©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2023; 15(3): 353-363
Published online Mar 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.353
Published online Mar 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.353
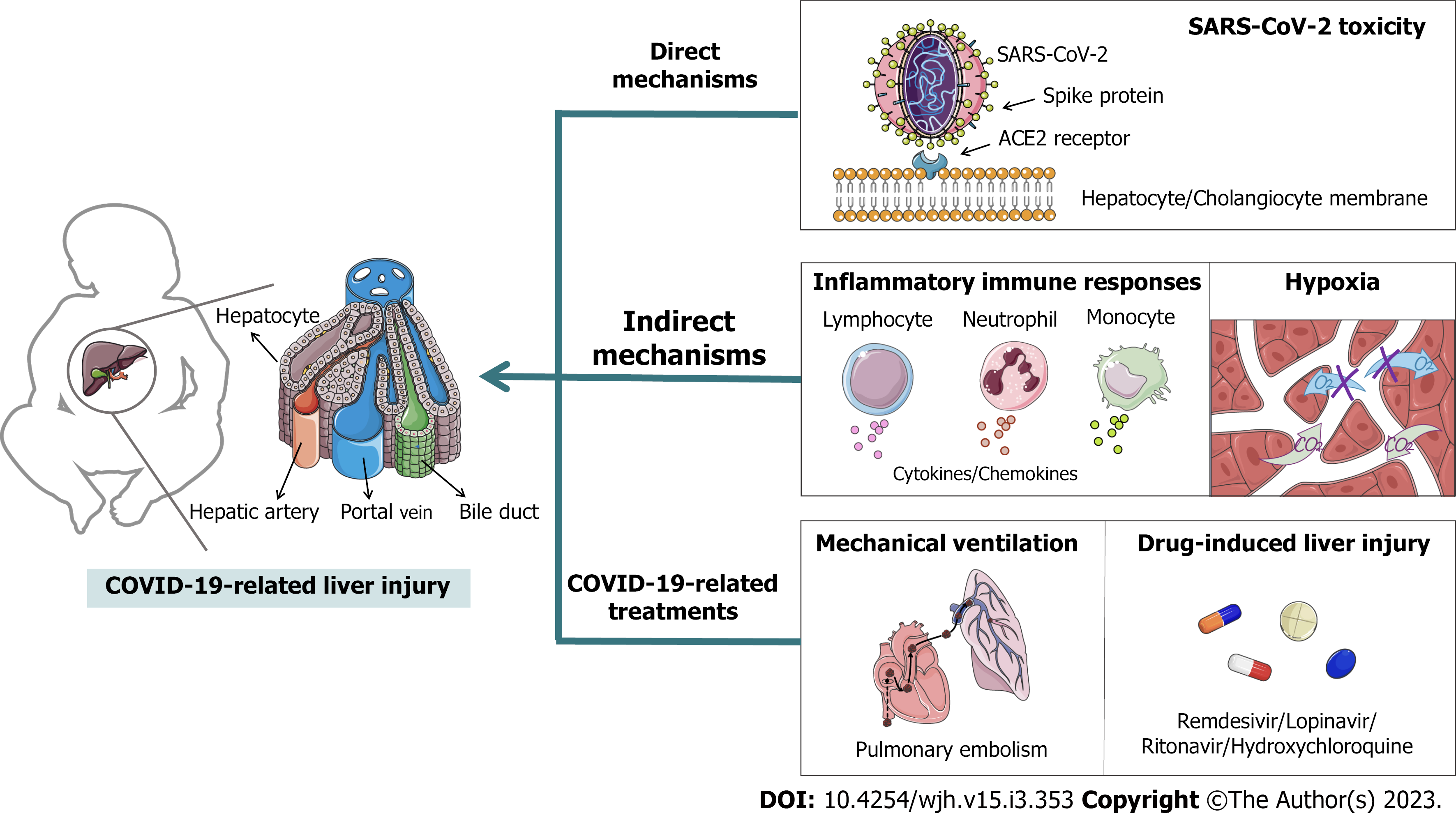
Figure 1 The possible pathophysiological mechanisms of Coronavirus disease 2019-related liver injury in children.
SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Yun YF, Feng ZY, Zhang JJ. COVID-19 and liver dysfunction in children: Current views and new hypotheses. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(3): 353-363
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i3/353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.353