©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2022; 14(9): 1730-1738
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i9.1730
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i9.1730
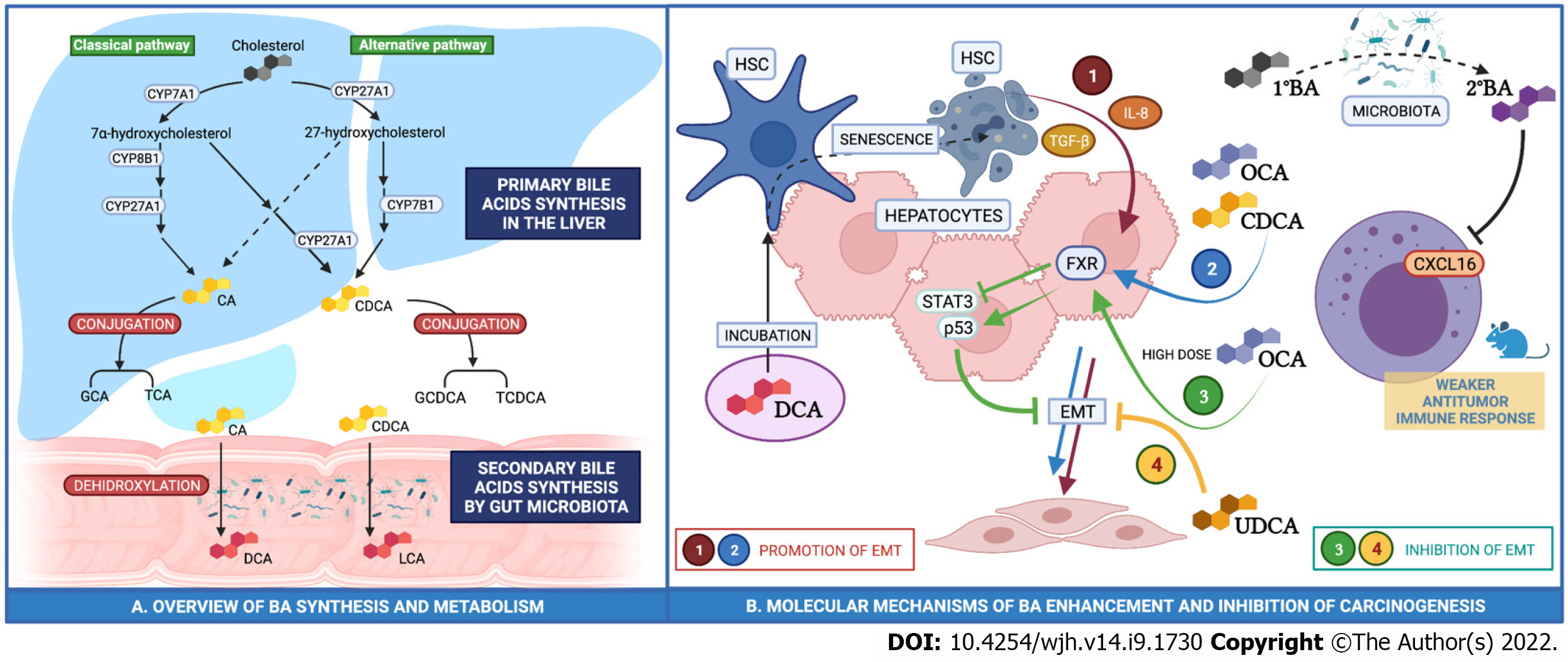
Figure 1 The primary bile acids are dehydroxylated to secondary bile acids by gut microbiota, reabsorbed in the intestine and conjugated in the liver.
A: Primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are dehydroxylated into deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, respectively, by the gut microbiota. Bile acids (BA) are reabsorbed by the intestine and reach the liver through the portal circulation. Primary BA and secondary BA are conjugated to either glycine or taurine in the liver; B: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by primary (1º) and secondary (2º) BA in human hepatocytes. GCA: Glycocholic acid; TCA: Taurocholic acid; GCDCA: Glycochenodeoxycholic acid; TCDCA: Taurochenodeoxycholic acid. OCA: Obeticholic acid; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; UDCA: Ursodeoxycholic acid; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HSC: Hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Colosimo S, Tomlinson JW. Bile acids as drivers and biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(9): 1730-1738
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i9/1730.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i9.1730