©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2022; 14(6): 1099-1110
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1099
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1099
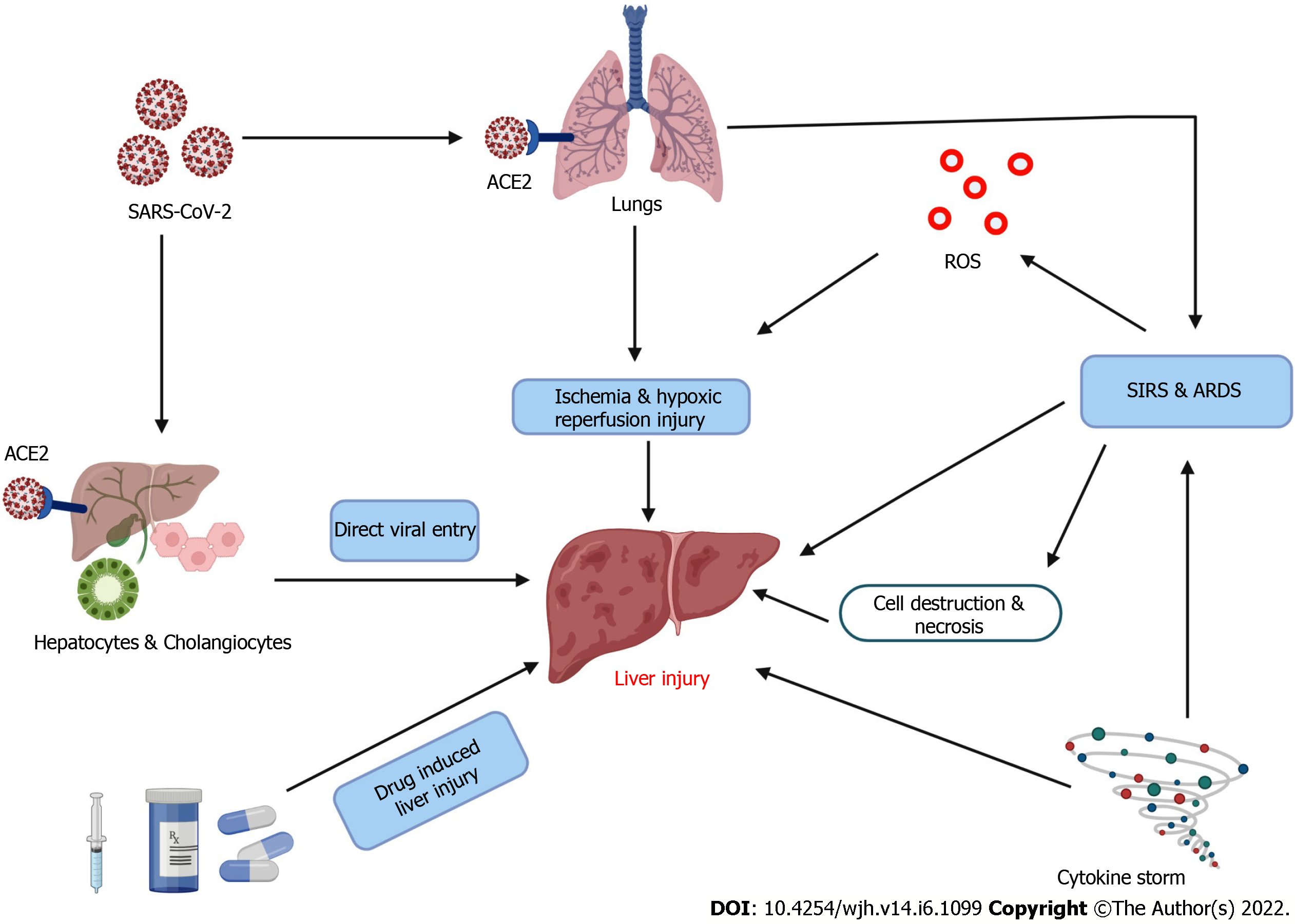
Figure 1 Schematic representation of possible causes of liver injury.
ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
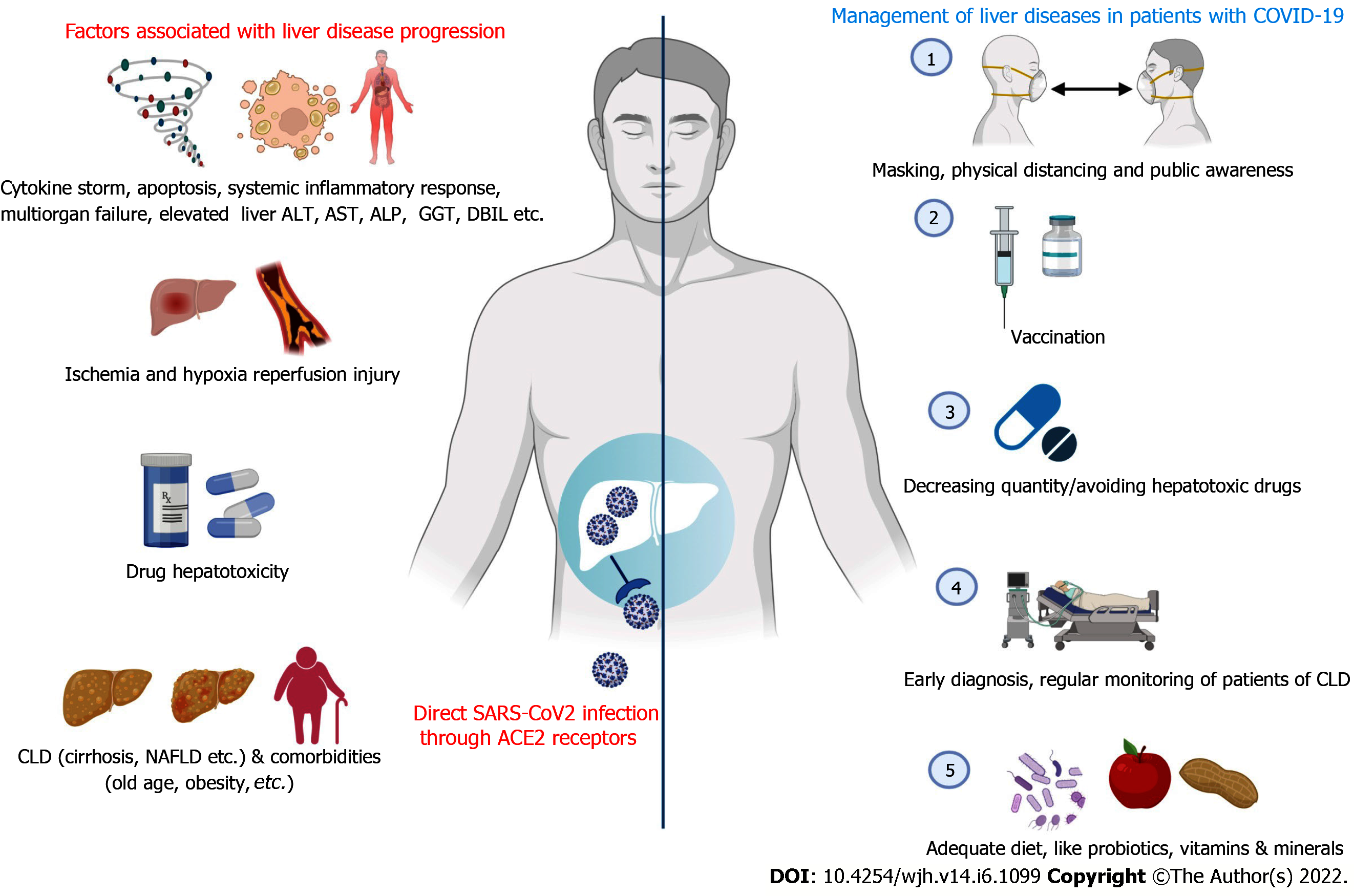
Figure 2 Associated factors for liver disease progression and its management strategies in patients with coronavirus disease 19.
CLD: Chronic liver disease; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyltransferase; DBIL: Direct bilirubin. Created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Sahu T, Pande B, PL M, Verma HK. Liver dysfunction during COVID-19 pandemic: Contributing role of associated factors in disease progression and severity. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(6): 1099-1110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i6/1099.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1099