©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2021; 13(1): 132-143
Published online Jan 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i1.132
Published online Jan 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i1.132
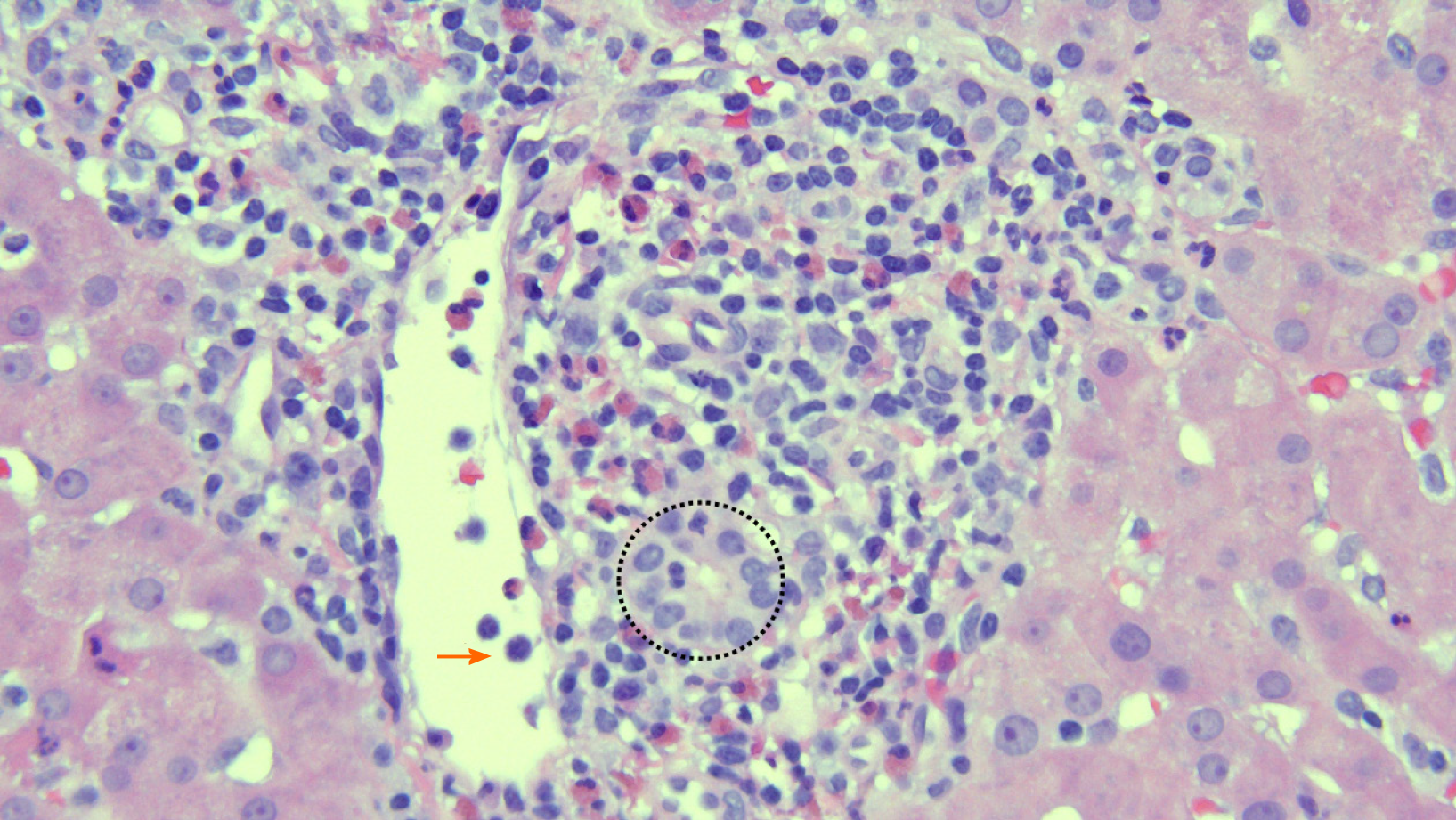
Figure 1 Photomicrograph of representative portal tract in acute cellular rejection.
Mixed, lymphocyte predominant portal-based inflammation, bile duct inflammation characterized by lymphocyte infiltration (circle), and a large portal venule with subendothelial lymphocyte infiltration and intraluminal lymphocyte tethering[24] (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 40 ×).
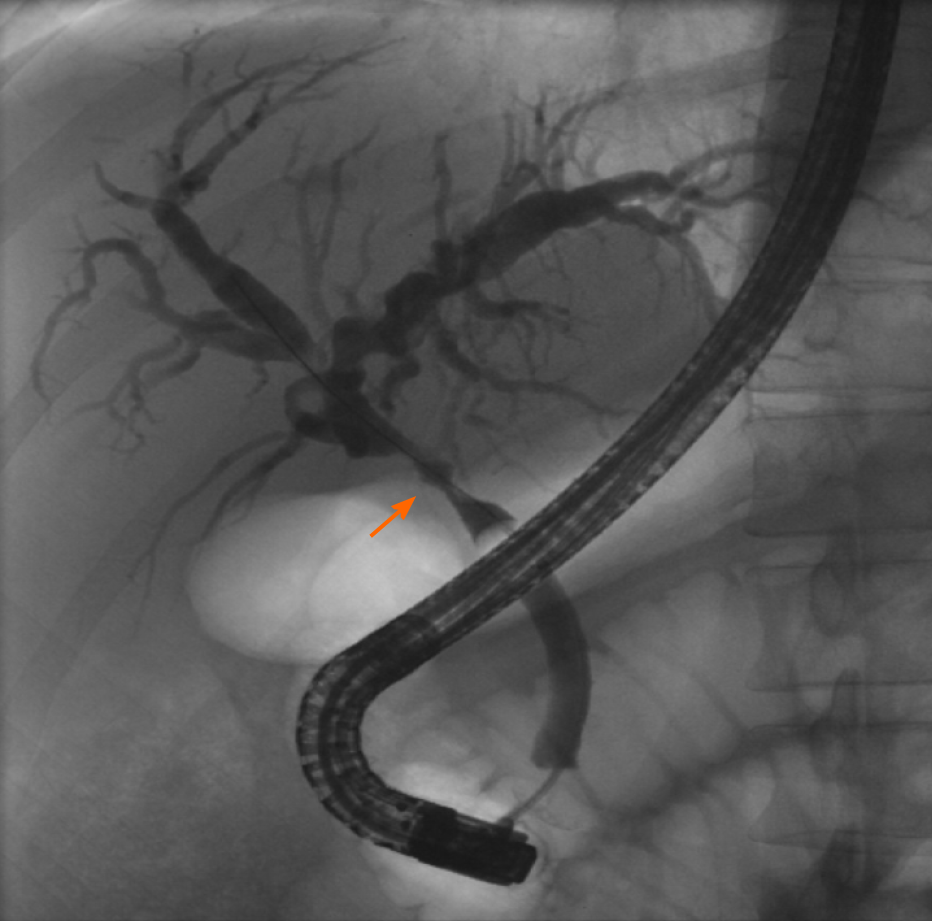
Figure 2 Cholangiogram during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography demonstrating an anastomotic stricture (arrow).
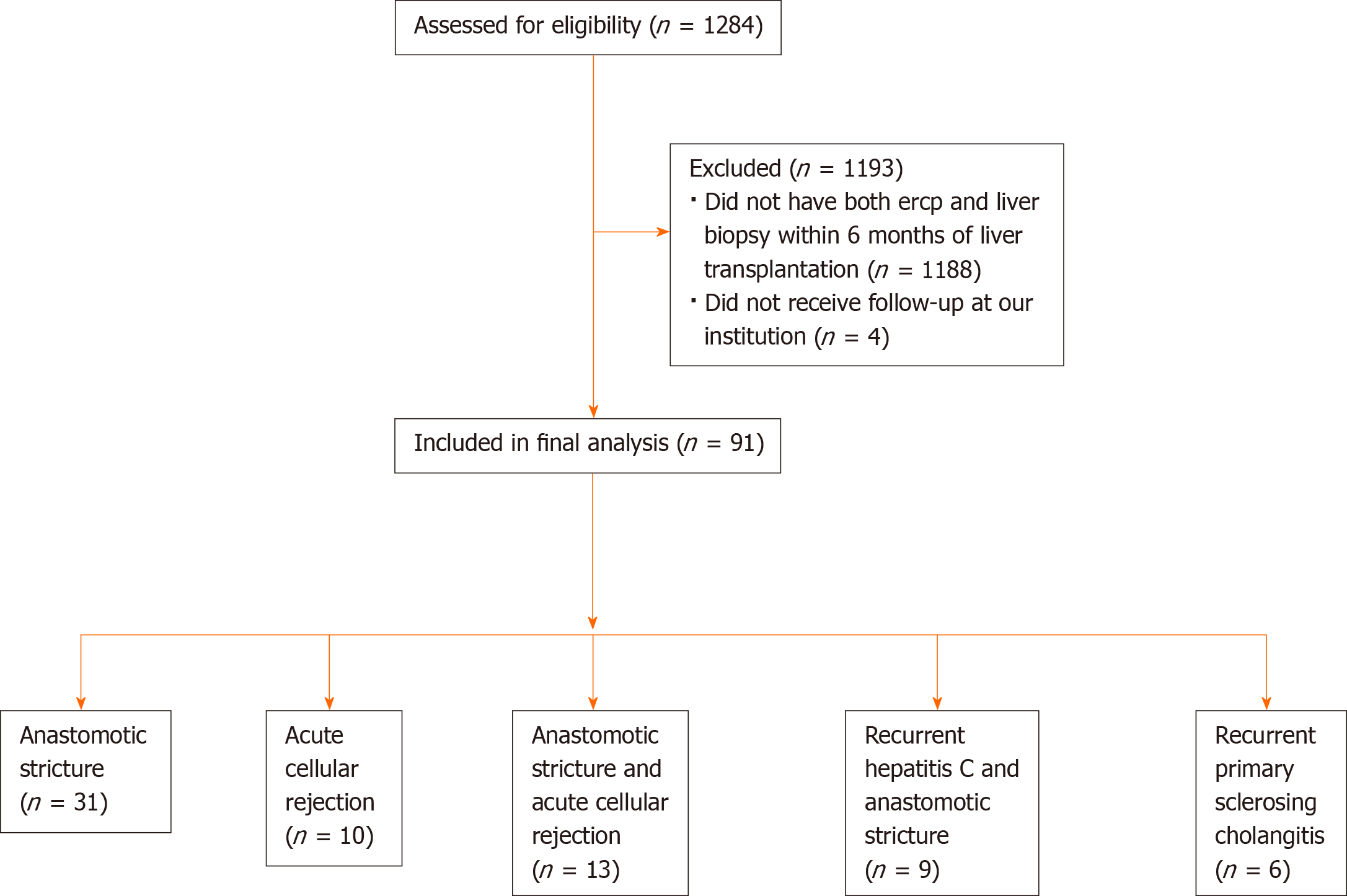
Figure 3 Flow diagram of patients.
ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
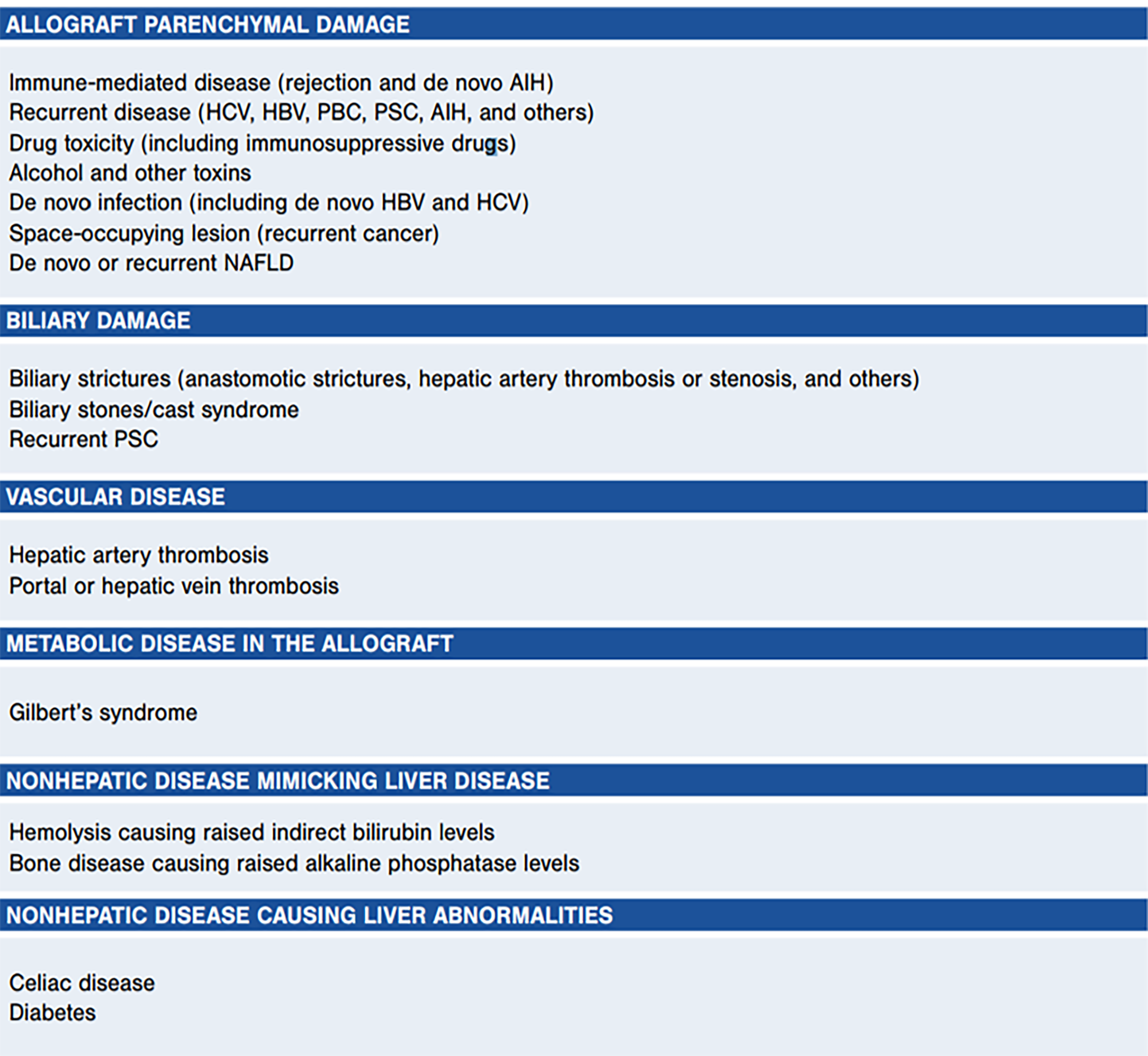
Figure 4 Causes of liver test abnormalities after liver transplantation.
Legend: Used with permission from Lucey et al[2], 2013. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis; PSC: Pulmonary scar cancer.
- Citation: Attwell A, Han S, Kriss M. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and liver biopsy in the evaluation of elevated liver function tests after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(1): 132-143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i1/132.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i1.132