©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2018; 10(12): 911-923
Published online Dec 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i12.911
Published online Dec 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i12.911
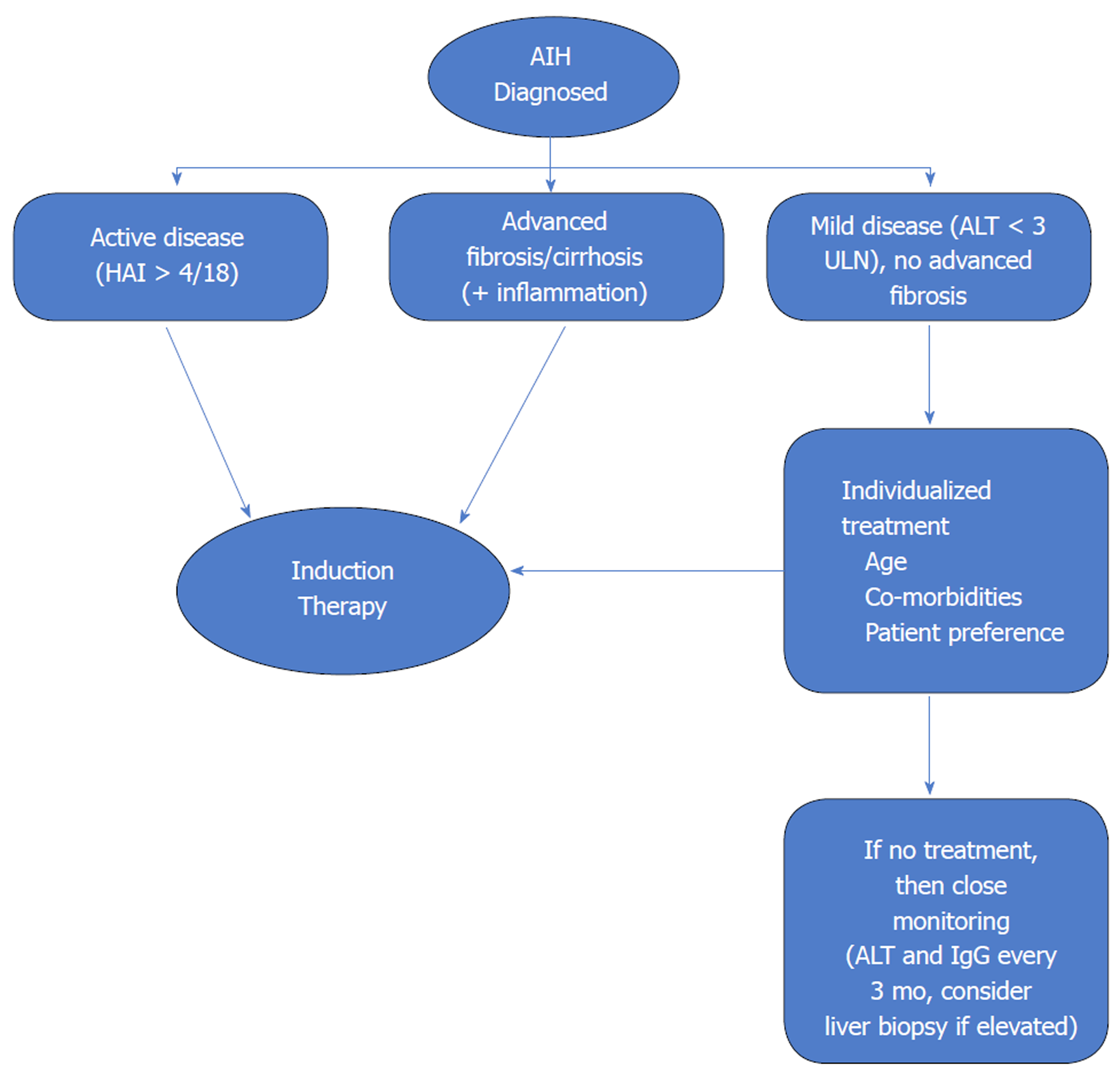
Figure 1 Algorithm for decision making regarding initiation of induction immunosuppressive therapy.
Patients with active disease and advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis need initiation of therapy. Patients with mild or asymptomatic disease need an individualized approach. Patients with cirrhosis who have decompensated disease or no inflammatory activity on histology do no benefit from treatment. AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ULN: Upper limit of normal; HAI: Hepatic activity index[4].
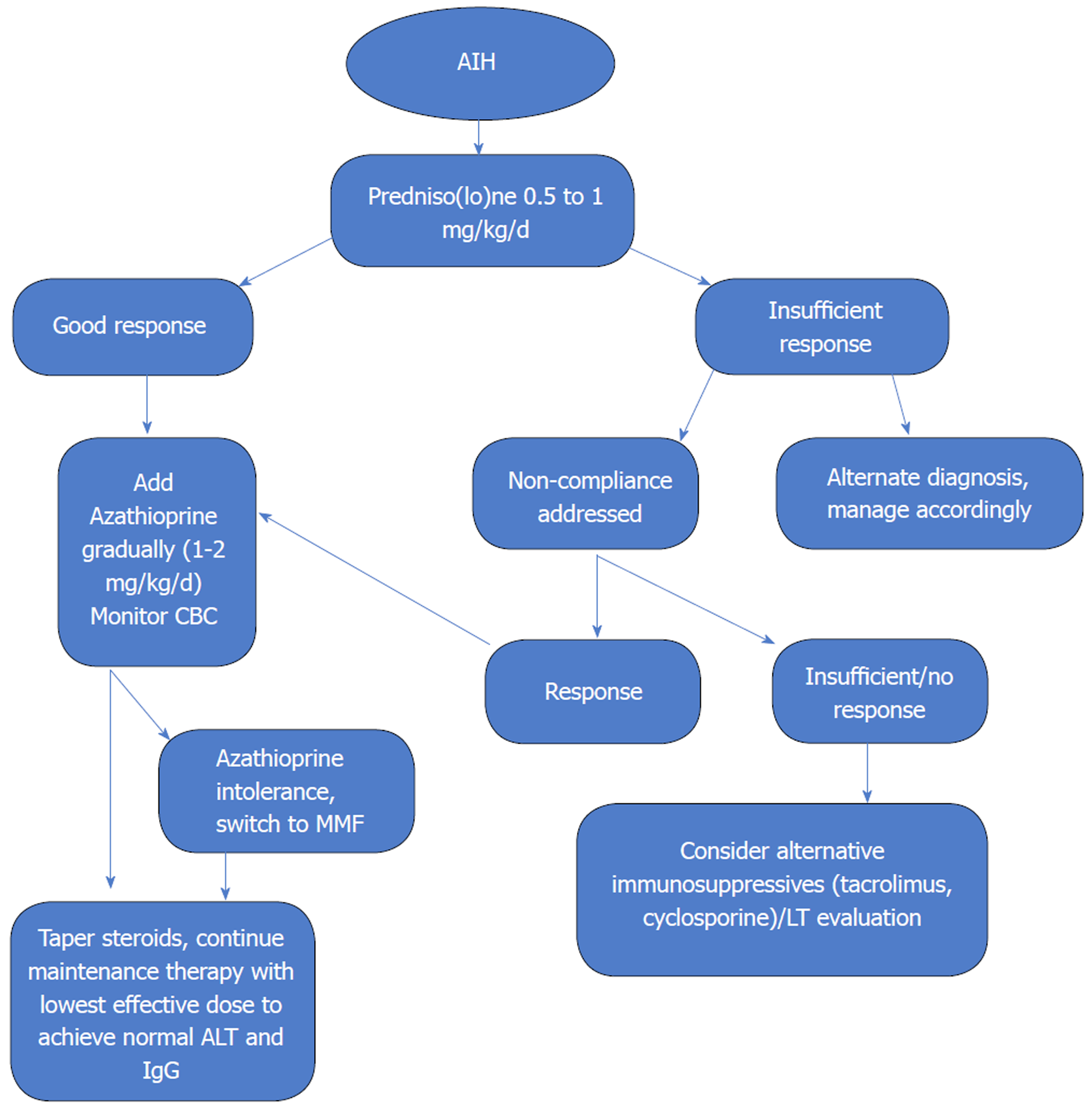
Figure 2 Treatment strategy in autoimmune hepatitis.
Treatment includes induction and maintenance therapy to achieve biochemical remission. Induction is achieved by steroids and after a positive response (more than 25% reduction in serum aminotransferases after two weeks) is seen, azathioprine is introduced to achieve long term remission. Timely and appropriate maintenance therapy with azathioprine allows for steroid withdrawal. AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; CBC: Complete blood count; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil; LT: Liver transplant[4].
- Citation: Lowe D, John S. Autoimmune hepatitis: Appraisal of current treatment guidelines. World J Hepatol 2018; 10(12): 911-923
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i12/911.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i12.911