©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1584-1610
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584
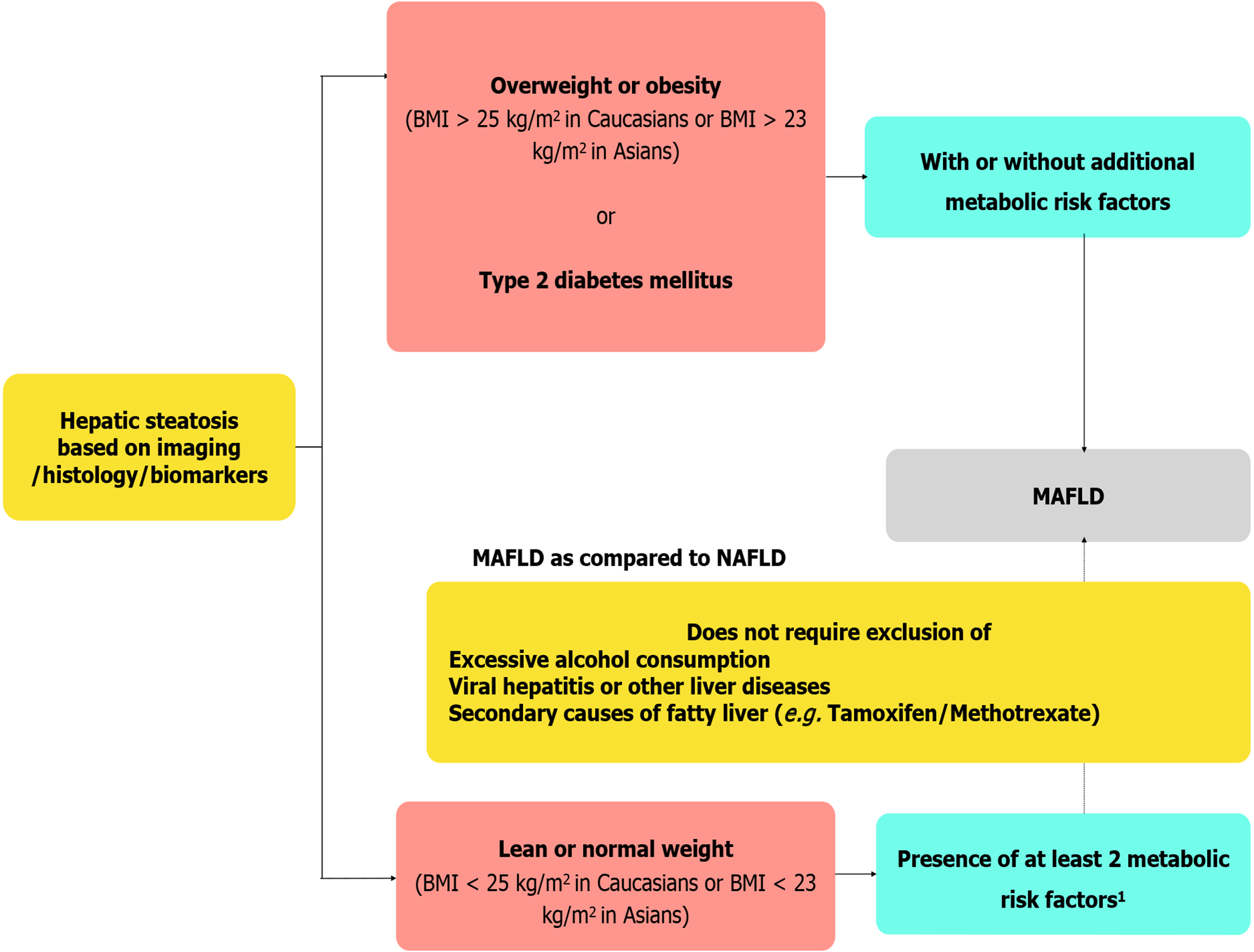
Figure 1 Proposed diagnostic criteria of metabolic associated fatty liver disease and key differences with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease definition.
1Metabolic risk factors include (1) Waist circumference ≥ 102/88 cm in Caucasian men and women (≥ 90/80 cm for Asian men and women); (2) Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or on drug treatment; (3) Triglyceride levels ≥ 150 mg/dL (≥ 1.70 mmol/L) or on drug treatment; (4) Plasma high density lipoprotein [HDL < 40 mg/dL (< 1.0 mmol/L) for men and < 50 mg/dL (< 1.3 mmol/L)] for women or on drug treatment; (5) Pre-diabetes [i.e., fasting glucose levels 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L), or 2-h post-load glucose levels 140 to 199 mg/dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmoL) or HbA1c 5.7% to 6.4% (39 to 47 mmol/moL)]; (6) Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance score ≥ 2.5; and (7) Plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level > 2 mg/L. BMI: Body mass index; MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
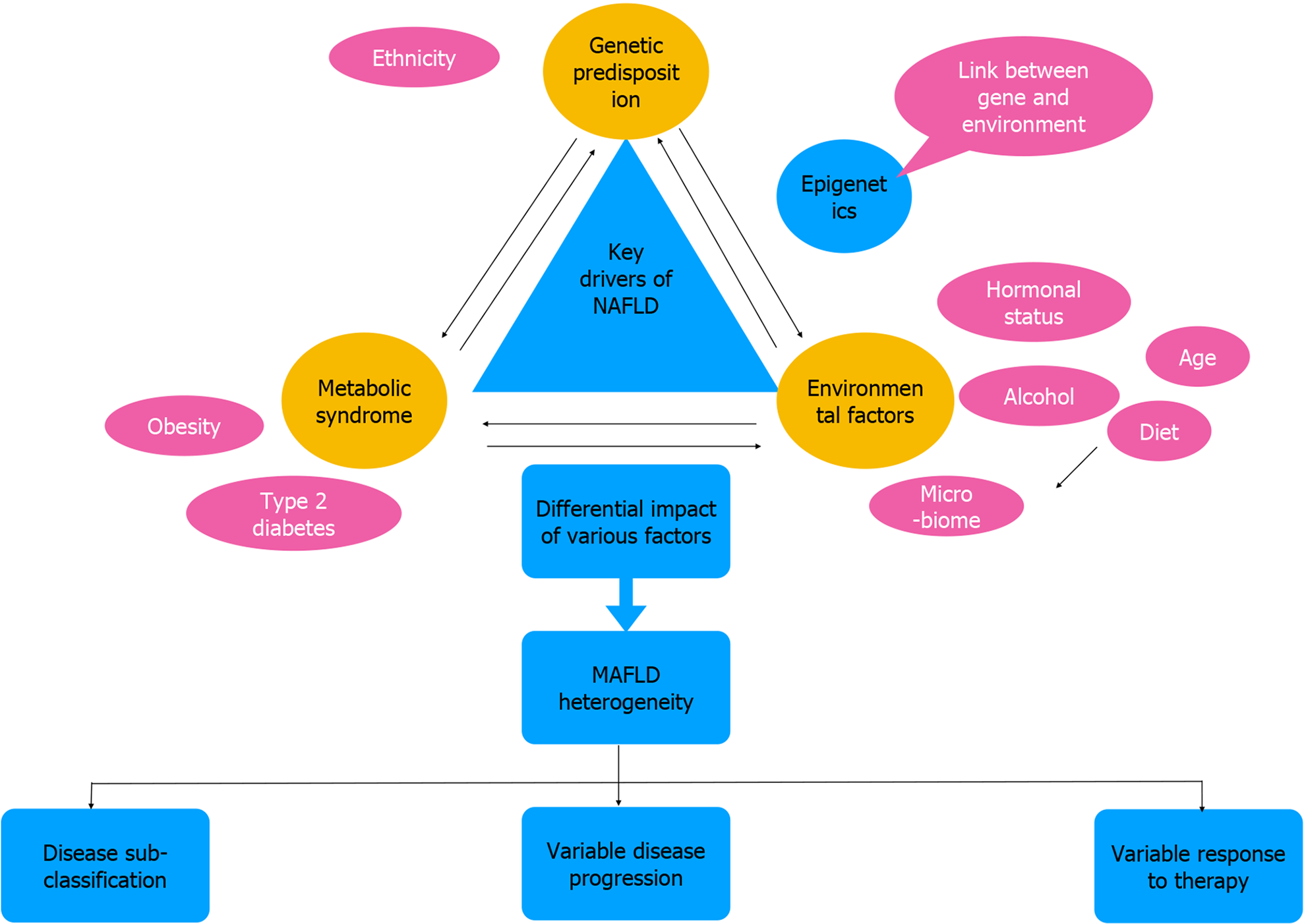
Figure 2 Key drivers of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, resulting in disease heterogeneity and its clinical implications.
Genetic predisposition, metabolic health, and environmental factors influence molecular and phenotypical heterogeneity of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease leading to various disease subtypes, variable disease progression, and response to therapy. MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
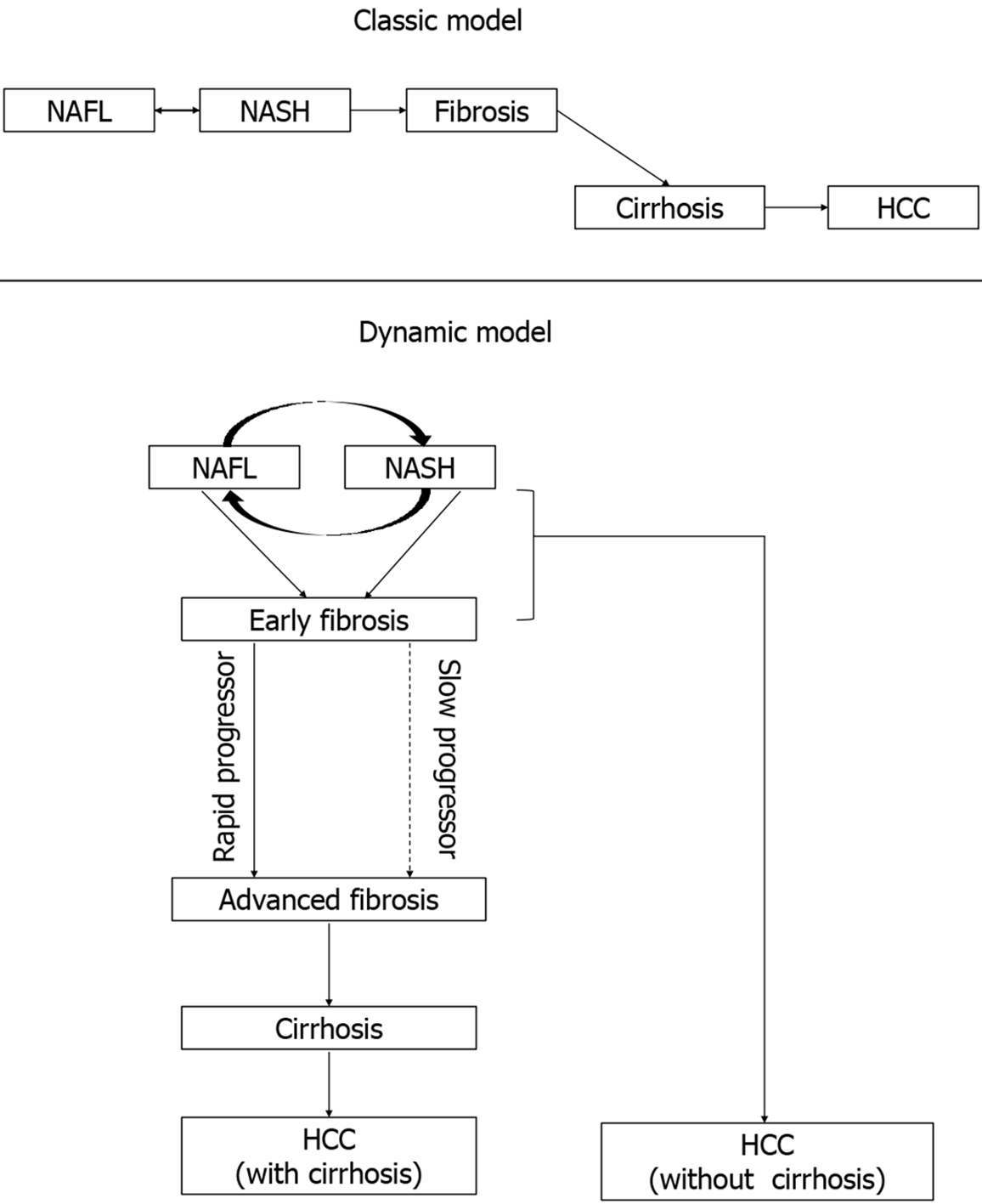
Figure 3 Natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (classic and dynamic model).
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NAFL: Nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
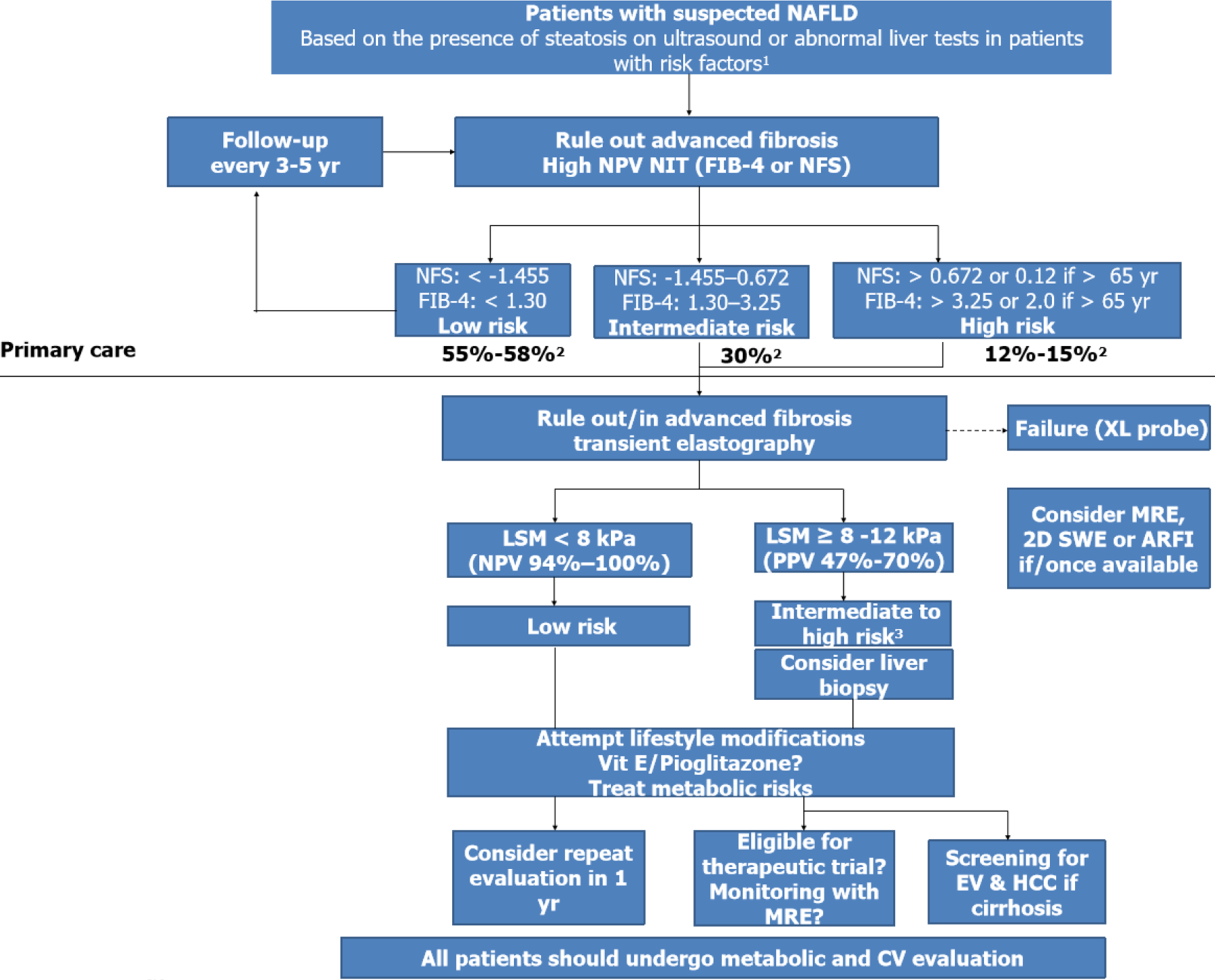
Figure 4 A suggested algorithm for the use of non-invasive tests for risk stratification of patients with suspected non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in clinical practice.
1Obesity, type 2 diabetes, or metabolic syndrome; 2Estimated prevalence for low, intermediate, and high risks groups; 3Patented serum biomarkers (FibroTest, Fibrometer, or ELF) could be considered in patients with intermediate-risk. ARFI: Acoustic radiation force imaging; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; MRE: Magnetic resonance elastography; NPV: Negative predictive value; PPV: Positive predictive value; SWE: Shear wave elastography.
- Citation: Pal P, Palui R, Ray S. Heterogeneity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for clinical practice and research activity. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1584-1610
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584