Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2336
Peer-review started: August 17, 2014
First decision: September 15, 2014
Revised: September 30, 2014
Accepted: December 8, 2014
Article in press: December 8, 2014
Published online: February 28, 2015
Processing time: 195 Days and 3.1 Hours
AIM: To determine the mechanism of the radiation-induced biological effects of 125I seeds on pancreatic carcinoma cells in vitro.
METHODS: SW1990 and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines were cultured in DMEM in a suitable environment. Gray’s model of iodine-125 (125I) seed irradiation was used. In vitro, exponential phase SW1990, and PANC-1 cells were exposed to 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy using 125I radioactive seeds, with an initial dose rate of 12.13 cGy/h. A clonogenic survival experiment was performed to observe the ability of the cells to maintain their clonogenic capacity and to form colonies. Cell-cycle and apoptosis analyses were conducted to detect the apoptosis percentage in the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells. DNA synthesis was measured via a tritiated thymidine (3H-TdR) incorporation experiment. After continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with 125I radioactive seeds, the survival fractions at 2 Gy (SF2), percentage apoptosis, and cell cycle phases of the SW1990 and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines were calculated and compared.
RESULTS: The survival fractions of the PANC-1 and SW1990 cells irradiated with 125I seeds decreased exponentially as the dose increased. No significant difference in SF2 was observed between SW1990 and PANC-1 cells (0.766 ± 0.063 vs 0.729 ± 0.045, P < 0.05). The 125I seeds induced a higher percentage of apoptosis than that observed in the control in both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells. The rate of apoptosis increased with increasing radiation dosage. The percentage of apoptosis was slightly higher in the SW1990 cells than in the PANC-1 cells. Dose-dependent G2/M cell-cycle arrest was observed after 125I seed irradiation, with a peak value at 6 Gy. As the dose increased, the percentage of G2/M cell cycle arrest increased in both cell lines, whereas the rate of DNA incorporation decreased. In the 3H-TdR incorporation experiment, the dosimetry results of both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells decreased as the radiation dose increased, with a minimum at 6 Gy. There were no significant differences in the dosimetry results of the two cell lines when they were exposed to the same dose of radiation.
CONCLUSION: The pancreatic cancer cell-killing effects induced by 125I radioactive seeds mainly occurred via apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest.
Core tip: We compared the radiobiological effects observed in SW1990 and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines after irradiation with 125I seeds through a clonogenic cell survival assay and 3H-TdR incorporation experiment. Continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with 125I seeds was found to induce apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest.
-
Citation: Wang ZM, Lu J, Zhang LY, Lin XZ, Chen KM, Chen ZJ, Liu FJ, Yan FH, Teng GJ, Mao AW. Biological effects of low-dose-rate irradiation of pancreatic carcinoma cells
in vitro using 125I seeds. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(8): 2336-2342 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i8/2336.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2336
Pancreatic cancer is a fatal disease that is a serious health problem worldwide; the overall five-year survival rate for patients with this disease is approximately 5%. Risk factors for pancreatic cancer include smoking, family history of chronic pancreatitis, advancing age, vitamin D deficiency, and occupational exposure[1]. In general, mortality is nearly the same as morbidity[1]. Due to the absence of a capsule, the tumor can easily infiltrate the surrounding tissue; local invasion and distant metastasis of the tumor occurs rapidly in most patients. Patients are usually diagnosed at an advanced stage, with the effectiveness of chemotherapy being very limited for such patients. Interstitial brachytherapy is an ideal treatment that can prevent recurrence, prolong life expectancy, and improve the quality of life in advanced patients[2]. The most commonly used radioactive seeds for interstitial brachytherapy are 131Cs and 103Pd, among others. As reported that the relative biological effectiveness of 103Pd vs 250 kVp X-rays and iodine-125 (125I) vs60Co X-rays are 1.24 and 1.39, respectively[3-5]. 125I emits 27.4 keV X-rays and 35.5 keV γ-rays, which increase the radiosensitivity of the tumor[6-8]. 125I has a T1/2 of 60.1 d and can therefore provide continuous irradiation for nearly 200 d. The advantages of 125I have led to its widespread application in China[9-11]. There are various pancreatic cancer cell lines available, including PANC-1, SW1990, P3, Capan-1, Capan-2, AsPC-1, and Hs766T. Among them, PANC-1 and SW1990 are used most often in experiments[12-15]. According to the American Type Culture Collection, the SW1990 line was established from a spleen metastasis of a grade II pancreatic adenocarcinoma derived from the exocrine pancreas, and PANC-1 originated from the epithelium of the pancreas duct. The difference between the radiobiological effects induced by 125I seeds on SW1990 and PANC-1 cells has not been described in the literature. In this study, we compared the radiobiological effects observed in SW1990 and PANC-1 cells after irradiation using 125I seeds through clonogenic cell survival assay and tritiated thymidine (3H-TdR) incorporation experiment.
Cells from the SW1990 and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines (kindly provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai cell library) were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 100 IU/mL penicillin, 100 mg/mL streptomycin, and 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Biotrom Company, Germany) in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2 at 37 °C.
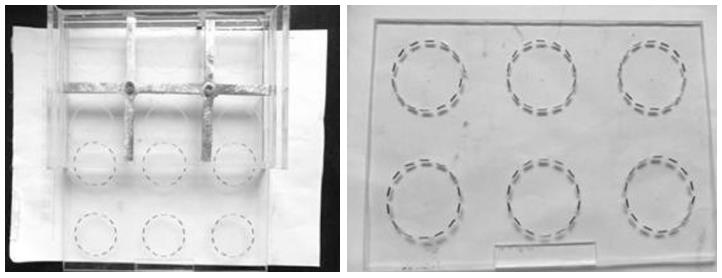
125I radioactive seeds (BT-125-I) were purchased from the Shanghai Xinke Limited Corporation. We used Gray’s model of 125I seed irradiation[16,17], as shown in Figure 1. The model consists of a lower seed plaque layer and an upper cell culture plaque layer. In the seed plaque, 14 seeds with the same activity were equally spaced within recesses located around a 35 mm circumference. In the cell culture plaque, identical recesses were created, also around a 35 mm circumference. The absorbed dose and the exposure time could be calculated. The initial dose rate was 12.13 cGy/h and the accumulated doses were 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy. The entire model was housed in an incubator throughout the study.
SW1990 and PANC-1 cells in the exponential phase of growth were irradiated in a tissue culture flask (35 mm in diameter) using the model described above. After irradiation, the cells were incubated for a further 21 d at constant temperature and humidity.
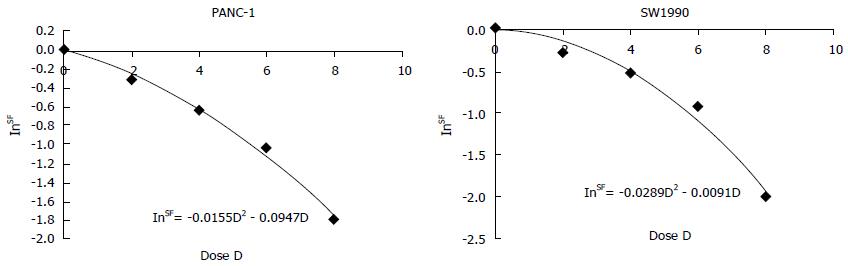
Clonogenic survival is defined as the ability of cells to maintain their clonogenic capacity and to form colonies[18]. Cells in the control and irradiation groups were briefly exposed to various radiation dosages (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy). After incubation for 14 d, the colonies were stained and manually counted. Colonies that contained more than 50 cells were regarded as survivors. The plating efficiency (PE) and survival fraction (SF) were calculated as follows: PE = (number of colonies/number of inoculating cells) × 100% and SF = PE (tested group)/PE (0 Gy group) × 100%. The dose-survival curves were fitted using the linear quadratic model SF = e-αD-βD^2. A dose-survival curve was obtained for each experiment and the values of SF2 (the fitted SF value at 2 Gy) were calculated based on the dose-survival curves of the PANC-1 and SW1990 cells in the presence of 125I seeds.
An annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI) apoptosis kit was purchased from Invitrogen Corporation. The cells of the control group and the CLDR treated groups were exposed to various radiation dosages (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy). The cells were collected 48 h after irradiation. For the detection of apoptotic cells, the cells were trypsinized, stained with acridine orange, and observed under a fluorescence microscope. At the same time, the cells were counted. The cells used for the apoptosis analysis were stained with PI and annexin V. The cells used for cell cycle analysis were stained with PI after ethanol fixation. Each analysis was performed 3 times.
DNA synthesis was measured via a 3H-TdR incorporation experiment. Thymidine phosphorylase was added during cell proliferation to mark the TdR with the radioactive nuclide 3H and to introduce the resulting 3H-TdR into the culture system, where it could be incorporated into DNA molecules. The same amounts (about 1 × 105) of SW1990 and PANC-1 cells were plated and irradiated with 125I seeds at doses of 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy. A volume of 10 μL of 3H-TdR was injected into each culture system after irradiation. A liquid scintillation counter was used to estimate the relative dosimetry for each group, with the value corresponding to the control group set to 1. After 24 h of culture, the amounts of 3H-TdR that had been incorporated were estimated and compared between the control group and treated groups for both cell lines.
The data were plotted as the mean ± standard deviation, with P < 0.05 being considered significant. SAS 9.1 (NC, USA) software was used to acquire the cell survival curves.
PANC-1 and SW1990 cells were irradiated using 125I seeds at doses of up to 8 Gy and their survival fractions were measured based on colony formation. Figure 2 presents the dose–response curves for the cell-killing effects of irradiation with 125I seeds on these 2 human pancreatic cancer cell lines. The survival fractions of the PANC-1 and SW1990 cells that were irradiated with 125I seeds decreased exponentially with an increasing dose of radiation. The SF2 value for SW1990 was 0.766 ± 0.063 and the SF2 value for PANC-1 was 0.729 ± 0.045. No significant differences between the two cell lines were observed.
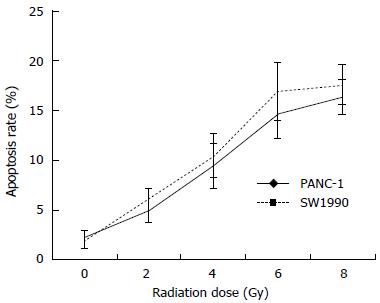
The results indicated that for a higher absorbed dose, the 125I seeds induced a higher percentage of apoptosis in both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells (Figure 3). The percentage of apoptosis was slightly higher in the SW1990 cells than in the PANC-1 cells, but the difference was not significant.
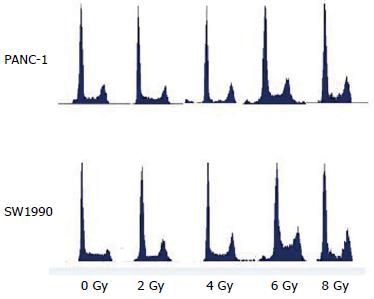
The results of cell cycle analysis performed via flow cytometry are presented in Table 1 and Figure 4. The results indicated that dose-dependent G2/M cell-cycle arrest occurred after irradiation with 125I seeds, with a peak value at 6 Gy.
| Gy | n | G1 (%) | S (%) | G2/M (%) | G2/G1 (%) | |
| PANC-1 | 0 | 3 | 49.22 ± 3.92 | 25.38 ± 1.8 | 21.31 ± 1.91 | 1.94 ± 0.16 |
| 2 | 3 | 51.34 ± 4.14 | 26.63 ± 3.9 | 22.48 ± 2.13 | 1.95 ± 0.12 | |
| 4 | 3 | 52.94 ± 3.83 | 28.12 ± 1.2 | 26.24 ± 2.15 | 1.98 ± 0.19 | |
| 6 | 3 | 55.83 ± 4.28 | 30.82 ± 2.2 | 33.21 ± 2.21 | 1.99 ± 0.15 | |
| 8 | 3 | 54.03 ± 3.21 | 27.83 ± 3.5 | 28.14 ± 3.81 | 1.99 ± 0.13 | |
| SW1990 | 0 | 3 | 43.79 ± 4.52 | 37.31 ± 2.8 | 19.08 ± 1.36 | 1.93 ± 0.14 |
| 2 | 3 | 42.47 ± 3.27 | 36.03 ± 4.2 | 20.08 ± 1.72 | 1.94 ± 0.09 | |
| 4 | 3 | 40.98 ± 3.94 | 38.42 ± 3.2 | 24.36 ± 1.18 | 1.96 ± 0.12 | |
| 6 | 3 | 41.99 ± 4.39 | 30.82 ± 2.2 | 31.99 ± 3.29 | 1.98 ± 0.19 | |
| 8 | 3 | 52.08 ± 3.80 | 32.83 ± 3.5 | 27.63 ± 2.94 | 1.97 ± 0.20 |
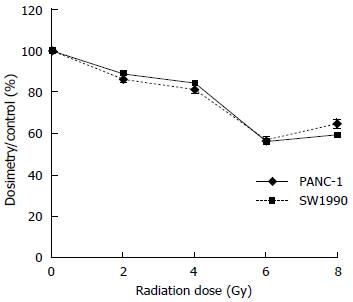
In the 3H-TdR incorporation experiment, the dosimetry results for both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells decreased as the radiation dose increased, with the lowest dosimetry readings at 6 Gy. There were no significant differences in the dosimetry results between the two cell lines at the same radiation dose. Additionally, the dosimetry readings at 2 Gy exhibited no significant difference compared with the control group. This result suggested that a cumulative dose of 2 Gy may not have been sufficient to suppress DNA synthesis. The dosimetry readings at 4 Gy were higher than those at 6 Gy and 8 Gy for both cell lines (P < 0.05) and there were no significant differences between the readings at 8 Gy and 6 Gy (P > 0.05). However, the dosimetry readings for the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells at 8 Gy were slightly higher than those at 6 Gy, especially for the SW1990 cells (Figure 5).
Interstitial brachytherapy with radioactive seeds has a history spanning more than 100 years. 125I, 103Pd, and 131Cs are the most commonly used types of radioactive seeds. The advantages of interstitial brachytherapy using radioactive seeds are the low dose rates and conformal irradiation[19,20], which increases the dose applied within the target area, thereby decreasing the incidental radiation injury to normal tissues and the attendant complications[21,22]. Hennequin et al[23] have demonstrated that low-dose-rate brachytherapy offers certain radiobiological advantages compared with external beam radiotherapy: subtle damage repair during irradiation, leading to the relative protection of healthy tissues; lack of tumor cell repopulation; cell cycle redistribution; and a low oxygen enhancement ratio. Radioactive seeds were first used for the treatment of prostate cancer and demonstrated high efficacy[24,25]. Irradiation therapy may encourage tumor cells to remain in the sensitive resting period, thereby resulting in tumor cell apoptosis, and cause damage to their DNA, thereby killing the cancer cells. In this study, we assessed the radiobiological effects of 125I seeds on human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro.
Clonogenic survival experiments can reflect the ability of cells to proliferate in vitro[26]. The clonogenic survival experiment performed in this study revealed similar SF2 values between the two investigated pancreatic cancer cell lines after irradiation at doses of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 Gy using 125I radioactive seeds. This result indicated that the cellular radiosensitivity of the two pancreatic cancer cell lines to continuous low-dose-rate irradiation produced by 125I seeds was similar.
Our results demonstrated that a higher absorbed dose of 125I induced a higher percentage of apoptosis in both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells. This finding indicated that apoptosis may play an important role in the therapeutic effects exerted by the application of continuous low-energy 125I irradiation to SW1990 and PANC-1 cells. A study by Jian et al[27] also demonstrated that cell apoptosis was the key factor in 125I seed brachytherapy in a pancreatic carcinoma xenograft. Organisms exposed to ionizing radiation (IR) exhibit increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are determining factors in the induction of apoptosis[28]. ROS damage critical cellular components such as DNA, proteins, and lipids, eventually causing cellular apoptosis[29]. Therefore, the apoptosis induced by 125I irradiation is a key mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of 125I seed implantation in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
As suggested by the data obtained in our cell cycle analysis, continuous low-energy 125I irradiation causes the arrest of both SW1990 and PANC-1 cells in the G2/M phase. It is well known that progression through the various phases of the cell cycle is a tightly regulated process that involves the activities of various cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases, which are specific to different cell cycle phases[30]. Our results indicate that dose-dependent G2/M cell cycle arrest occurs after 125I seed irradiation, with a peak value at 6 Gy.
Previous studies have shown that apoptosis and G2/M cell-cycle arrest are the predominant mechanisms involved in the inhibition of tumor growth[31-33]. Several studies[34] that have focused on the operational mechanism of 125I radioactive seeds in the treatment of prostate cancer have demonstrated that this inhibition is achieved through the down-regulation of BCL-2 and certain influences on caspase. Some scholars[35,36] believe that a change in DNA methyltransferase is also a key element. The results of our study were consistent with those of previous studies. In our study, the percentages of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest increased with increasing irradiation dose. Our 3H-TdR phosphorylase incorporation experiment explored the decrease in DNA synthesis after irradiation. We found that continuous low-dose-rate irradiation at 6 Gy using 125I seeds is effective for tumor inhibition in vitro. Although many issues remain to be addressed, we believe that with further developments in fundamental research, the applications of 125I radioactive seed implantation in clinical practice will continue to be explored.
We demonstrated that two human pancreatic cancer cell lines (PANC-1 and SW1990) exhibited similar radiosensitivity to continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with 125I seeds and that a dose of 6 Gy is effective for tumor inhibition in vitro. The radiobiological effects induced by continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with 125I seeds were most likely due to apoptosis and G2/M cell-cycle arrest.
Pancreatic cancer is a fatal disease and a serious health problem worldwide. Patients are usually diagnosed at an advanced stage, with the effectiveness of chemotherapy for such patients being very limited. Interstitial brachytherapy is an ideal treatment that can prevent recurrence, prolong life expectancy, and improve the quality of life in advanced patients.
This study focused on whether continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with iodine-125 (125I) seeds would cause radiation-induced biological effects on pancreatic carcinoma cells in vitro. The mechanism(s) through which this would occur were also explored.
This experiment assessed the radiobiological effects of 125I seeds on human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. The difference between the radiobiological effects induced by irradiation with 125I seeds on SW1990 and PANC-1 cells has not been described in the literature. This study demonstrated that the survival fractions of PANC-1 and SW1990 cells irradiated with 125I seeds decreased exponentially with an increasing dose of radiation. Furthermore, the 125I seeds induced a higher percentage of apoptosis than that observed in the control in both SW1990 and PANC-1 cells.
The 125I seeds induced a higher percentage of apoptosis than that observed in the control for both the SW1990 and PANC-1 cells. This finding indicated that apoptosis may play an important role in the therapeutic effects exerted by continuous low-energy 125I irradiation in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Clonogenic survival experiment, cell cycle and apoptosis analyses, and tritiated thymidine (3H-TdR) incorporation experiment were the major experiments conducted to assess the ratios of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and to perform comparisons between the different cell lines and radiation doses.
This study was well-designed and clarified that the radiobiological effects induced in pancreatic cancer cells by continuous low-dose-rate irradiation with 125I seeds were mainly caused by apoptosis and G2/M cell-cycle arrest. These conclusions will be very useful in guiding the treatment of tumors via interstitial brachytherapy using 125I seeds.
| 1. | Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an update. Dig Dis. 2010;28:645-656. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 147] [Cited by in RCA: 165] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Weiwei W, Yupei Z, Quan L. Study on radiosensitivity of 6 pancreatic cancer cells lines in vitro. Zhonghua Gandanwaike Zazhi. 2004;10:821-823. |
| 3. | Nath R, Bongiorni P, Chen Z, Gragnano J, Rockwell S. Dose rate dependence of the relative biological effectiveness of 103Pd for continuous low dose rate irradiation of BA1112 rhabdomyosarcoma cells in vitro relative to acute exposures. Int J Radiat Biol. 2005;81:689-699. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Wang J, Wang J, Liao A, Zhuang H, Zhao Y. The direct biologic effects of radioactive 125I seeds on pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1, at continuous low-dose rates. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009;24:409-416. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Reniers B, Verhaegen F. The microdosimetry of low-energy photons in radiotherapy. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2006;122:401-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Beger HG, Rau B, Gansauge F, Poch B, Link KH. Treatment of pancreatic cancer: challenge of the facts. World J Surg. 2003;27:1075-1084. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 133] [Cited by in RCA: 128] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Dale R, Carabe-Fernandez A. The radiobiology of conventional radiotherapy and its application to radionuclide therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2005;20:47-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Roeder F, Timke C, Uhl M, Habl G, Hensley FW, Buechler MW, Krempien R, Huber PE, Debus J, Werner J. Aggressive local treatment containing intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) for patients with isolated local recurrences of pancreatic cancer: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:295. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zhuo SQ, Chen L, Zhang FJ, Zhao M, Zhang L, Liu J, Li K, Wu PH, Zheng QS, Wang Y. [Environmental radiation dose monitor after 125I radioactive seed implantation]. Ai Zheng. 2007;26:666-668. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Zhang FJ, Li CX, Zhang L, Wu PH, Jiao DC, Duan GF. Short- to mid-term evaluation of CT-guided 125I brachytherapy on intra-hepatic recurrent tumors and/or extra-hepatic metastases after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:585-590. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Zhongmin W, Yu L, Fenju L, Kemin C, Gang H. Clinical efficacy of CT-guided iodine-125 seed implantation therapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:1786-1791. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Zhang Y, Li M, Wang H, Fisher WE, Lin PH, Yao Q, Chen C. Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World J Surg. 2009;33:698-709. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 243] [Cited by in RCA: 256] [Article Influence: 15.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Guo JC, Zhao YP, Liao Q, Chen G, Zhang LY. [Establishment, characterization, and biological analysis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell strain SW1990/FU]. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005;27:592-596. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Szepeshazi K, Schally AV, Halmos G, Sun B, Hebert F, Csernus B, Nagy A. Targeting of cytotoxic somatostatin analog AN-238 to somatostatin receptor subtypes 5 and/or 3 in experimental pancreatic cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:2854-2861. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Li WG, Yuan YZ, Qiao MM, Zhang YP. High dose glargine alters the expression profiles of microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2630-2639. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Benchimol A, Marsh CA, Desser KB. Discordant left ventricular pressure and apexcardiographic pulsus alternans. Chest. 1975;67:477-479. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Verhoeff JJ, Stalpers LJ, Coumou AW, Koedooder K, Lavini C, Van Noorden CJ, Haveman J, Vandertop WP, van Furth WR. Experimental iodine-125 seed irradiation of intracerebral brain tumors in nude mice. Radiat Oncol. 2007;2:38. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Munshi A, Hobbs M, Meyn RE. Clonogenic cell survival assay. Methods Mol Med. 2005;110:21-28. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Peretz T, Nori D, Hilaris B, Manolatos S, Linares L, Harrison L, Anderson LL, Fuks Z, Brennan MF. Treatment of primary unresectable carcinoma of the pancreas with I-125 implantation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;17:931-935. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Mazeron JJ, Noël G, Simon JM, Racadot S, Jauffret E. [Brachytherapy in head and neck cancers]. Cancer Radiother. 2003;7:62-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Verellen D, De Ridder M, Linthout N, Tournel K, Soete G, Storme G. Innovations in image-guided radiotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:949-960. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 269] [Cited by in RCA: 286] [Article Influence: 15.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Wang Z, Lu J, Liu L, Liu T, Chen K, Liu F, Huang G. Clinical application of CT-guided (125)I seed interstitial implantation for local recurrent rectal carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 23. | Hennequin C, Mazeron JJ. [Radiobiology in brachytherapy]. Cancer Radiother. 2013;17:81-84. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Casas F, Ferrer F, Casals J, Farrus B, Rovirosa A, Biete A. [Brachytherapy in the treatment of prostatic carcinoma]. Actas Urol Esp. 1995;19:662-669. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Glajchen N, Shapiro RD, Stock RG, Stone NN, Ramos R. CT findings after laparoscopic pelvic lymph node dissection and transperineal radioactive seed implantation for prostatic carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166:1165-1168. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 26. | Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:2315-2319. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2487] [Cited by in RCA: 3229] [Article Influence: 169.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Jian L, Zhongmin W, Kemin C, Yunfeng Z, Gang H. MicroPET-CT evaluation of interstitial brachytherapy in pancreatic carcinoma xenografts. Acta Radiol. 2013;54:800-804. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Kim SY, Yang ES, Lee YS, Lee J, Park JW. Sensitive to apoptosis gene protein regulates ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis. Biochimie. 2011;93:269-276. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Pinthus JH, Bryskin I, Trachtenberg J, Lu JP, Singh G, Fridman E, Wilson BC. Androgen induces adaptation to oxidative stress in prostate cancer: implications for treatment with radiation therapy. Neoplasia. 2007;9:68-80. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 88] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Bloom J, Cross FR. Multiple levels of cyclin specificity in cell-cycle control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:149-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 370] [Cited by in RCA: 379] [Article Influence: 19.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Ho YS, Duh JS, Jeng JH, Wang YJ, Liang YC, Lin CH, Tseng CJ, Yu CF, Chen RJ, Lin JK. Griseofulvin potentiates antitumorigenesis effects of nocodazole through induction of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2001;91:393-401. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Bai Y, Qu XY, Yin JQ, Wu L, Jiang H, Long HW, Jia Q. Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014;10:318-324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Yin X, Zhang R, Feng C, Zhang J, Liu D, Xu K, Wang X, Zhang S, Li Z, Liu X. Diallyl disulfide induces G2/M arrest and promotes apoptosis through the p53/p21 and MEK-ERK pathways in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:1748-1756. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Szostak MJ, Kaur P, Amin P, Jacobs SC, Kyprianou N. Apoptosis and bcl-2 expression in prostate cancer: significance in clinical outcome after brachytherapy. J Urol. 2001;165:2126-2130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 35. | Ma JX, Jin ZD, Si PR, Liu Y, Lu Z, Wu HY, Pan X, Wang LW, Gong YF, Gao J. Continuous and low-energy 125I seed irradiation changes DNA methyltransferases expression patterns and inhibits pancreatic cancer tumor growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:35. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Liu YB, Gao X, Deeb D, Arbab AS, Gautam SC. Pristimerin Induces Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells by Down-regulating Bcl-2 through ROS-dependent Ubiquitin-proteasomal Degradation Pathway. J Carcinog Mutagen. 2013;Suppl 6:005. [PubMed] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
P- Reviewer: Boeckxstaens GE S- Editor: Yu J L- Editor: Rutherford A E- Editor: Wang CH