©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2025; 17(11): 109051
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i11.109051
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i11.109051
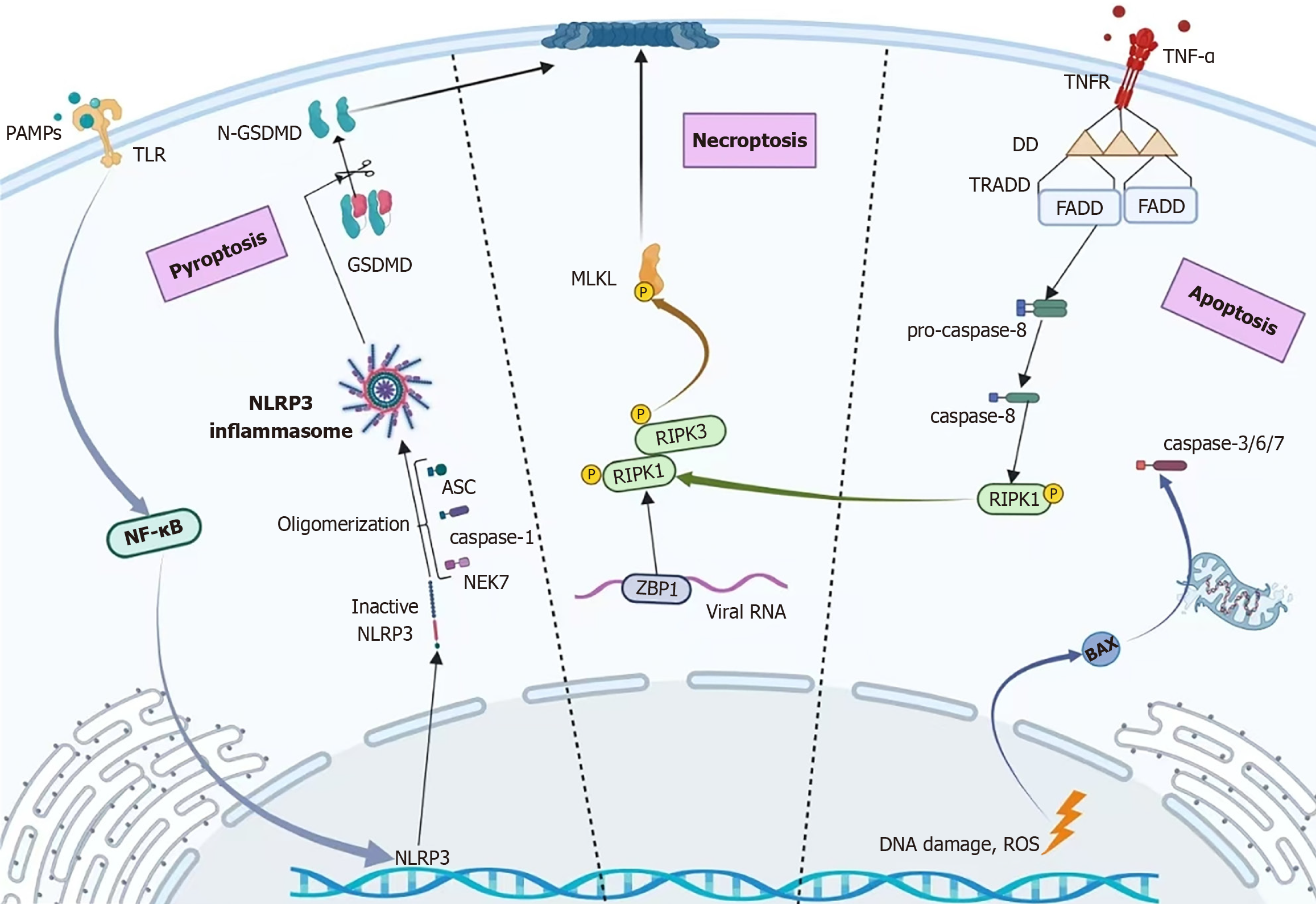
Figure 1 Molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis, necroptosis, and apoptosis.
ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; BAX: Bcl-2 associated X protein; DD: Death domain; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain; GSDMD: Gasdermin D; N-GSDMD: N-terminal fragment of gasdermin D; MLKL: Mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase; NEK7: Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 7; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; RIPK1: Receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 1; RIPK3: Receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 3; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRADD: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein.
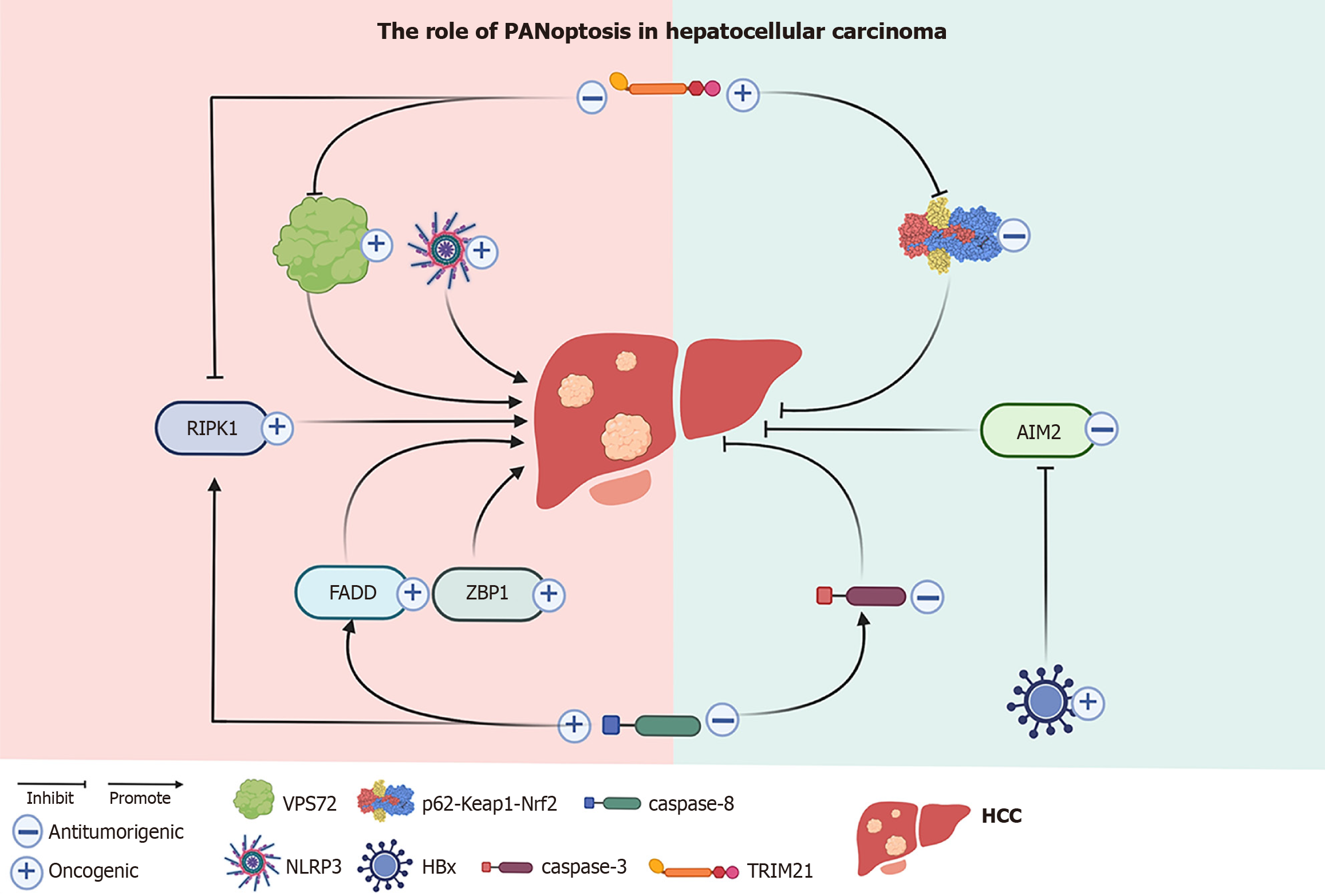
Figure 2 Role of PANoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mechanisms of PANoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Factors that inhibit the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) process are covered in green, like hepatitis B virus X (HBx) protein. Factors that can promote the HCC process are covered in red. Triple motif protein 21 (TRIM21) and caspase-8 exhibit both positive and negative regulatory mechanisms in HCC. Through positive regulation, TRIM21 can inhibit tumor suppression by inhibiting the p62 sequestosome 1-kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (p62-Keap1-Nrf2) antioxidant pathway. In contrast, its negative regulation involves two inhibitory pathways, receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 1 and vacuolar protein sorting 72 (VPS72), which suppress HCC progression. Caspase-8, while enhancing the tumor-suppressive activity of caspase-3, can also promote HCC development through interactions with Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) and receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 1 (RIPK1). AIM2: Absent in melanoma 2; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; ZBP1: Z-DNA binding protein 1.
- Citation: Li MJ, Wen CL, Cheng HT, Lyu HN, Han YY. PANoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Underlying mechanisms. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(11): 109051
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i11/109051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i11.109051