Published online Apr 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.4027
Peer-review started: November 8, 2015
First decision: November 27, 2015
Revised: December 13, 2015
Accepted: January 9, 2016
Article in press: January 11, 2016
Published online: April 21, 2016
Processing time: 147 Days and 8.5 Hours
AIM: To present a retrospective analysis of clinical and endoscopic features of 4 cases of immunocompetent hosts with intestinal histoplasmosis (IH).
METHODS: Four immunocompetent adults were diagnosed with IH between October 2005 and March 2015 at West China Hospital of Sichuan University. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics were summarized and analyzed retrospectively. GMS (Gomori methenamine silver), PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) and Giemsa staining technique were used to confirm Histoplasma capsulatum(H. capsulatum). The symptoms, signs, endoscopic presentations, radiographic imaging, pathological stain results and follow-up are presented as tables and illustrations.
RESULTS: The cases were male patients, ranging from 33 to 61 years old, and primarily presented with non-specific symptoms such as irregular fever, weight loss, abdominal pain and distention. Hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy were the most common signs. Endoscopic manifestations were localized or diffuse congestion, edema, ulcers, and polypoid nodules with central erosion involving the terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum, similar to intestinal tuberculosis, tumor, and inflammatory bowel disease. Numerous yeast-like pathogens testing positive for PAS and GMS stains but negative for Giemsa were detected in the cytoplasm of the histiocytes, which were highly suggestive of H. capsulatum.
CONCLUSION: Immunocompetent individuals suffering from histoplasmosis are rarely reported. It is necessary that gastroenterologists and endoscopists consider histoplasmosis as a differential diagnosis, even in immunocompetent patients.
Core tip: Intestinal histoplasmosis (IH) is an uncommon disease. It is more likely to be encountered in immunocompromised patients. No case series of IH in immunocompetent patients has been published so far. This retrospective study included 4 cases of immunocompetent adults with intestinal histoplasmosis and focused on presenting the endoscopic characteristics. It is necessary that gastroenterologists and endoscopists consider histoplasmosis as a differential diagnosis, even in immunocompetent patients.
- Citation: Zhu LL, Wang J, Wang ZJ, Wang YP, Yang JL. Intestinal histoplasmosis in immunocompetent adults. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(15): 4027-4033
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i15/4027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.4027
Disseminated histoplasmosis (DH) is more likely to be encountered in patients whose CD4+ cell counts are < 200 cells/mm3[1,2], a condition mostly found in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients, and extremely rarely in patients with human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) infection. Gastrointestinal (GI) involvement in disseminated histoplasmosis can occur at any site along the GI tract, and particularly in the terminal ileum due to its abundance of lymphoid tissue. Intestinal involvement is also primarily found in immunocompromised patients, whereas cases of intestinal histoplasmosis (IH) in immunocompetent hosts have rarely been reported. Although more than 20000 colonoscopies are performed in our department every year, we found only one patient who presented with intestinal multiple ulcers as an initial manifestation in 2012. Therefore, we searched all patients with intestinal histoplasmosis and summarized the results. Here, we present a retrospective analysis of clinical and endoscopic features of 4 cases of immunocompetent hosts at our hospital between 2005 and 2015. Among them, 3 cases were DH; the other case was localized ascending colon IH. Diagnoses were confirmed by bone marrow or GI tissue culture. Few of the physicians and endoscopists considered this disease as a differential diagnosis, and colonoscopies and fungal cultures were rarely performed. Based on the collection of clinical and endoscopic manifestations, gastroenterologists and endoscopists should consider histoplasmosis as a differential diagnosis, even in immunocompetent patients.
We reviewed the medical records of 4 patients at our hospital in whom intestinal histoplasmosis was diagnosed from 2005 to 2015. The diagnosis of IH was made if lesions of the small bowel, colon or rectum were identified on endoscopy results in conjunction with any of the following: positive blood, bone marrow, or GI tissue culture for Histoplasma capsulatum (H. capsulatum); histopathologic observation of microorganisms morphologically consistent with H. capsulatum in tissue specimens[3]. The baseline characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1. All these immunocompetent patients were male. Two cases were diagnosed in 2008, one in 2012 and the last in 2014. None of the patients were infected with the human immunodeficiency virus or treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
| Case A | Case B | Case C | Case D | |
| Age (yr) | 61 | 33 | 59 | 28 |
| Sex | Male | Male | Male | Male |
| Underlying diseases | Arthritis1 | No | AP, HBV2 | Onychomycosis3 |
| Risk factor | ||||
| HIV | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Injection drug use | Deny | Deny | Deny | Deny |
| Glucocorticoids | Not used | Not used | Not used | Not used |
| Other-immunosuppressive agents | Not used | Not used | Not used | Not used |
| CD4 counts (/mm3) | ||||
| Before treatment | Not reported | 159 | 145 | 86 |
| After treatment | Not reported | 221 | 229 | Not reported |
The most common presenting symptoms were irregular fever (75%) and weight loss of different degrees (75%). The highest body temperature was 40.3 °C, accompanied or not by night sweats and chills. Abdominal pain and distention (75%) and anorexia (75%) were the main manifestations of the GI system. However, empirical antibiotic treatment was ineffective in improving symptoms. On physical examination, 3 of the patients showed hepatosplenomegaly and 2 showed peripheral lymphadenectasis involving the submentum or the left armpit, with only one patient having abdominal tenderness and rebound pain while he experienced peritonitis.
Among the 4 IH patients, 3 had multiple colon lesions, though only one lesion was localized at the ascending colon (Case A). Multiple intestinal lesions involving the terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum were in continuous or multifocal distribution. DH lesions were mainly distributed in the bone marrow and in the lung (Table 2).
| Case A | Case B | Case C | Case D | |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Fever | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Temperature (°C) | 35.3-40.3 | 35.8-38.7 | 35-40.3 | |
| Night sweat | No | Yes | Yes | Not reported |
| Chills | No | No | No | Yes |
| Antibiotic1 | Moxifloxacin2 | Levofloxacin3 | Anqi4 | Penicillin5, Amikacin5 |
| Metronidazole2 | Azithromycin5 | |||
| Levofloxacin6 | ||||
| Ceftriaxone5, Xianshu7 | ||||
| Abdominal pain | Right abdomen | No | Yes | Whole abdomen |
| Abdominal distention | Yes | No | Yes | Upper abdomen |
| Diarrhea | No | No | No | Yes8 |
| Anorexia | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not reported |
| Pharyngalgia | No | Yes | No | Not reported |
| Cough | No | Yes | No | No |
| Expectoration | No | Yes | No | No |
| Weight loss | Not apparent | 15 kg | 4 kg | 10 kg |
| Signs | ||||
| Lymphadenectasis | No | Yes9 | No | Yes |
| Abdominal tension | No | No | No | Yes |
| Hepatomegaly | No | Not palpable | Yes10 | Yes |
| Splenomegaly | No | Yes11 | Yes12 | Yes |
| (Rebound) tenderness | No | No | No | Yes |
| Shifting dullness | Negative | Negative | Negative | Positive |
| Involvement | ||||
| Bone marrow | √ | √ | √ | |
| Pulmonary | ||||
| Colon | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Terminal ileum | √ | √ | √ |
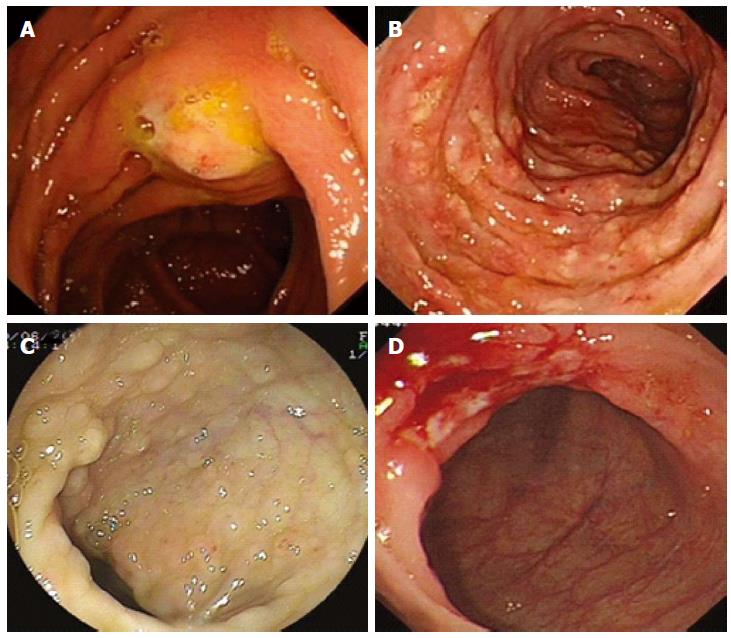
The details of endoscopic and radiographic analyses are available in Tables 3 and 4. Abnormal findings of radiographic imaging included bowel wall thickening, retroperitoneal or intraperitoneal lymphadenopathy, ascites and hepatosplenomegaly. Colonoscopy showed the following: an isolated mucosal nodular bulging lesion approximately 2 cm in diameter with its central erosion at the ascending colon near the hepatic flexure (Figure 1A); manifestation as edematous mucosa, diffuse nodular changes accompanied by aphthoid ulcers or erosion measuring 0.5-1.0 cm, with colon marsupium disappearing and intestinal strictures (Figure 1B); a 1.5 × 1 cm area of isolated swollen rough mucosa in the terminal ileum and 0.3 cm × 0.3 cm, 0.8 cm × 1.0 cm ulcers covered with white fur located in the ascending and transverse colon, with the surrounding mucosa hyperemic and swollen (Figure 1D); diffuse flat polypoid mucosa measuring 0.3-0.5 cm located in the rectum, sigmoid colon, descending colon, transverse colon, ascending colon, and terminal ileum (Figure 1C).
| Case A (cm) | Case B (cm) | Case C (cm) | Case D (cm) | |
| Lesions | ||||
| Protrusions with erosion | √ | |||
| Flat polypoid uplift | √ | |||
| Nodular deposits | √ | √ | ||
| Edematous mucosa | √ | √ | √ | |
| Multiple ulcers | √ | √ | ||
| Stricture | √ | |||
| Location and size | ||||
| Ascending colon | 2.0 | 0.5-1.01 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.5 |
| Transverse colon | 0.5-1.01 | 1 × 0.8 | 0.3-0.6 | |
| Descending colon | 0.5-1.01 | 0.3-0.6 | ||
| Sigmoid colon | 0.5-1.01 | 0.3-0.6 | ||
| Terminal ileum | 1.5 × 1.0 | 0.5 | ||
| Rectum | 0.5-1.01 | 0.3-0.6 | ||
| Biopsy texture | Soft | Fragile | Soft | Soft |
| hemorrhage |
| Case A | Case B | Case C | Case D | |
| Abdominal | ||||
| Lesions | Bowel-wall thickening | Hepatosplenomegaly | Hepatic cyst | Hepatosplenomegaly |
| Splenic infarction | ||||
| Lymphadenopathy | ||||
| Ascending colon | Ascites | |||
| Location | Ileocecal | Intraperitoneal | ||
| Retroperitoneal | ||||
| Chest | ||||
| Lesions | Small nodular | Nodular shadows1 | Pleural-effusion | Pleural-effusion |
| right middle lobe | Atelectasis | |||
| Location | left inferior lobe | right lower lobe | right lower lobe |
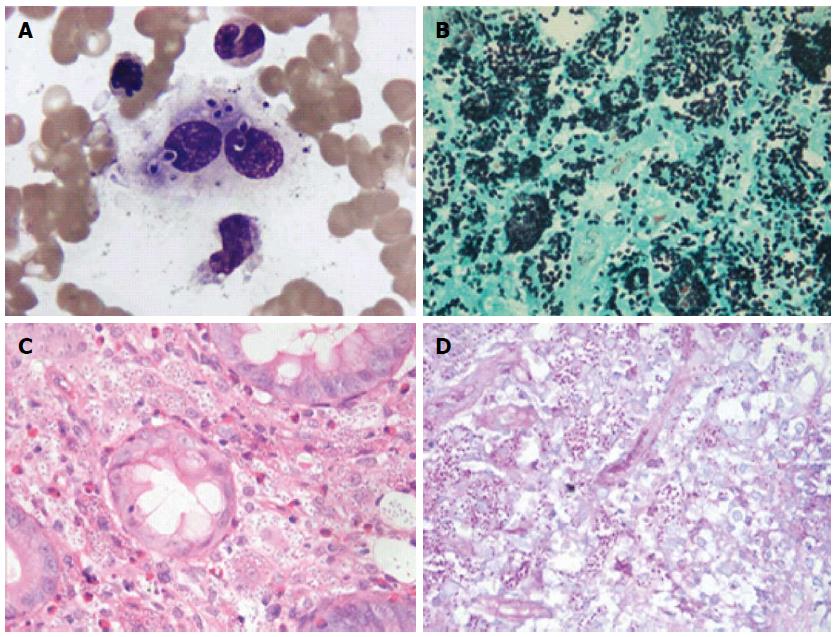
All of the biopsy specimens of the ascending colon, transverse colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and descending colon showed increased accumulation of histiocytes, with formations of multinucleated giant cells in the mucosa; numerous yeast-like pathogens testing positive for PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) and GMS (Gomori methenamine silver) stains but negative for Giemsa were detected in the cytoplasm of the histiocytes (Cases B, C;). No specific staining was observed for Case D. The ascending colon specimen of Case A showed inflamed granulated tissue, with a large number of interstitial foam cells; PAS, GMS, and Giemsa stains were positive, whereas acid-fast staining was negative, indicating mycotic granulomatous inflammation consistent with histoplasmosis. Bone marrow smears showed multiple oval or round organisms with amaranth nuclei and surrounding capsule-like unstained halos, which within the context of phagocytes are highly suggestive of H. capsulatum (Cases B, D; Figure 2A-D). Bone marrow biopsy was also positive for PAS and GMS staining, compatible with a diagnosis of histoplasmosis (Case C).
Three of the DH patients were started on intravenous amphotericin B deoxycholate at an initial dose of 1 mg/d for a total of 1.47-2.79 g followed by oral itraconazole 200 mg bid for 6 mo. There was a dramatic response with a rapid change in temperature. Follow-up endoscopic examinations involving second and third colonoscopies after 42 d to 1 year (Cases B, C) were normal. Case D was lost during follow-up. It is worth noting that the localized ascending colon histoplasmosis patient (Case A) had fully recovered without any anti-fungal drugs by his second colonoscopy after 35 d.
H. capsulatum is a 2-4 μm yeast which enters the body primarily through the lungs via inhalation, and largely causes a self-limited respiratory infection in healthy individuals[4], mainly observed at endemic levels in areas of the upper Mississippi and Ohio river valleys[5]. As it is difficult for macrophages to eliminate these organisms in immunodeficient patients due to the absence of cellular immunity, the infection can disseminate to other organs such as the skin, bone marrow, spleen, liver, lymphoid node, adrenal gland, renal tract, central nervous system, and even the GI tract, which presents as disseminated histoplasmosis. Reported immunodeficiency conditions include AIDS[1], HTLV-1 infection[6], hepatitis C infection[4], renal failure, and the recent use of a glucocorticosteroid or biological agents such as infliximab or etanercept[7]. However, less than 0.05% of patients have no obvious immunosuppressive risk factors[8], which is difficult to reconcile with DH. Regarding our cases, because the CD4+ count was initially 86-159/mm3 but increased to 221-229/mm3 after the infection was treated, we considered this to be an outcome of the infection, though we did not find any evidence that H. capsulatum impairs the immune function of T-cells[9]. GI involvement occurs in 70%-90% of cases of DH[10], whereas the colon may be involved in 59.6%. Symptomatic GI histoplasmosis (GIH) is uncommon (3%-12% of patients)[11], primarily manifesting as abdominal pain, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, bilious vomiting, constipation, tenesmus, and abdominal tenderness[10]. There are also reports of GI complications such as bleeding[12], bowel obstruction and perforation[1], and even protein loss due to enteropathy and hypogammaglobulinemia[11]. Missed diagnoses can occur because healthcare providers often do not arrange GI endoscopy examinations due a lack of GI symptoms.
Four distinct pathological forms have now been recognized: (1) subclinical, with microscopic clusters of macrophages in the lamina propria; (2) plaques and pseudopolyps caused by fungus-containing macrophages; (3) tissue necrosis and ulceration leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea and bleeding; and (4) localized thickening with inflammation of the bowel that can mimic malignancy or Crohn’s disease[13,14]. Lesions found during endoscopies, laparotomies, or autopsies include single or continuous superficial mucosal ulcerations, deep bleeding ulcers with or without frank perforations, friable and mass-containing areas of necrosis, and obstructions due to circumferential exophytic thickening[10]. Diffuse ulcerations were detected in 85.7% (12/14) of AIDS GIH patients, with 10/14 (71.4%) involving only the colon or cecum[3]. Despite the fact that these manifestations mimic many other GI diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, tuberculosis, carcinomas, and lymphomas, the cause is often not considered to be histoplasmosis in the differential diagnosis, leading to inappropriate therapies and unnecessary surgical interventions[10].
A variety of diagnostic exams, including direct microscopic examination, cultures, antigen detection, and serological tests for antibodies have been described, and a tissue biopsy should be performed as soon as possible. Samples can be obtained from the blood, bone marrow, liver, skin lesions, or any other site of infection. Cultures are positive in approximately 85% of cases, though multiple specimens must be cultured to achieve the highest yield[10,15]. Overall, 52.9% of patients exhibited positive culture results for blood, bronchoalveolar lavage, lymph node, liver, and spleen specimens, whereas 90.9% of GI specimens were positive[1]. Thus, in addition to pathoscopy, specimens should be submitted for microscopic examination, and fungi from mucosal lesions of the GI tract identified at endoscopy should be cultured[10]. GIH has excellent long-term survival with aggressive therapy, such as anti-mycete therapies. However, untreated disseminated histoplasmosis is almost always fatal.
In summary, it is important to arrange GI endoscopies for DH cases, even with a lack of GI tract symptoms or in patients with normal immune function. Endoscopists and GI physicians should be aware of histoplasmosis in the GI tract, especially when it manifests as ulceration, and a sample should be sent for culture as soon as possible.
Intestinal histoplasmosis (IH) is an uncommon disease. The majority of IH cases are found in disseminated histoplasmosis (DH), which is more likely to be encountered in immunodeficient patients, such as those with AIDS. Conversely, immunocompetent individuals suffering from histoplasmosis are rarely reported. To our knowledge, no case series of IH in immunocompetent patients has been published. This retrospective study concluded 4 cases of immunocompetent adults with intestinal histoplasmosis, and focused on presenting the endoscopic characteristics.
IH in immunocompetent adults is an uncommon disease. Few reports have included this disease so far. It is necessary that gastroenterologists and endoscopists consider it as a differential diagnosis.
To improve the clinical recognition of intestinal histoplasmosis, this study presents the symptoms, signs, endoscopic presentations, radiographic imaging, pathological staining, and follow-up of 4 IH patients.
Endoscopic manifestations of IH are somewhat similar to intestinal tuberculosis, tumor, and inflammatory bowel disease. Based on collection of clinical and endoscopic manifestations, gastroenterologists and endoscopists should consider histoplasmosis as a differential diagnosis, even in immunocompetent patients.
DH: is an AIDS defining illness which usually involves the gastrointestinal tract.
This study summarized the characteristics of 4 cases of immunocompetent adults with intestinal histoplasmosis. Although the cases are few, they are interesting.
| 1. | Suh KN, Anekthananon T, Mariuz PR. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:483-491. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Wheat LJ, Connolly-Stringfield PA, Baker RL, Curfman MF, Eads ME, Israel KS, Norris SA, Webb DH, Zeckel ML. Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical findings, diagnosis and treatment, and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1990;69:361-374. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 473] [Cited by in RCA: 399] [Article Influence: 11.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Assi M, McKinsey DS, Driks MR, O’Connor MC, Bonacini M, Graham B, Manian F. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: report of 18 cases and literature review. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006;55:195-201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Rodriguez-Waitkus PM, Bayat V, George E, Sule N. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in a hepatitis C-infected individual. Mycopathologia. 2013;176:161-164. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Jain S, Koirala J, Castro-Pavia F. Isolated gastrointestinal histoplasmosis: case report and review of the literature. South Med J. 2004;97:172-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Canelo-Aybar C, Cuadra-Urteaga J, Atencia F, Romani F. Human T Lymphotropic virus-1 associated gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in Peru. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2011;5:484-488. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Seminerio JL, Loftus EV, Colombel JF, Thapa P, Sandborn WJ. Infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the first 500 patients followed up through 2009. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:797-806. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Rana C, Krishnani N, Kumari N. Bilateral adrenal histoplasmosis in immunocompetent patients. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39:294-296. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Yang B, Lu L, Li D, Liu L, Huang L, Chen L, Tang H, Wang L. Colonic involvement in disseminated histoplasmosis of an immunocompetent adult: case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:143. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kahi CJ, Wheat LJ, Allen SD, Sarosi GA. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:220-231. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kok J, Chen SC, Anderson L, Berglund L, Sleiman S, Moss A, Bourke M, Fulcher D, Gilroy N. Protein-losing enteropathy and hypogammaglobulinaemia as first manifestations of disseminated histoplasmosis coincident with Nocardia infection. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59:610-613. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Koh PS, Roslani AC, Vimal KV, Shariman M, Umasangar R, Lewellyn R. Concurrent amoebic and histoplasma colitis: a rare cause of massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1296-1298. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Lamps LW, Molina CP, West AB, Haggitt RC, Scott MA. The pathologic spectrum of gastrointestinal and hepatic histoplasmosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;113:64-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Panchabhai TS, Bais RK, Pyle RC, Mitchell CK, Arnold FW. An Apple-core Lesion in the Colon: An Infectious Etiology. J Glob Infect Dis. 2011;3:195-198. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Kauffman CA. Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:115-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 847] [Cited by in RCA: 791] [Article Influence: 41.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
P- Reviewer: Chaturvedi P, Sugano S S- Editor: Qi Y L- Editor: Cant MR E- Editor: Liu XM