©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2022; 14(7): 1307-1318
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1307
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1307
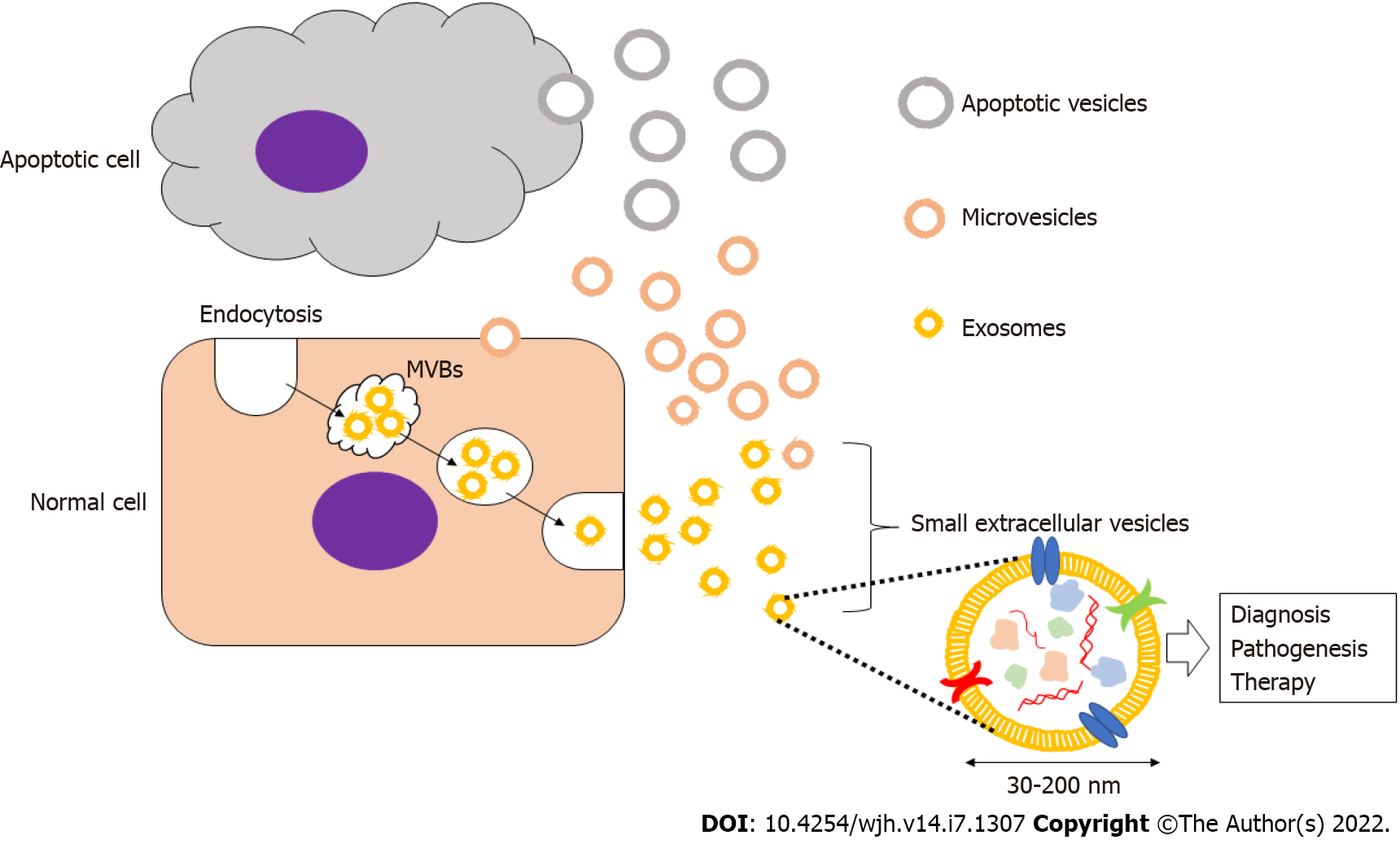
Figure 1 Extracellular vesicles and liver diseases.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) include apoptotic vesicles, microvesicles, and exosomes. Small EVs (sEVs), or exosomes, are formed from early endosomes that are generated by endocytosis and subsequently mature into late endosomes. The late endosomes expand to form intraluminal membrane vesicles, also referred to as multivesicular bodies, which fuse with the plasma membrane and are released into extracellular space. These sEVs, or exosomes, are analyzed for diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy of various diseases including liver diseases.
- Citation: Tsuchiya A, Natsui K, Ishii Y, Koseki Y, Takeda N, Tomiyoshi K, Yamazaki F, Yoshida Y, Terai S. Small extracellular vesicles and liver diseases: From diagnosis to therapy. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(7): 1307-1318
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i7/1307.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1307