©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1629-1641
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1629
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1629
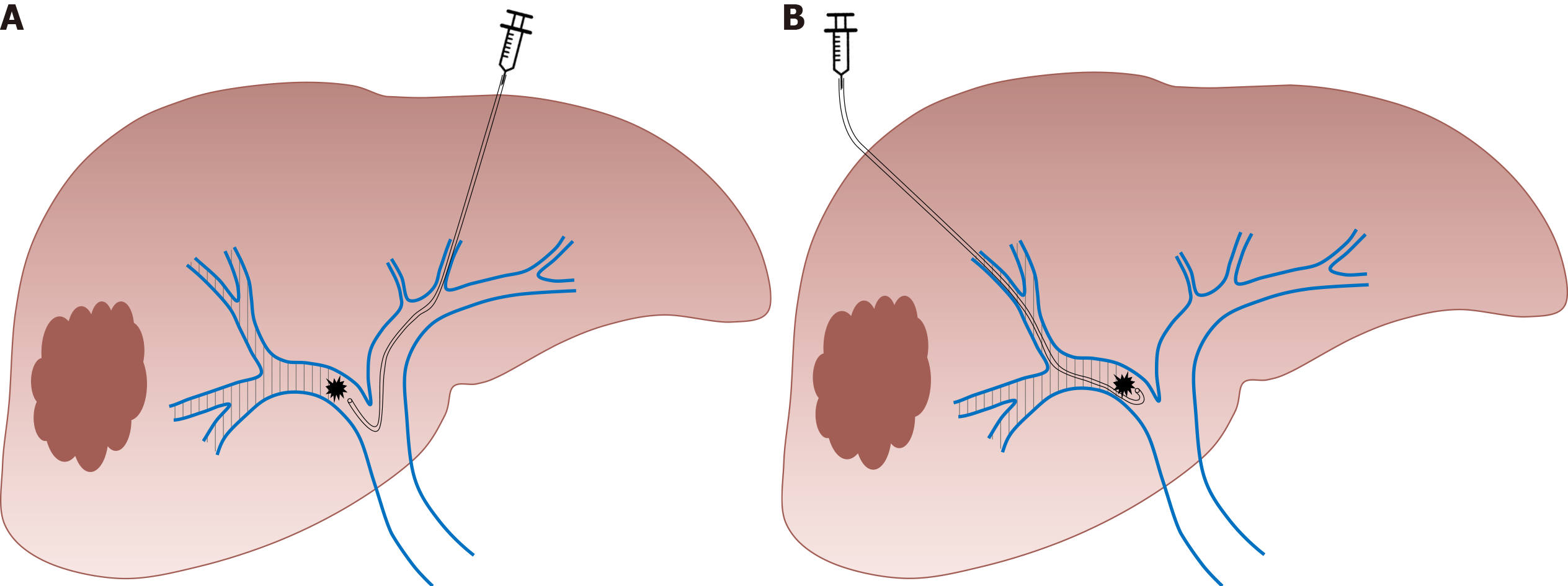
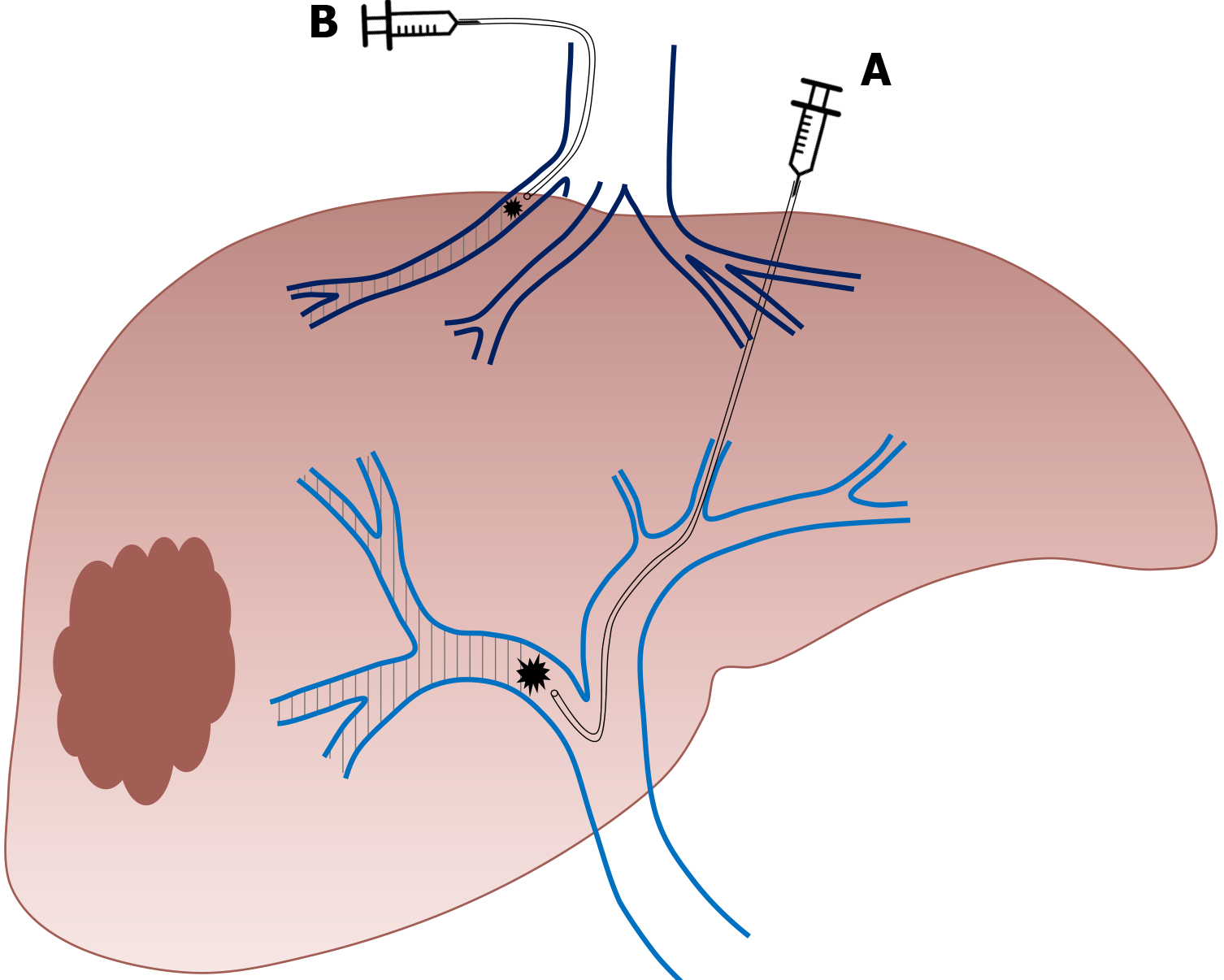
Figure 1 Right portal vein embolization using.
A: Contralateral; B: Ipsilateral approach.
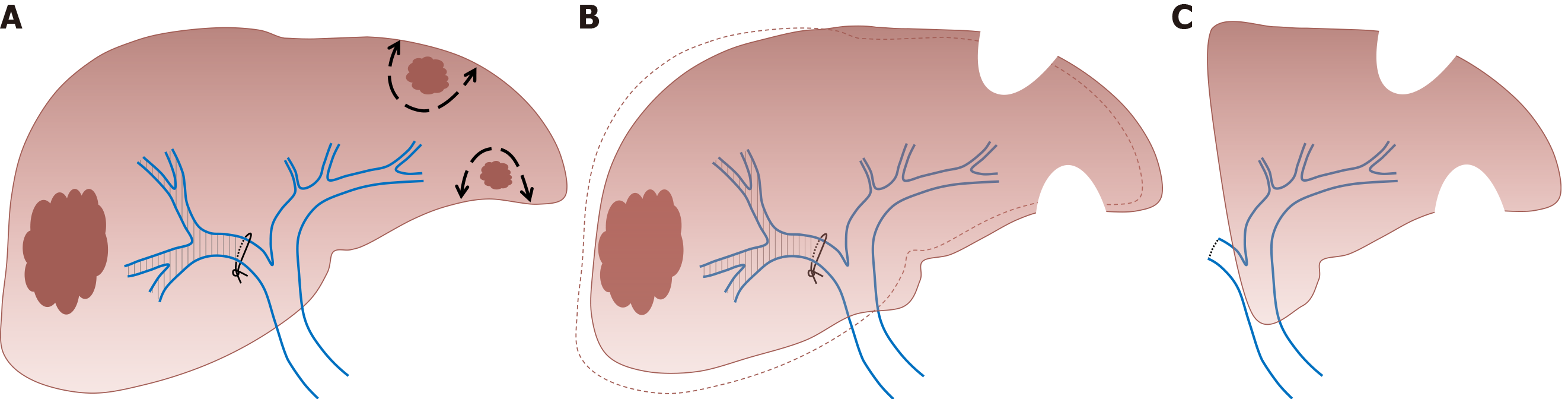
Figure 2 Two-stage hepatectomy procedure starts with tumoral clearance of the future liver remnant.
A: Concomitant right portal vein ligation; B: Allowing left liver growth; C: Ends with right hepatectomy.
Figure 3 Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy procedure.
A: Starts with in situ splitting of the liver parenchyma with concomitant right portal vein ligation; B: Ends with right hepatectom.
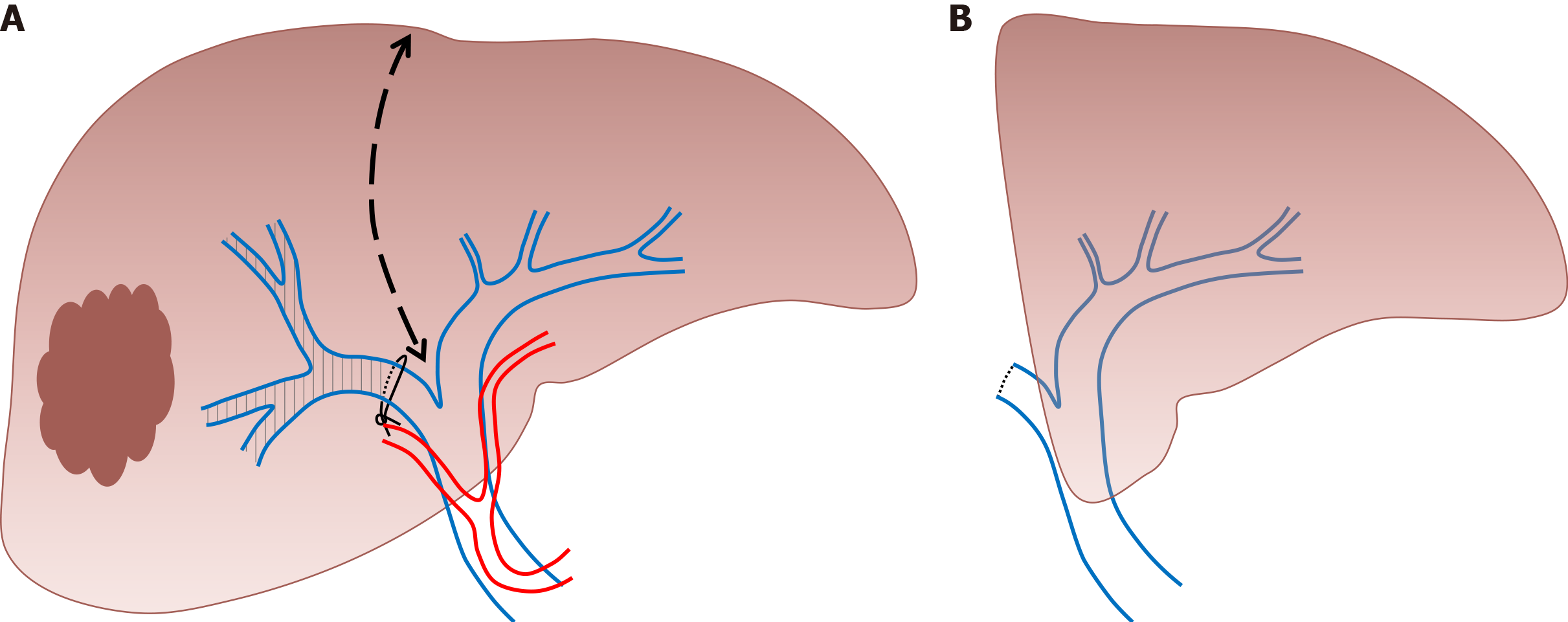
Figure 4 Sequential embolization.
A: Trans-arterial embolization; B: Portal vein embolization of the right liver.
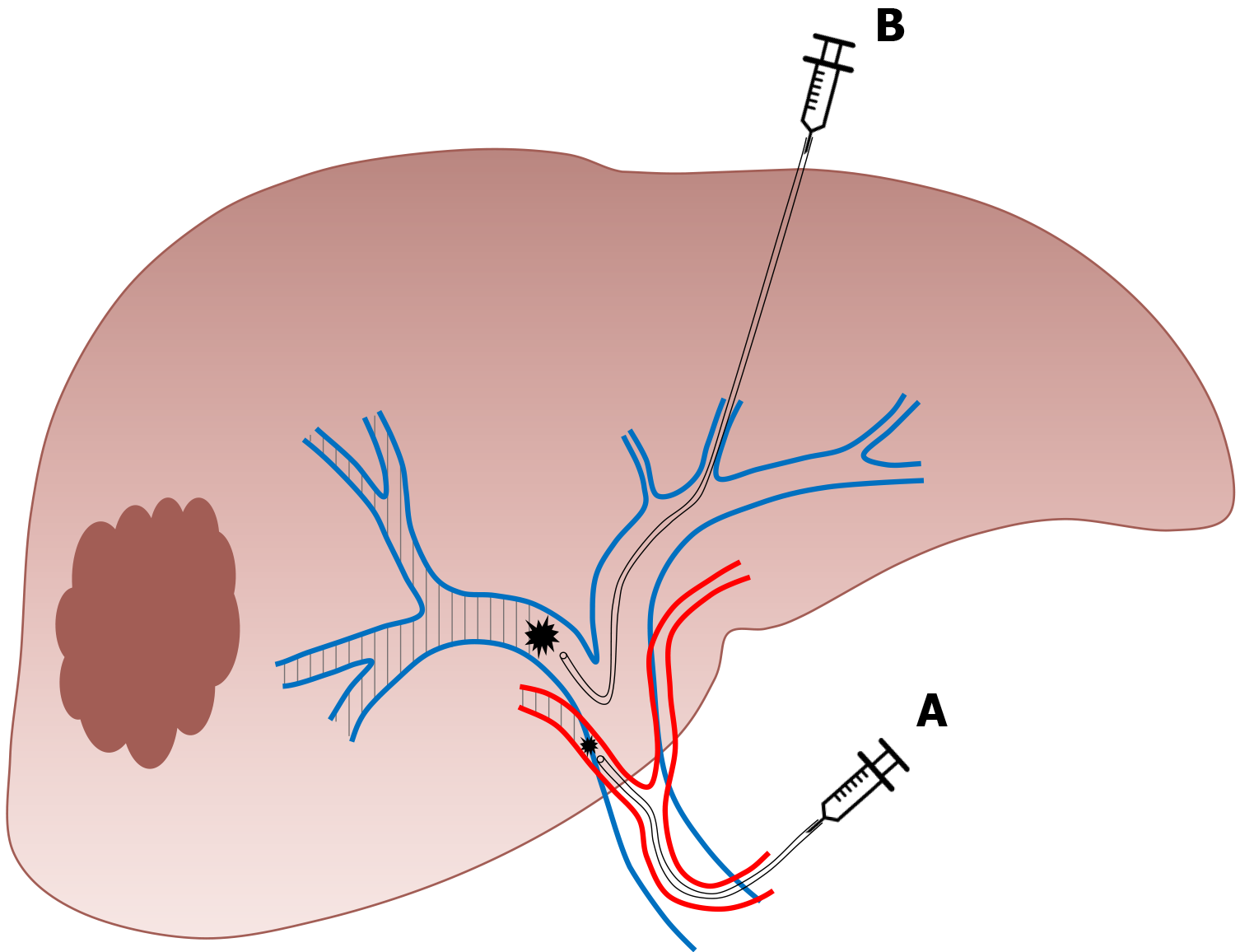
Figure 5 Right liver venous derivation associates in a sequential or concomitant approach.
A: Right portal vein embolization; B: Ipsilateral hepatic vein embolization.
- Citation: Del Basso C, Gaillard M, Lainas P, Zervaki S, Perlemuter G, Chagué P, Rocher L, Voican CS, Dagher I, Tranchart H. Current strategies to induce liver remnant hypertrophy before major liver resection. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1629-1641
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1629.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1629