©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2024; 16(9): 1278-1288
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1278
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1278
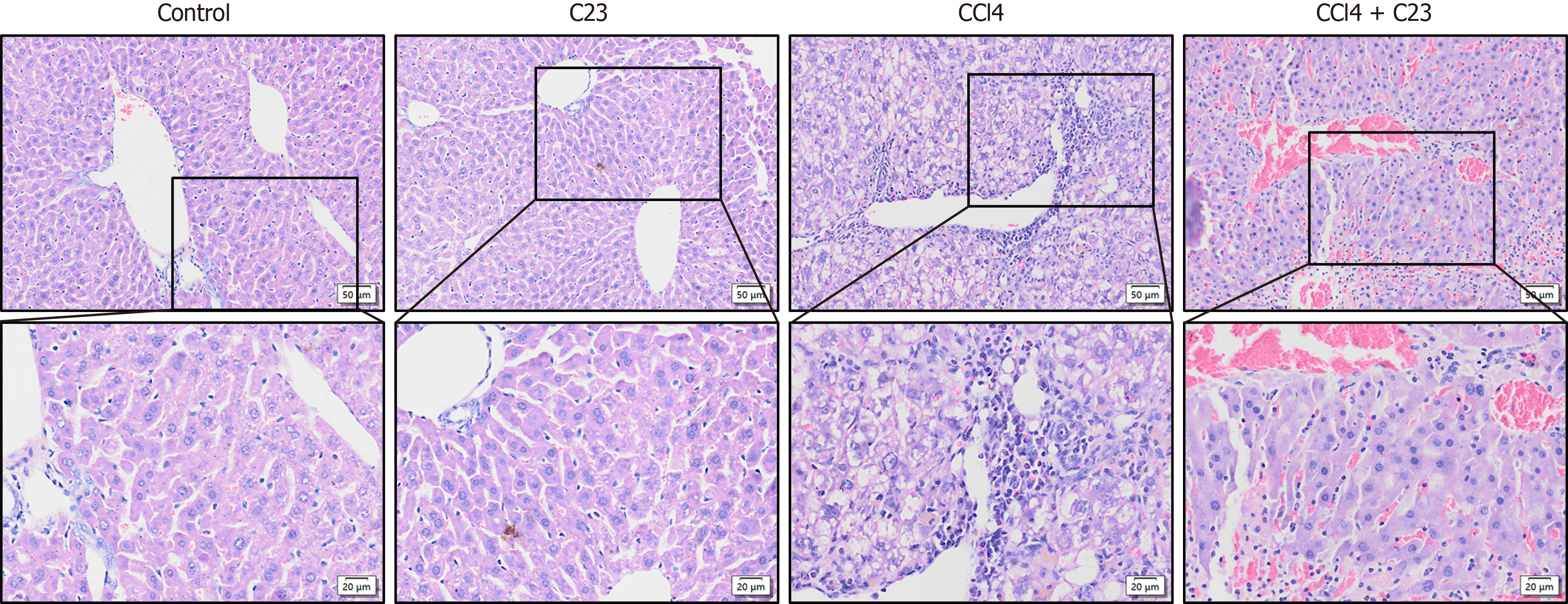
Figure 1 C23 inhibits carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and hepatocyte inflammation.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used to examine the effects of C23 on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and liver inflammation. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride.
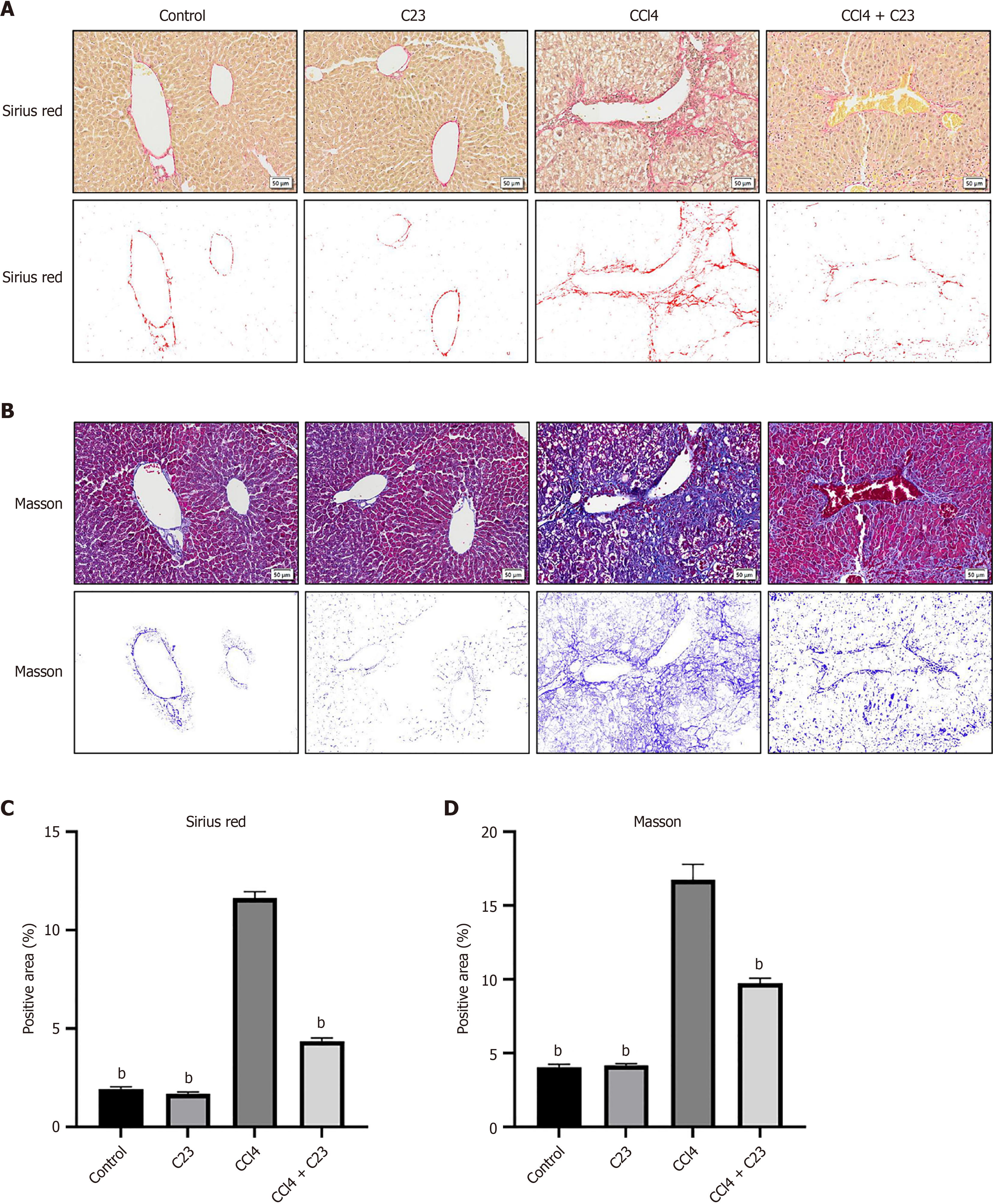
Figure 2 C23 inhibits carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic collagen synthesis.
A: Sirius red staining was used to examine changes in collagen fiber expression in each group; B: Masson staining was used to examine changes in collagen fiber expression in each group. The location of the collagen fibers was visualized with image-pro plus (IPP); C: The IPP concentration was used to calculate the Sirius red-positive area of each group; D: The IPP concentration was used to calculate the Masson positive area of each group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs carbon tetrachloride. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride.
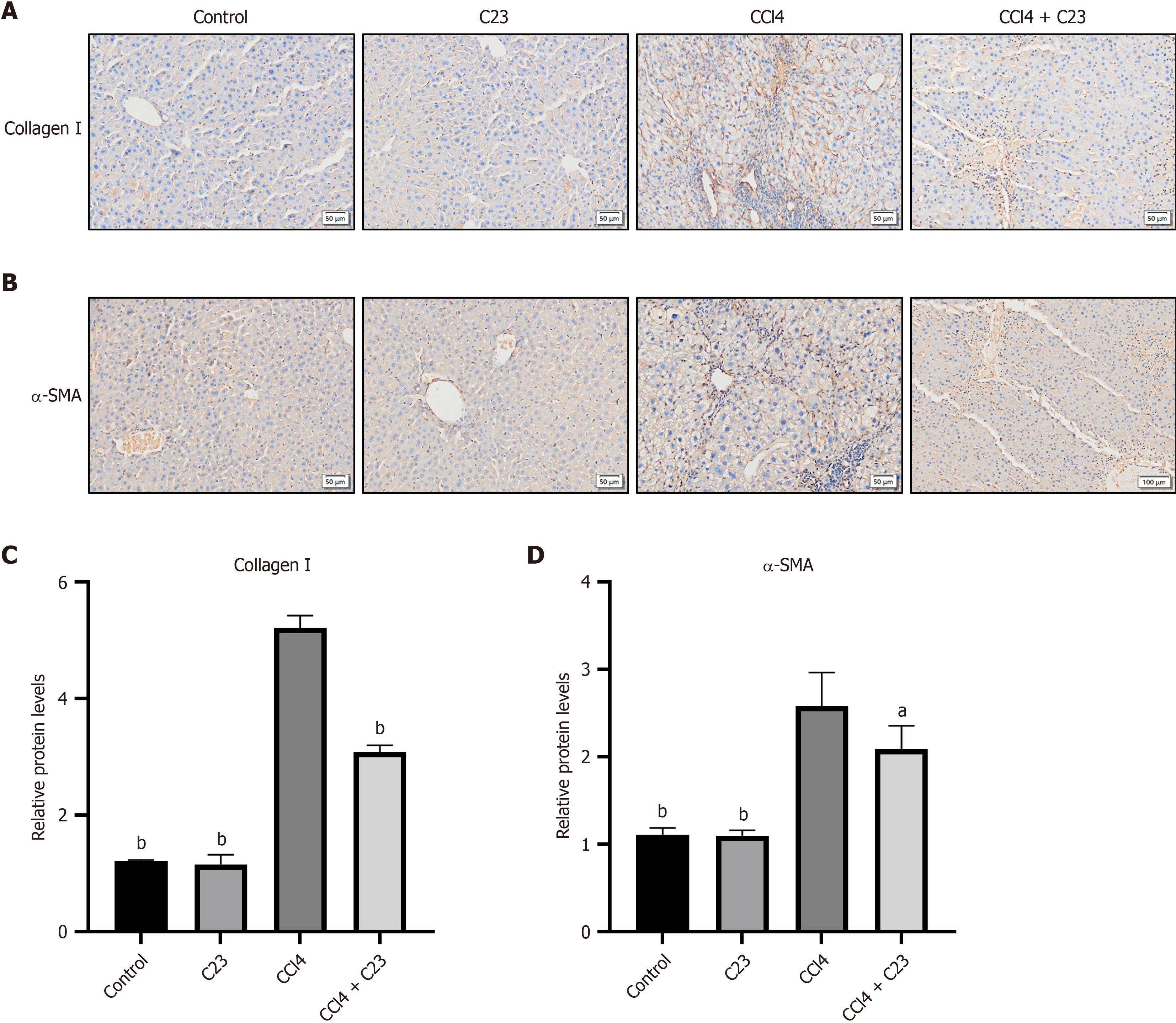
Figure 3 C23 inhibited the activation of hepatic stellate cells induced by carbon tetrachloride.
A: The generation and localization of collagen I in the liver were analyzed using immunohistochemistry (IHC); B: The generation and localization of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in the liver were analyzed using IHC; C: The expression ratio of collagen I in each group was determined with image-pro plus (IPP); D: The expression ratio of α-SMA in each group was determined with IPP. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs carbon tetrachloride. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
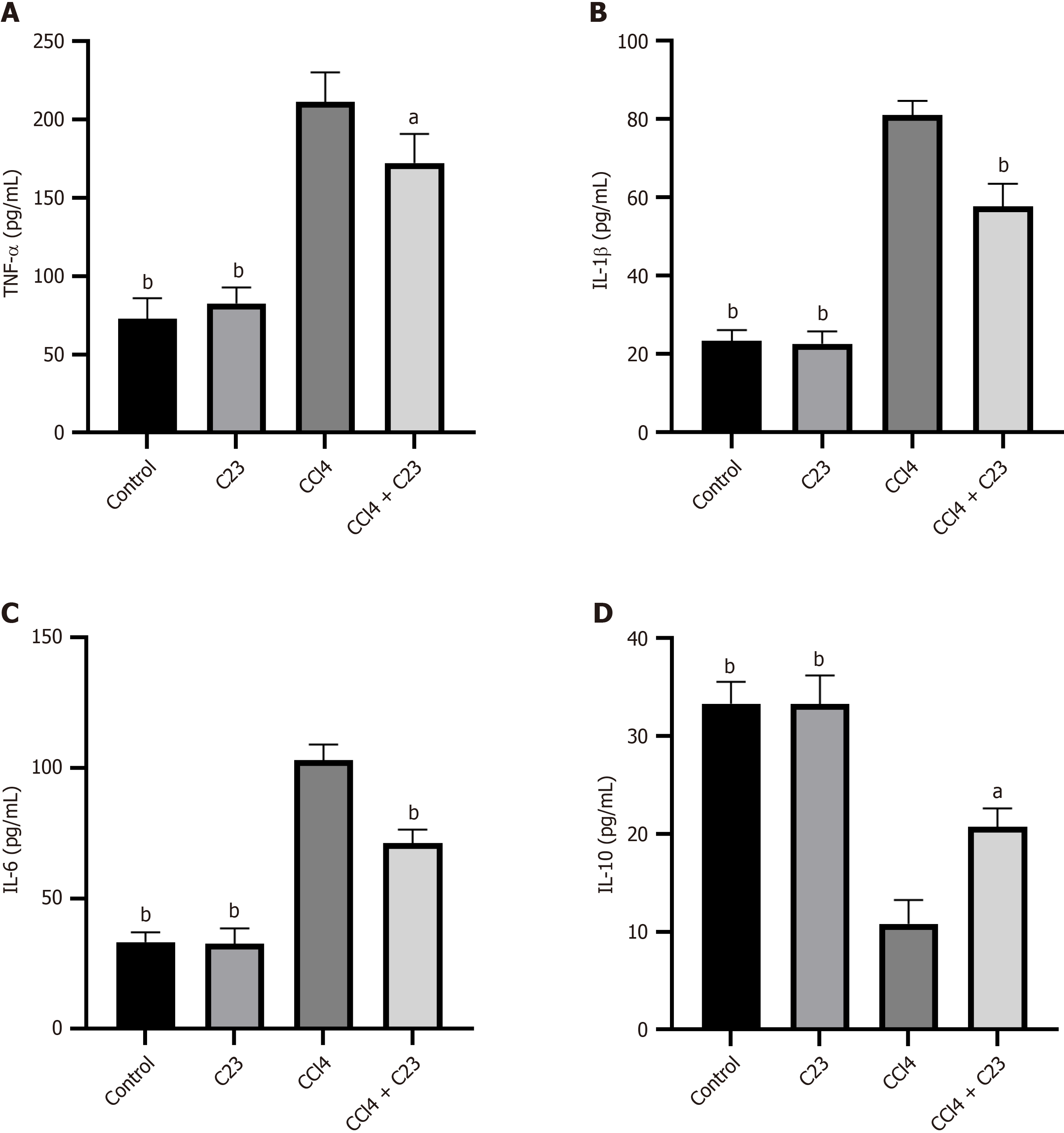
Figure 4 C23 inhibits carbon tetrachloride-induced liver inflammation.
A: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to examine changes in the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha in the liver; B: ELISA was used to examine changes in the expression of IL (interleukin)-1β in the liver; C: ELISA was used to examine changes in the expression of IL-6 in the liver; D: ELISA was used to examine changes in the expression of IL-10 in the liver. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs carbon tetrachloride. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin.
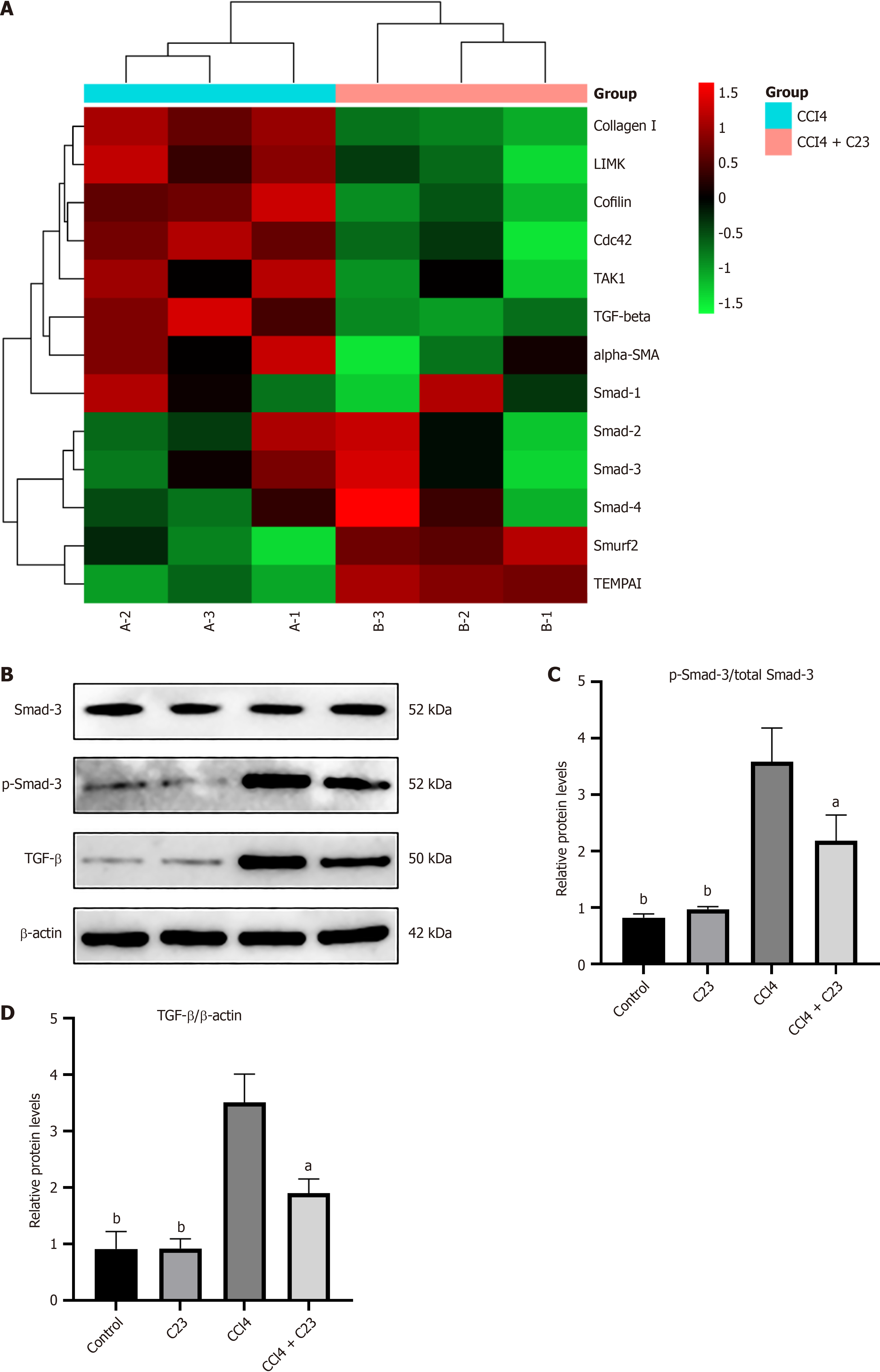
Figure 5 C23 inhibits transforming growth factor beta/Smad3 activation in the fibrotic pathway.
A: Heatmap of the transcriptome array comparing the expression of genes involved in the regulation of fibrosis function between carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-treated and CCl4+C23-treated mouse livers harvested 30 days after the procedure, n = 3; B: Western blotting was used to examine changes in the expression of factors involved in the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)/Smad3 signaling pathway during liver fibrosis. β-Actin was used as an internal reference protein; C: The gray value was calculated for p-Smad-3/Smad-3; D: The gray value was calculated for TGF-β/β-actin. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs carbon tetrachloride. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta.
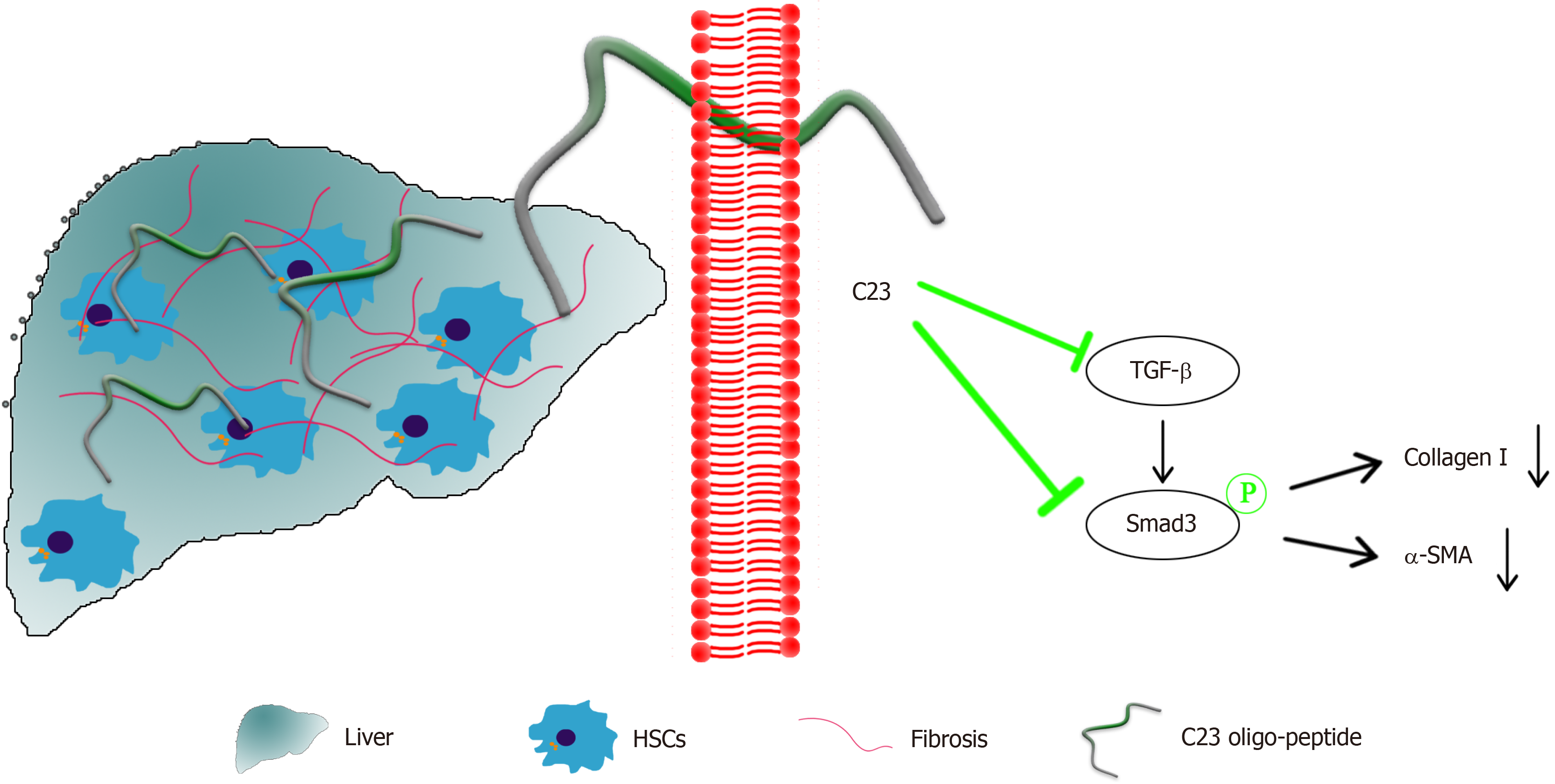
Figure 6 C23 ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice.
CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; HSCs: Hematopoietic stellate cells; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
- Citation: Tang RX, Xie XJ, Xiong Y, Li S, Luo C, Wang YG. C23 ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(9): 1278-1288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i9/1278.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1278