©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2020; 12(9): 533-557
Published online Sep 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.533
Published online Sep 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.533
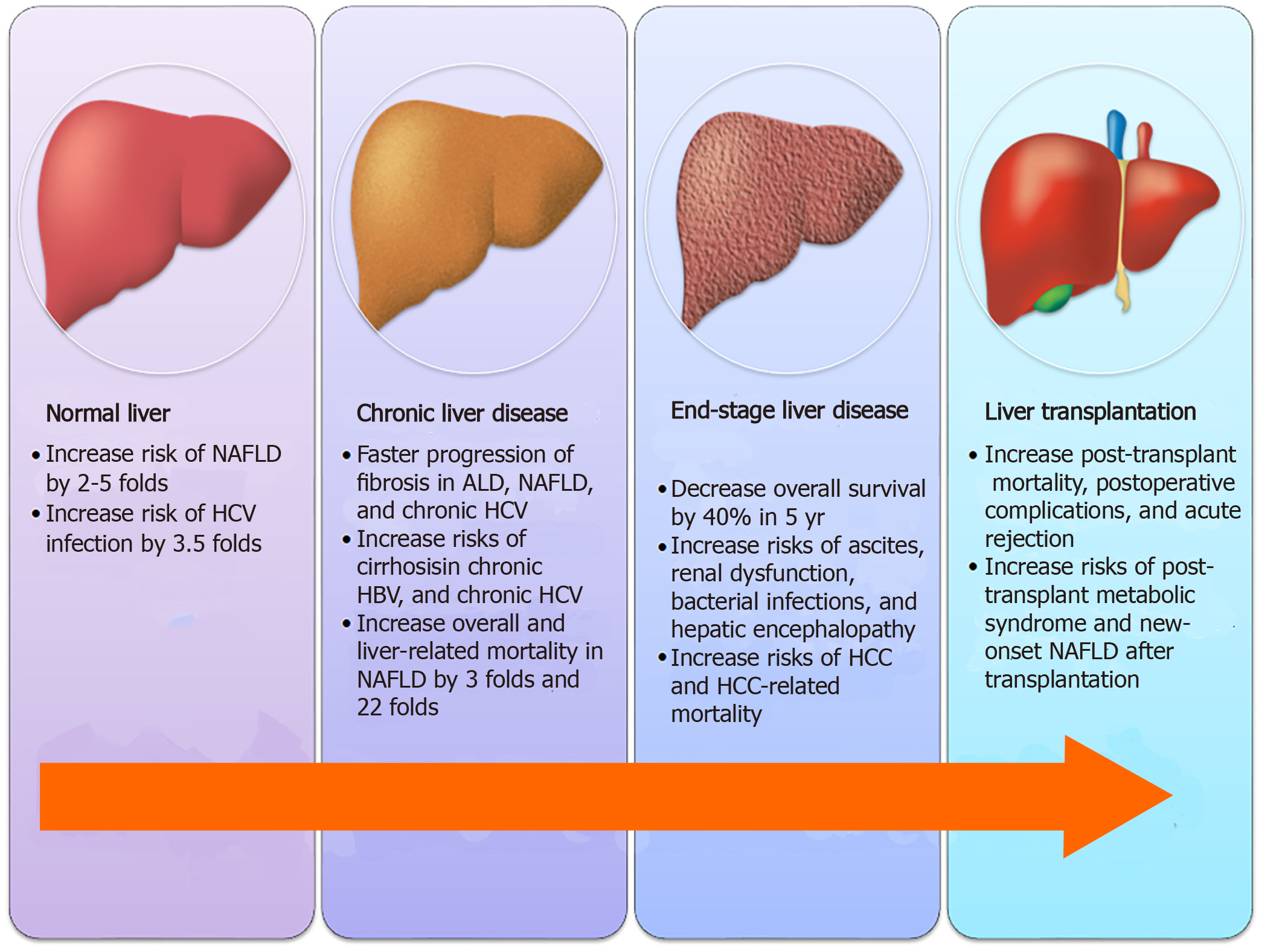
Figure 1 Impact of diabetes on various stages of chronic liver diseases.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ALD: Alcoholic liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
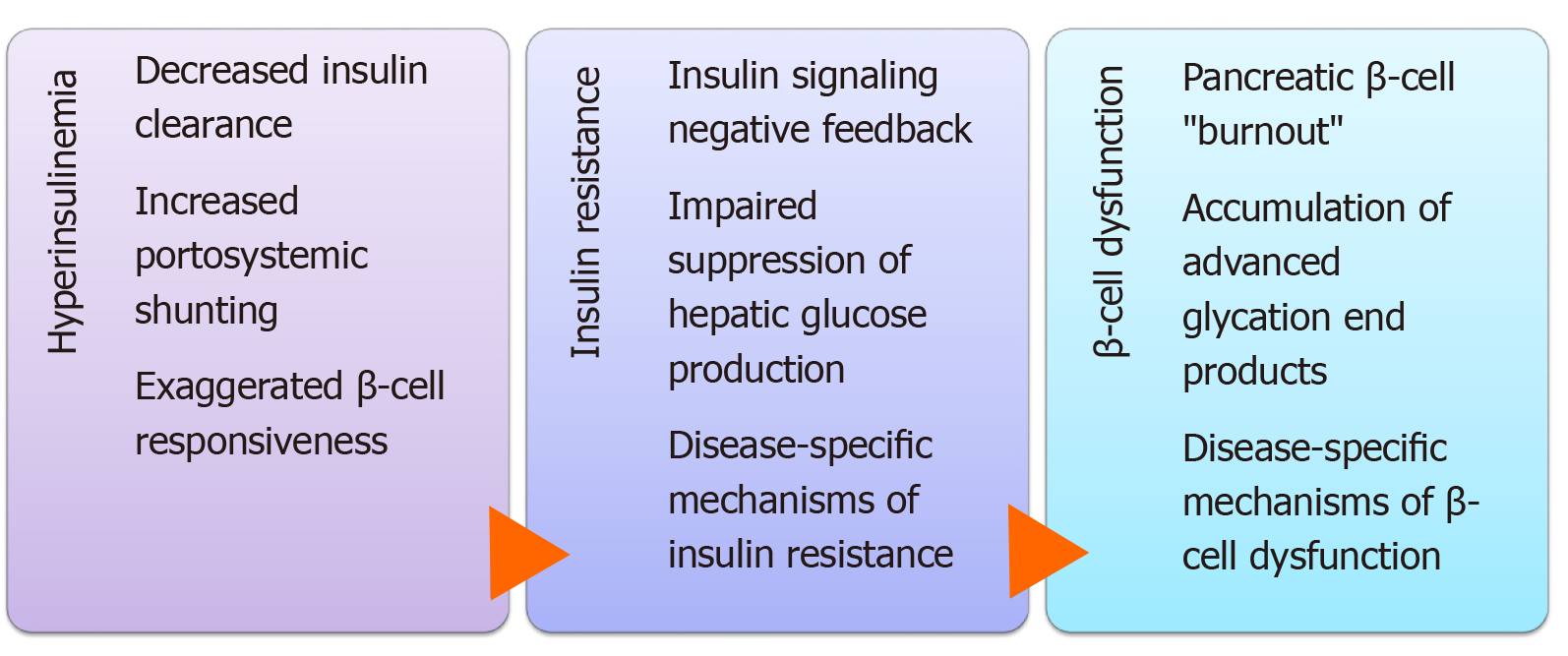
Figure 2 Mechanisms of action of hepatogenic diabetes.
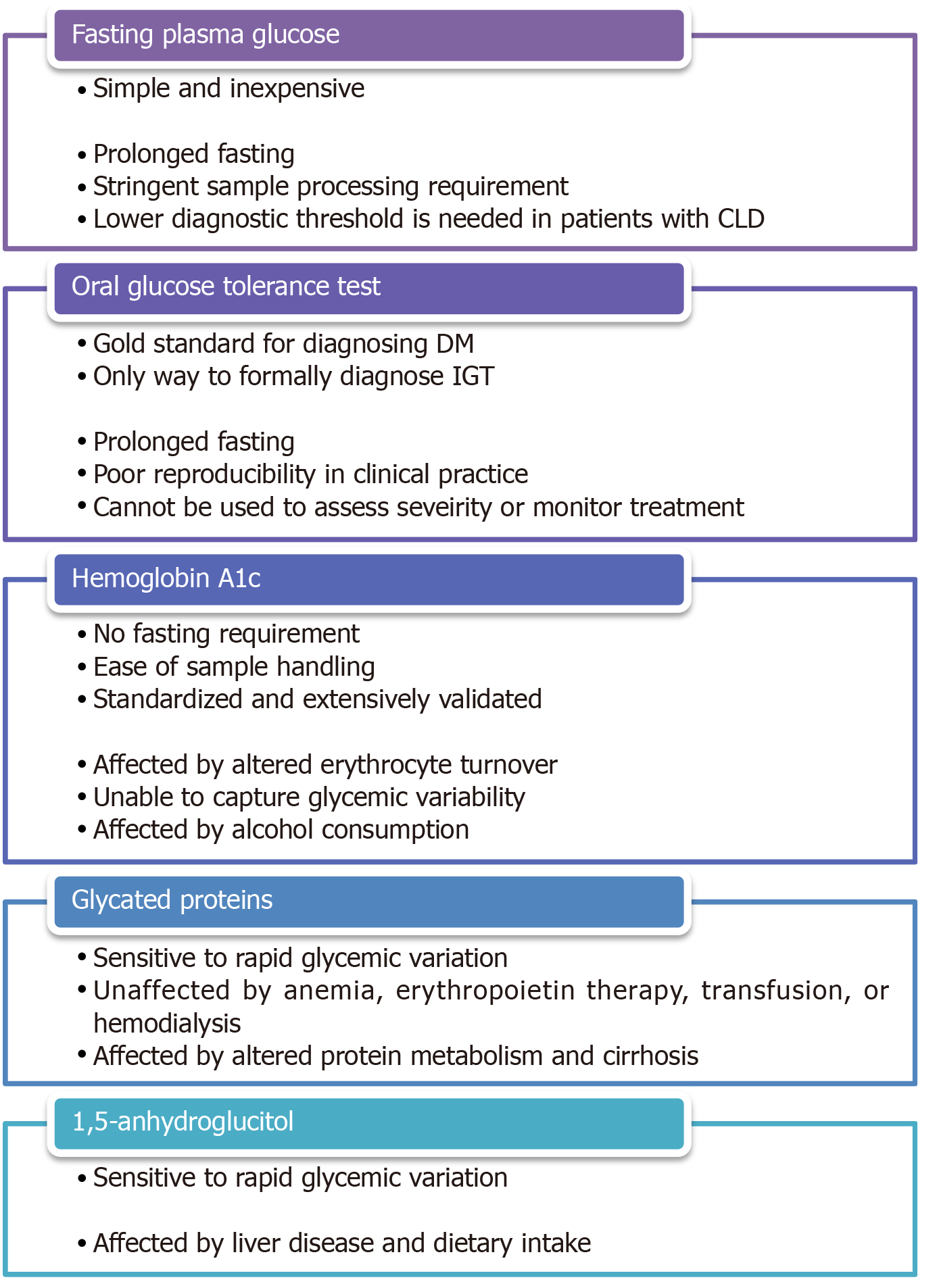
Figure 3 Pros and cons of various glycemic markers.
CLD: Chronic liver diseases; DM: Diabetes mellitus; IGT: Impaired glucose tolerance.
Figure 4 Pros and cons of various antihyperglycemic medications.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
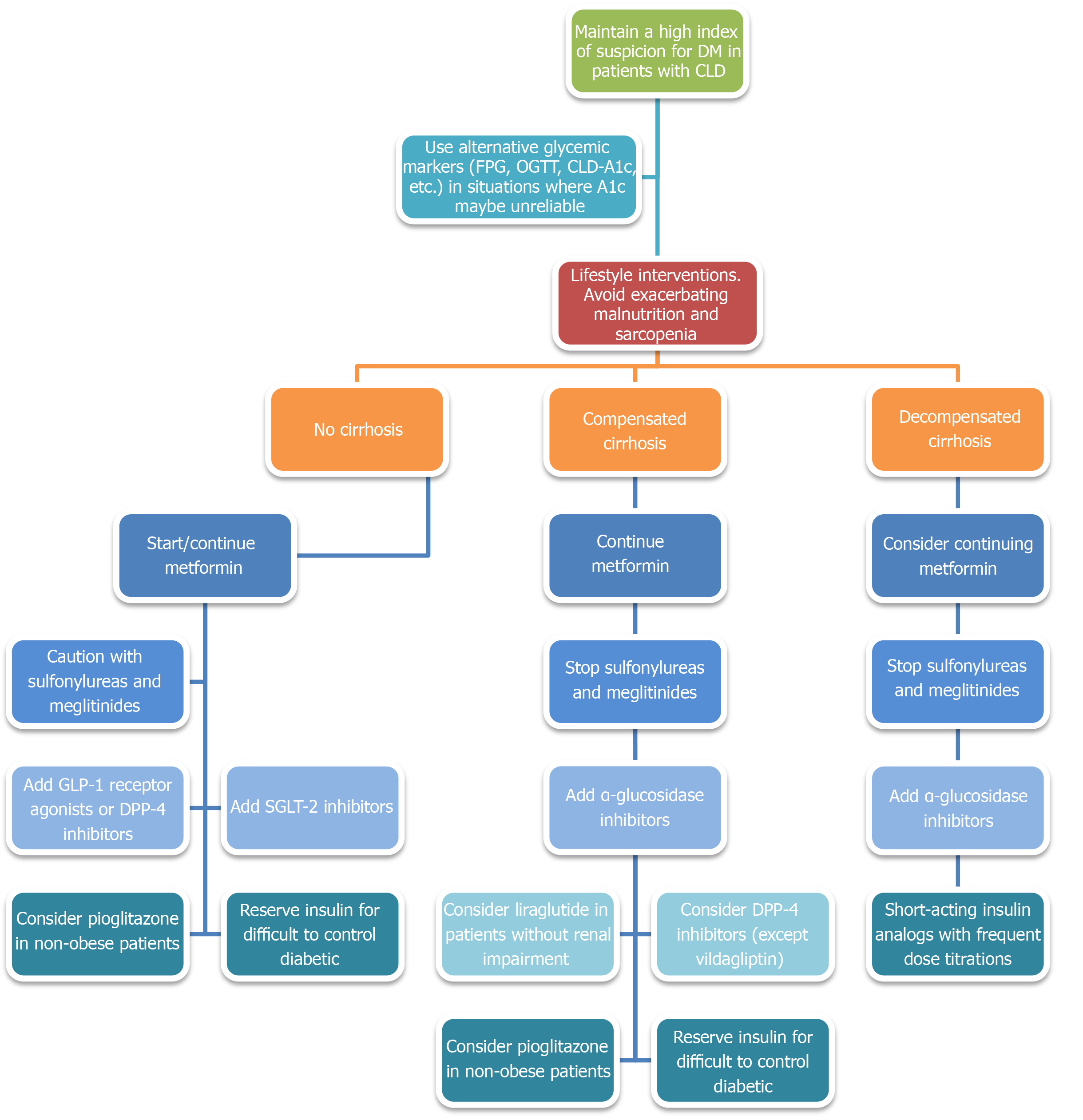
Figure 5 Proposed diabetes treatment algorithm in patients with chronic liver diseases.
CLD: Chronic liver diseases; DM: Diabetes mellitus; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; SGLT-2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl
- Citation: Chung W, Promrat K, Wands J. Clinical implications, diagnosis, and management of diabetes in patients with chronic liver diseases. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(9): 533-557
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i9/533.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.533