©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1552-1567
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1552
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1552
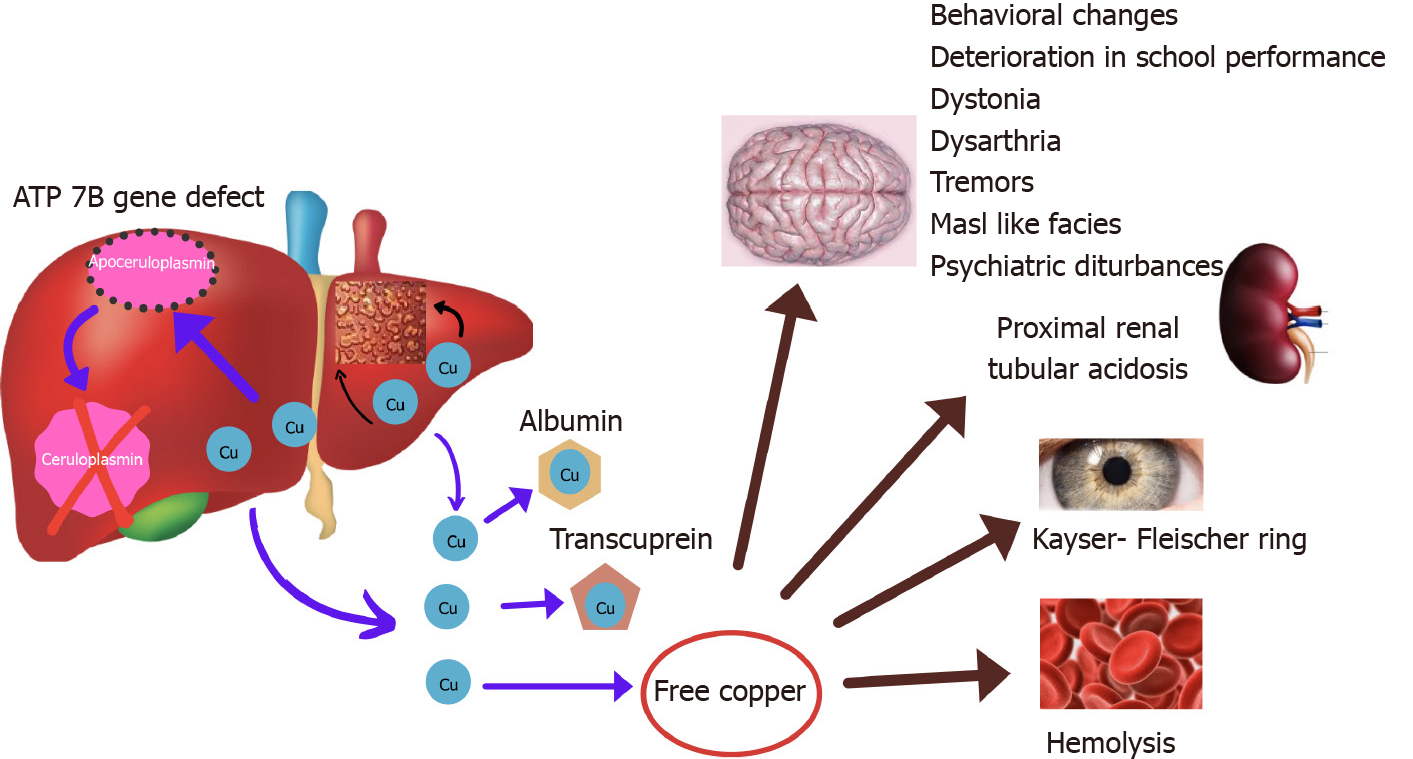
Figure 1 Pathophysiology of Wilson’s disease.
Due to mutation in ATP 7B gene, P type ATPase is defective and copper is not incorporated in ceruloplasmin. Free copper increases in blood and is deposited in liver and extrahepatic sites (brain, kidneys, bones, cornea, RBC).
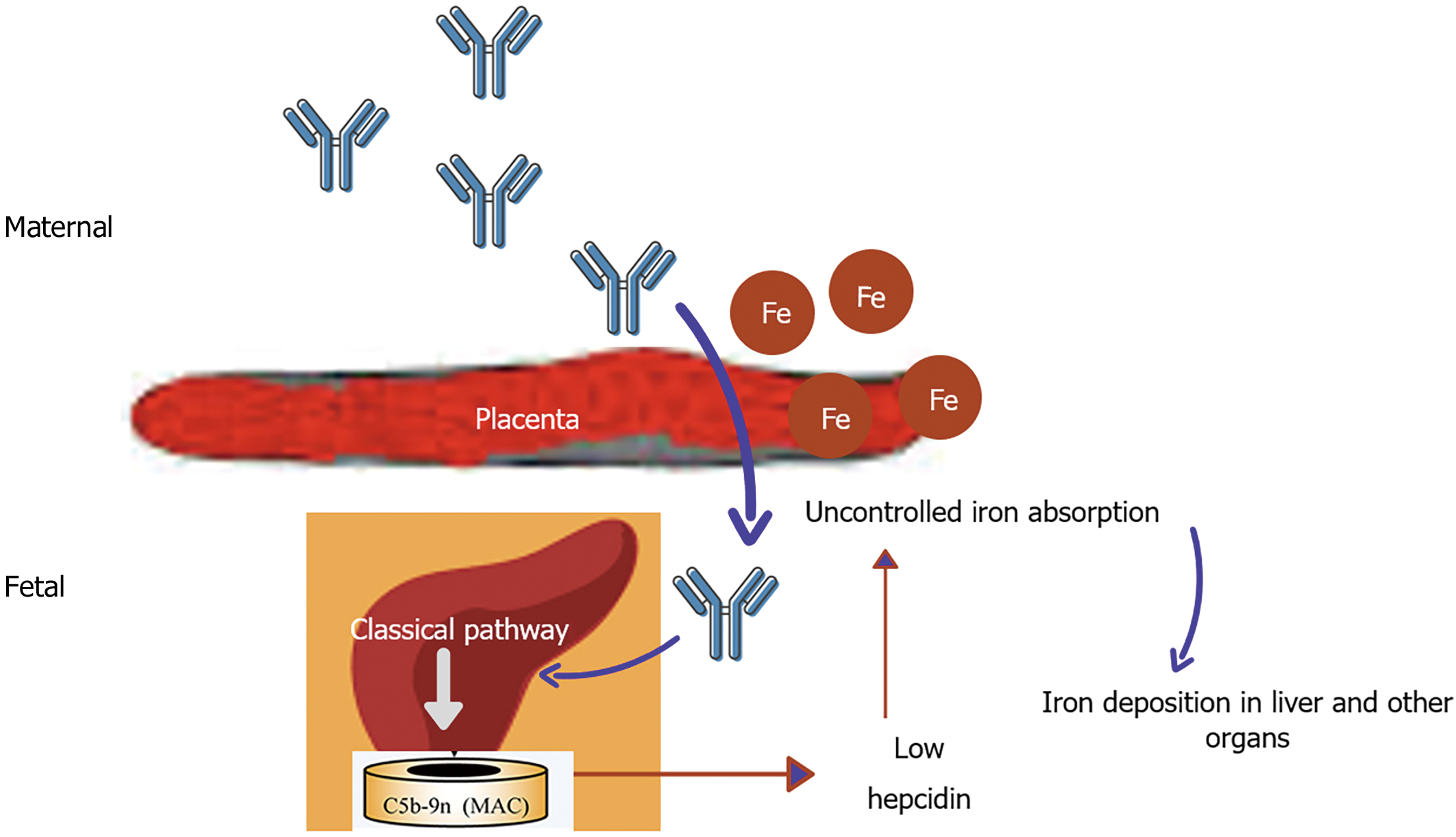
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of gestational alloimmune liver disease.
Alloimmunization of fetal liver antigen by maternal blood produces IgG antibody passively transferred through the placenta to cause fetal liver injury by complement activation. Liver injury reduces the hepatic synthesis of hepcidin resulting in uncontrolled placental iron absorption. Excess iron is deposited in liver, pancreas, heart, gonads, etc.
- Citation: Seetharaman J, Sarma MS. Chelation therapy in liver diseases of childhood: Current status and response. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1552-1567
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1552.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1552