©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2022; 14(2): 372-385
Published online Feb 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.372
Published online Feb 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.372
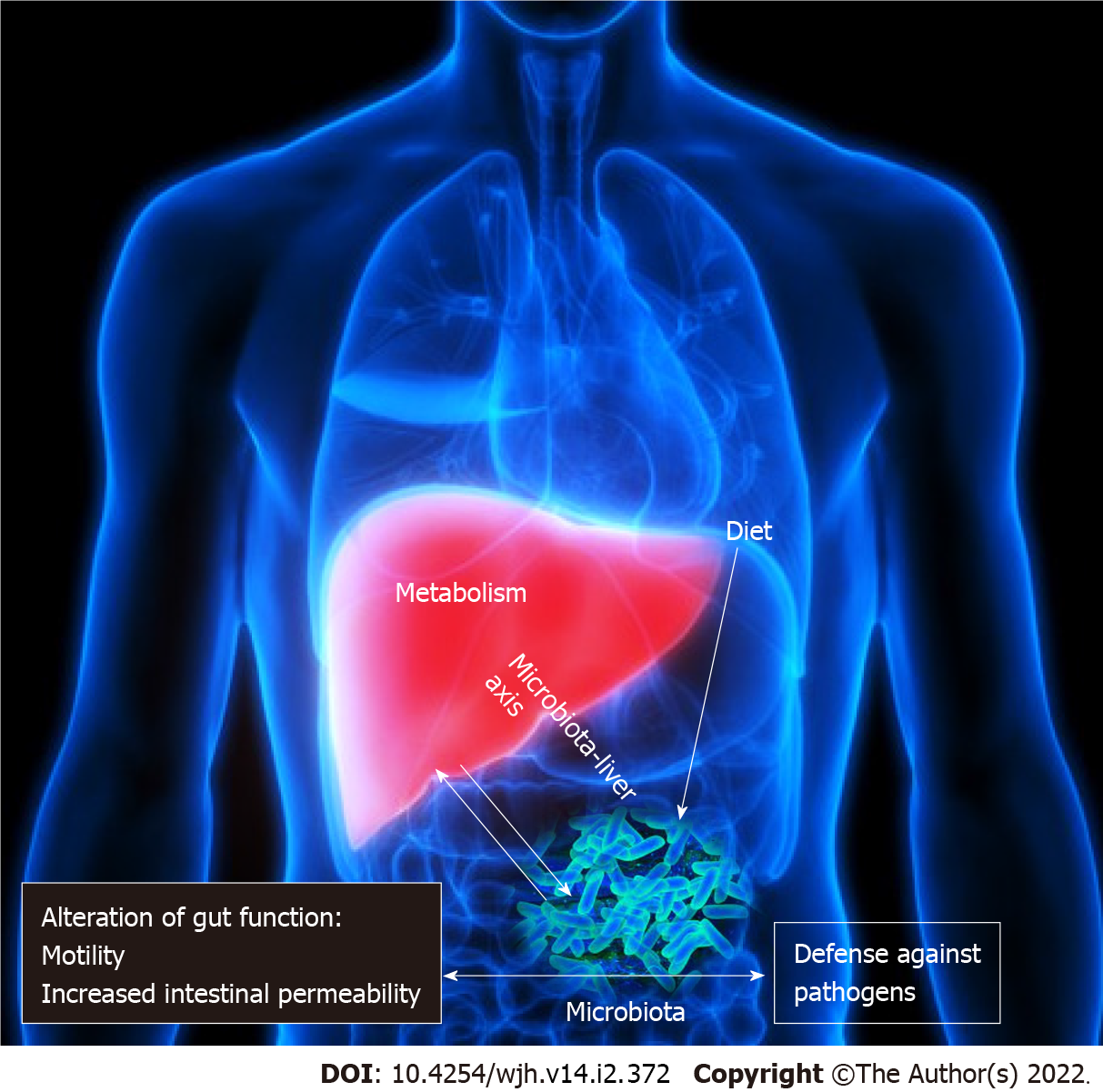
Figure 1 The gut liver axis and microbiota.
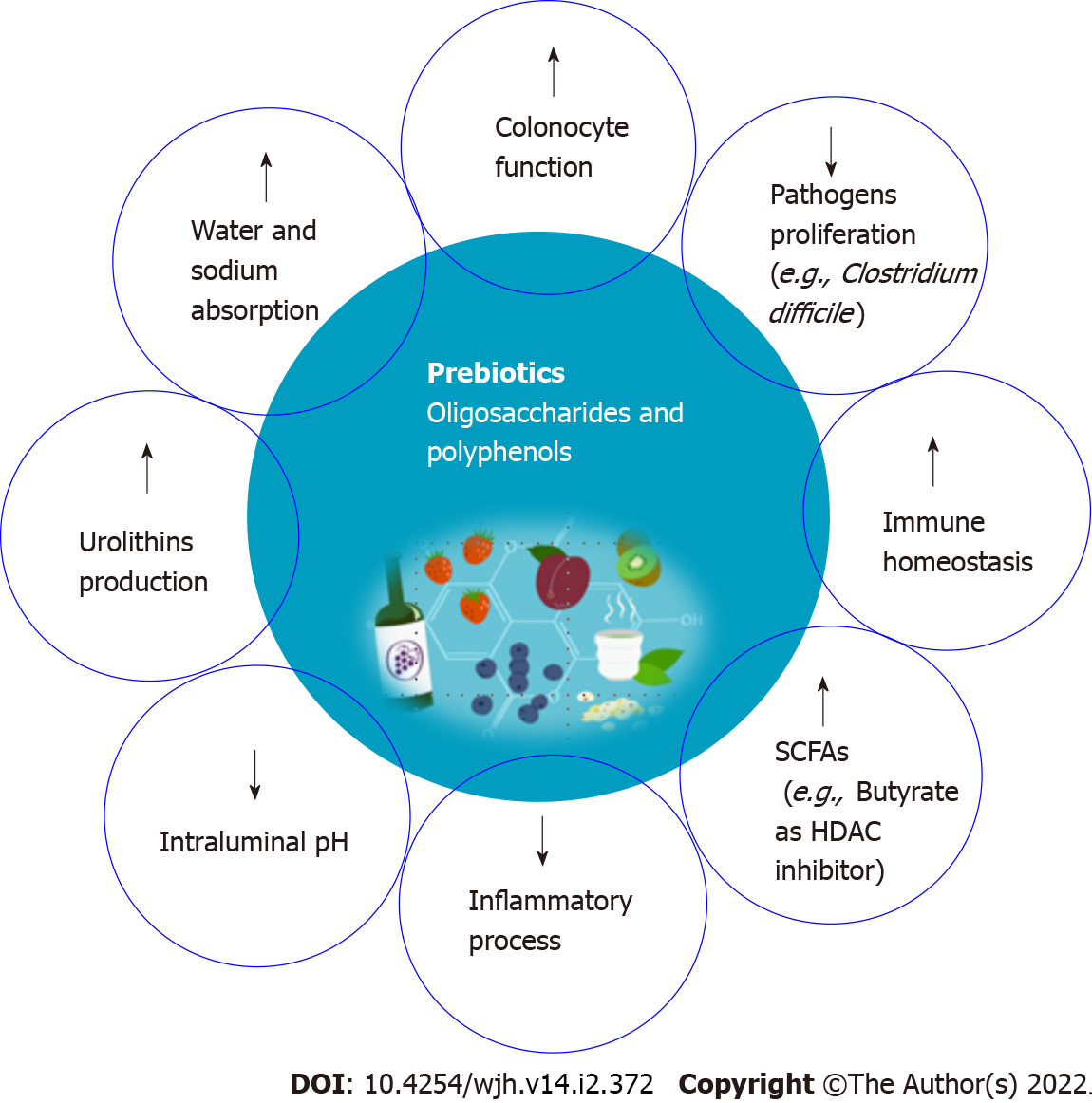
Figure 2 Proposed mechanism of action of probiotics against hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
HDAC: Histone deacetylase; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids.
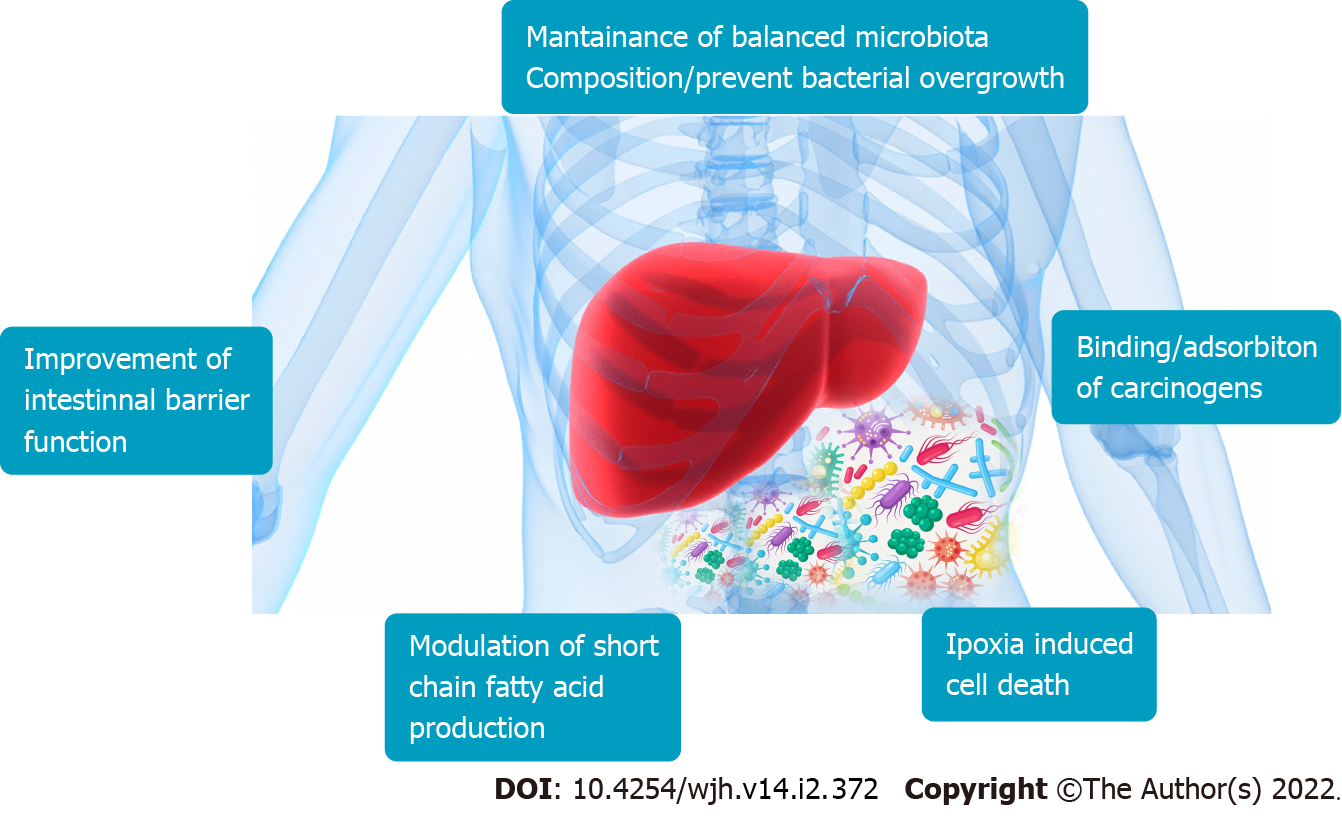
Figure 3 Role of prebiotics on immunomodulation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
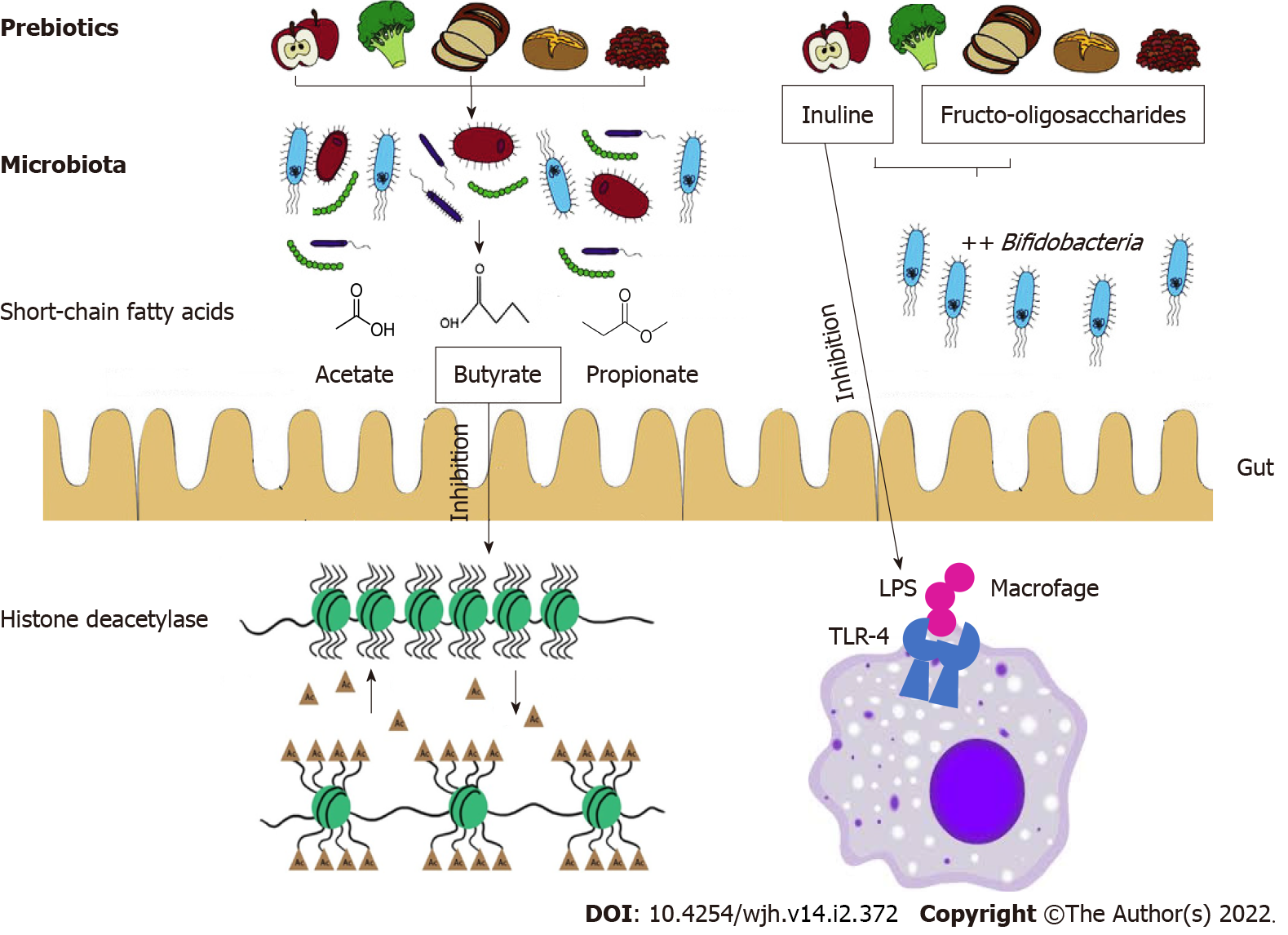
Prebiotics contribute to short-chain fatty acids such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate production, which positively influence the structure and function of the microbial community. Butyrate functions include inhibition of histone deacetylase, and decreased tumorigenesis. In addition, inulin improves gut barrier integrity, thereby reducing pro-inflammatory lipopolysaccharides-toll-like receptors 4 signaling in macrophages during alcoholic liver disease. Fructo-oligosaccharides and inulin stimulates the growth of beneficial Bifidobacteria that are implicated in cancer prevention.
Figure 4 Effect of prebiotics in cancer prevention.
LPS: Lipopolysaccharides; TLR: Toll-like receptors.
- Citation: Russo E, Fiorindi C, Giudici F, Amedei A. Immunomodulation by probiotics and prebiotics in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(2): 372-385
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i2/372.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.372