©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2024; 16(12): 1365-1370
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1365
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1365
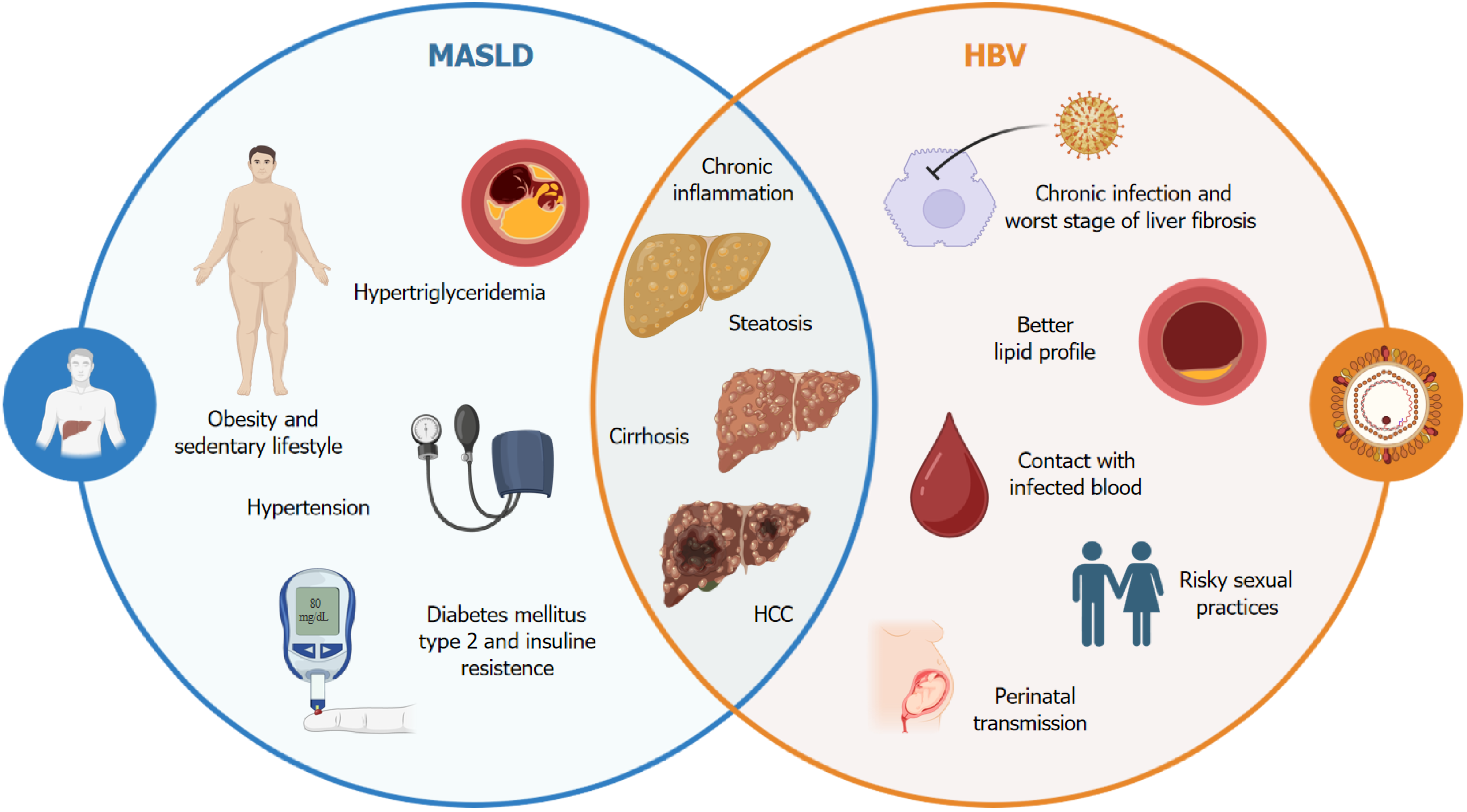
Figure 1 Multifactorial interaction between hepatitis B virus and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.
The complex relationship between chronic hepatitis B virus infection and the manifestations of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, including a predisposition to hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, is illustrated. Potential mechanisms involve chronic inflammation, metabolic alterations, and changes in the gut microbiome composition. This figure highlights the importance of considering integrated therapeutic interventions to mitigate the adverse effects of this interaction on hepatic and metabolic health. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; MASLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Morales-Galicia AE, Ramírez-Mejía MM, Ponciano-Rodriguez G, Méndez-Sánchez N. Revolutionizing the understanding of liver disease: Metabolism, function and future. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(12): 1365-1370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i12/1365.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1365