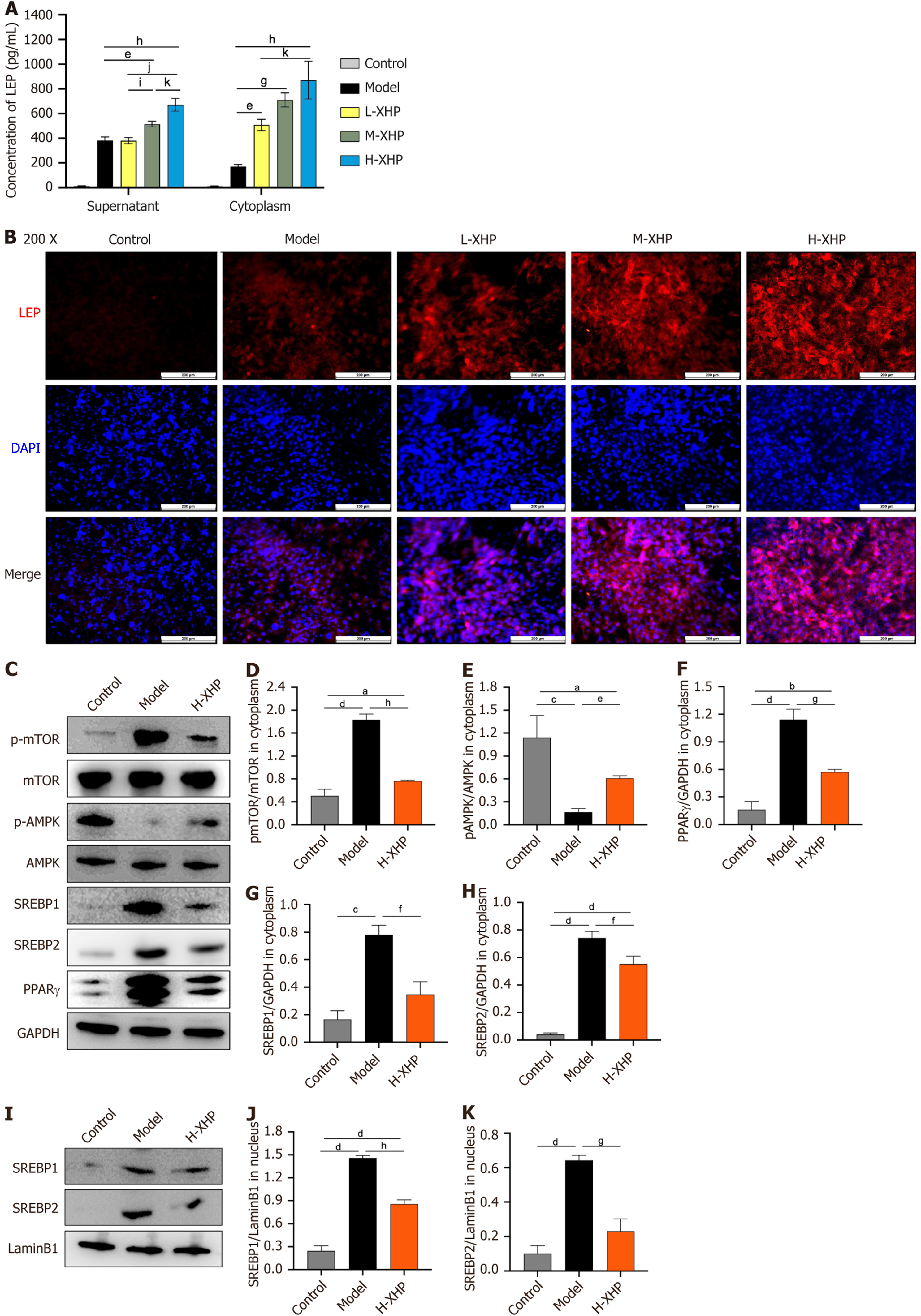
Figure 7 Xietu Hemu prescription inhibits lipid synthesis of mature 3T3-L1 cells through the leptin signal axis at the protein level of the nucleus and cytoplasm.
A: Secretion levels of leptin (LEP) at different time points during high dose of Xietu Hemu prescription (XHP) intervention in 3T3-L1 cell differentiation; B: Immunofluorescence assay for protein expression of LEP after 10 days of XHP intervention in 3T3-L1 cell differentiation at different concentrations; C-H: Detection and quantitative statistics of cytoplasm protein levels on day 10 (n = 3); I-K: Detection and quantitative statistics of nucleus protein levels on day 10 (n = 3). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. 200 ×, 50 μm; 400 ×, 25 μm; aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.005 vs control; dP < 0.001 vs control; eP < 0.05 vs model; fP < 0.01 vs model; gP < 0.005 vs model; hP < 0.001 vs model; iP < 0.05 vs low dose of XHP (L-XHP); jP < 0.001 vs L-XHP; kP < 0.001 vs medium dose of XHP. L-XHP: Low dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; M-XHP: Medium dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; H-XHP: High dose of Xietu Hemu prescription; LEP: Leptin.
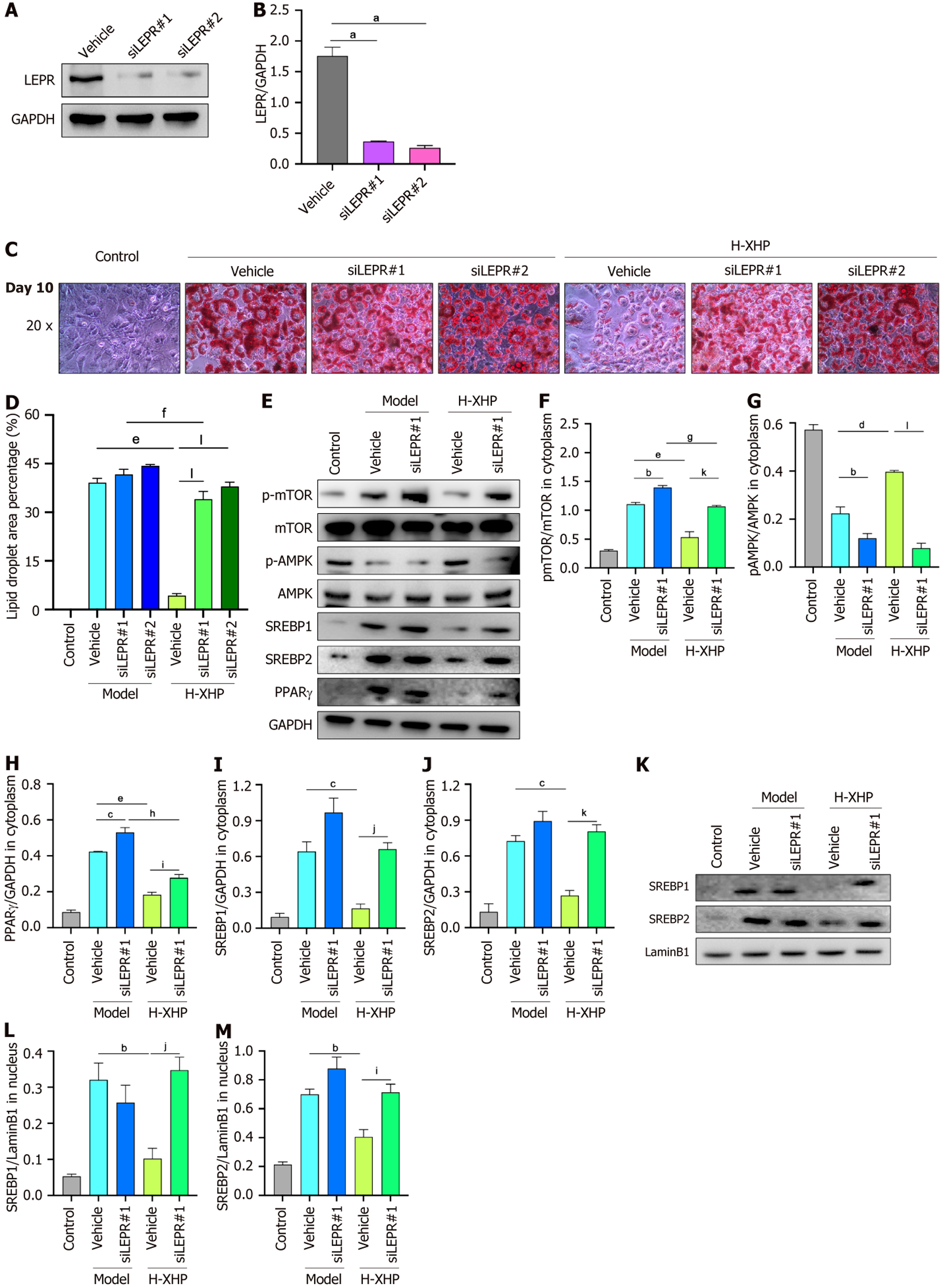
Figure 8 Inhibition of lipid synthesis by Xietu Hemu prescription following siRNA disruption of leptin receptor in 3T3-L1 cells.
A and B: SiRNA disruption of 3T3-L1 cell LEPR efficiency test; C and D: Oil red O staining micro camera and statistics of difference in lipid droplet area occupation on day 10 with/without high dose of Xietu Hemu prescription (H-XHP) or siLEPR intervention; E-J: Detection and quantitative statistics of cytoplasm protein levels on day 10 with/without H-XHP or siLEPR intervention (n = 3); K-M: Detection and quantitative statistics of nucleus protein levels on day 10 with/without H-XHP or siLEPR intervention (n = 3). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. 200 ×, 50 μm; 400 ×, 25 μm; aP < 0.05 vs vehicle; bP < 0.05 vs model-vehicle; cP < 0.01 vs model-vehicle; dP < 0.005 vs model-vehicle; eP < 0.001 vs model-vehicle; fP < 0.05 vs model-siLEPR1; gP < 0.01 vs model-siLEPR1;hP < 0.001 vs model-siLEPR1; iP < 0.05 vs high dose of Xietu Hemu prescription (H-XHP)-vehicle; jP < 0.01 vs H-XHP-vehicle; kP < 0.005 vs H-XHP-vehicle; lP < 0.001 vs H-XHP-vehicle. H-XHP: High dose of Xietu Hemu prescription.
- Citation: Cheng Z, Lu YF, He YX, Wei W, Xie YX, Lv TS, Wei Y, Lou Y, Yu JY, Zhou XQ. Integrated serum metabolomics reveal molecular mechanism of Xietu Hemu prescription on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-related obesity. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(12): 113660
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i12/113660.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113660